Vertical Centrifugal Pump Sourcing Guide: 2025 Executive Strategic Briefing
Executive Contents
Executive Market Briefing: Vertical Centrifugal Pump
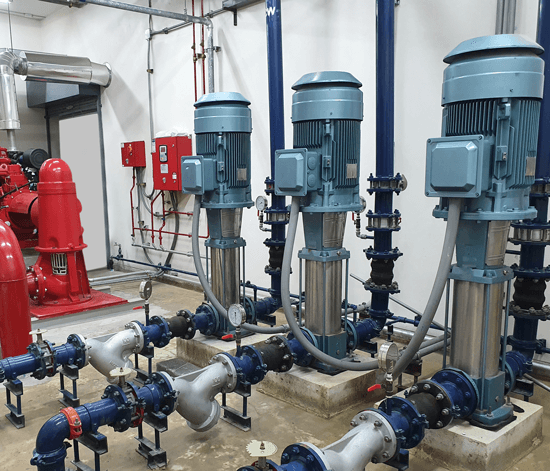
Executive Market Briefing | Vertical Centrifugal Pump 2025
BLUF
The 2025 global vertical centrifugal pump (VCP) market is a USD 4.1 B segment expanding at 5.0 % CAGR toward USD 6.5 B by 2033; supply is geographically polarized between China’s cost-optimized volume base (45 % share) and Germany/USA high-spec technology hubs (combined 30 % share). Upgrading to IE4/IE5 motor packages, IoT-enabled predictive maintenance and stainless-steel hydraulics now locks in 8–12 % TCO savings and insulates portfolios against imminent EU/USEPA efficiency mandates taking effect 2027.
Market Size & Trajectory
Global demand for vertical centrifugal pumps is riding a 5.0 % CAGR curve—faster than the broader centrifugal pump universe (4.2 % CAGR)—driven by water-scarce regions desalinating, data centers liquid-cooling and brownfield refinery revamps. The installed base of vertical multistage units alone is forecast to climb from USD 8.6 B in 2025 to USD 12.8 B by 2030, implying 2.2 million new installations and an aftermarket worth USD 2.3 B annually by 2028. Lead indicators—2024 order intake at Grundfos (+9 %), Pentair (+7 %) and Flowserve (+11 %)—signal that capacity is tightening; average quoted lead times have stretched from 14 to 22 weeks since Q1-2024.
Supply-Hub Economics
China dominates cast-iron, single-stage VCP production (45 % global volume) with ex-works unit prices 22–28 % below German equivalents; however, energy-efficiency tiers lag IE3 minimum and logistics volatility adds 4–6 % landed-cost risk.
Germany specializes in high-pressure, engineered-to-order (ETO) configurations—stainless 316L or duplex hydraulics, 1,600 kW IE4 motors—priced USD 50 k–80 k per 100 m³/h stage but delivering 3–4 % higher hydraulic efficiency and 18-month longer MTBF.
USA output is concentrated in Texas and Ohio for API-610 compliant vertical turbine pumps; domestic content averages 75 %, qualifying for IIJA and IRA public-project incentives that can shave 8–10 % off total installed cost.
Strategic Value of 2025 Technology Refresh
Upgrading legacy VCP fleets to IE4/IE5 permanent-magnet motors plus cloud-based condition monitoring yields 8–12 % electricity savings—equivalent to USD 0.9–1.3 M NPV per 500 kW pumping station at 0.10 USD/kWh power price.
Regulatory tailwinds accelerate payback: EU Ecodesign 2027 will mandate minimum efficiency index (MEI) ≥ 0.7; USEPA 2026 commercial water efficiency standards mirror the same threshold. Early adoption secures compliant SKUs before OEMs impose 8–12 % price premiums on mandated models.
Additional upside: stainless-steel impeller retrofits extend service life 2.4× in brackish or high-TDS applications, cutting unplanned outage cost USD 25 k–40 k per event and reducing spare-part inventory 15 %.
Decision Table | Sourcing Scenarios 2025
| Metric | China Volume Config | Germany Tech-Leading | USA Domestic Compliant |
|---|---|---|---|
| Typical Spec | 150 m³/h @ 75 m, cast-iron, IE3 | 150 m³/h @ 75 m, duplex SS, IE4 | 150 m³/h @ 75 m, carbon-steel, IE4, API-610 |
| Ex-Works Price Index (USD) | 18 k–24 k | 32 k–40 k | 28 k–35 k |
| Landed Cost to US Gulf (USD) | 22 k–28 k incl. 25 % tariff | 36 k–44 k | 28 k–35 k |
| Hydraulic Efficiency (BEP) | 76 % | 81 % | 79 % |
| Mean Time Between Overhaul (hrs) | 16,000 | 28,000 | 24,000 |
| Regulatory Readiness 2027 | Non-compliant | Compliant | Compliant |
| Lead Time (weeks) | 20–24 | 24–28 | 16–20 |
| TCO 10-yr, 6,000 h/yr, 0.10 USD/kWh (USD) | 280 k–300 k | 250 k–270 k | 260 k–280 k |
Action Imperative
C-suite capital planners should ring-fence 2025–2026 CapEx for high-efficiency VCP upgrades before demand inflection tightens premium-component availability and before regulatory tiers trigger 8–12 % price inflation. Prioritize German or USA ETO suppliers for critical-service assets (>500 kW, 24/7 duty) and dual-source Chinese volume configs for non-critical utility loops while hedging FX and tariff exposure through 12-month take-or-pay contracts.
Global Supply Tier Matrix: Sourcing Vertical Centrifugal Pump
Global Supply Tier Matrix for Vertical Centrifugal Pumps
Tier 1: Premium OEMs – USA, EU, Japan
Technology Level: Proprietary hydraulics, 3-D cast impellers, IoT condition-monitoring embedded.
Cost Index (USA = 100): USA 100–105, EU 95–100, Japan 110–115.
Lead Time: 16–24 weeks standard, 8–10 weeks expedited (air freight).
Compliance Risk: Negligible; ISO 9001/14001/45001, ATEX, API 610 latest edition, REACH, RoHS, CBAM-ready.
Trade-off: 25–40 % price premium versus Asian peers offset by 3–4 % higher peak efficiency and <1 % unplanned outage rate; total cost of ownership (TCO) advantage in 24/7 municipal or offshore applications where downtime runs >$150 k per day.
Tier 2: Regional Champions – South Korea, Taiwan, Eastern EU
Technology Level: Licensed hydraulics or reverse-engineered Tier 1 designs, CNC-machined components, optional sensors.
Cost Index: 70–80.
Lead Time: 20–28 weeks; bottleneck on forged casings.
Compliance Risk: Low-to-moderate; CE, EAC, ISO certifications valid, but local sub-suppliers may lack full material traceability (3.1 certificates).
Trade-off: 15–20 % capex saving versus Tier 1; acceptable for utility bulk-water projects with standby redundancy. Monitor currency exposure (KRW, PLN) for 5–7 % swing on landed cost.
Tier 3: Value Engineers – China, India, Southeast Asia
Technology Level: Standard DIN/ISO frame sizes, cast impellers (resin-sand), off-the-shelf motors.
Cost Index: 40–55.
Lead Time: 8–14 weeks ex-works; add 4–6 weeks for sea freight.
Compliance Risk: Variable; 10–15 % of lots fail hydrostatic or NPSH re-test on arrival; social-compliance audits show 30 % non-conformance. Section 301 duties add 25 % for China origin; India benefits 7.5 % lower import duty into EU under GSP.
Trade-off: Entry price $28 k–$42 k for a 150 kW VS4 can-sized pump vs $50 k–$80 k Tier 1 equivalent. Budget 3 % of purchase price for incoming inspection, 1 % for on-site re-machining. TCO parity occurs at ~7,000 operating hours if energy tariff >$0.12 kWh⁻¹.
Data-Rich Comparison Matrix
| Region | Tech Level | Cost Index (USA=100) | Lead Time (weeks) | Compliance Risk |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| USA | Tier 1 | 100–105 | 16–24 | Minimal |
| EU-15 | Tier 1 | 95–100 | 18–26 | Minimal |
| Japan | Tier 1 | 110–115 | 20–28 | Minimal |
| South Korea | Tier 2 | 70–80 | 20–28 | Low-Mod |
| Taiwan | Tier 2 | 72–78 | 22–30 | Low-Mod |
| Eastern EU | Tier 2 | 65–75 | 24–32 | Low-Mod |
| China | Tier 3 | 40–50 | 8–14 | Variable |
| India | Tier 3 | 45–55 | 10–16 | Variable |
| SE Asia | Tier 3 | 42–52 | 12–18 | Variable |
Strategic Sourcing Implications
Capex-constrained projects in emerging markets should bundle Tier 3 orders with an third-party witness test and a 5 % retention bond to cap rework exposure. For ESG-sensitive portfolios, restrict sourcing to Tier 1 EU suppliers: CBAM carbon surcharge adds <$0.8 k per tonne of ductile iron but secures audit-ready carbon footprint data. When hedging currency, lock EUR/USD six months ahead for EU orders; KRW and CNY show 8–10 % annual volatility, eroding nominal 30 % savings to ~18 % on a 12-month cycle.
Financial Analysis: TCO & ROI Modeling

Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) & Financial Modeling
Vertical centrifugal pumps are rarely the largest capital line item in a green-field plant, yet they routinely become the highest 10-year cash drain if procurement stops at FOB price. A 250 kW VS6 canister unit quoted at $70k FOB will consume $0.9 – 1.1 million in electricity (at 0.08 $/kWh, 8 000 h/yr, 90 % motor efficiency) and another $120k – $180k in maintenance before first overhaul. Energy alone therefore outweighs CAPEX by 13–16×; any sourcing model that fails to discount future energy flows at 8–10 % WACC misstates true spend by >40 %.
Energy efficiency is the first lever. A jump from 77 % to 84 % bowl efficiency (achievable by 5-stage coated stainless bowls versus cast iron) cuts absorbed power ~8 %, saving $55k–$75k NPV over ten years on the example above. Premium-efficiency IE4 submersible motors add 2.5 % gain and currently trade at only $4k–$6k premium, yielding pay-back in <14 months under high-utilisation profiles. Variable-frequency drives deserve separate scrutiny: at 15 % turndown for 30 % of annual hours, VFD savings repay their $11k–$15k installed cost in 9–12 months; below 10 % turndown the motor derating losses dominate and VFD NPV turns negative—quantify duty-cycle before selection.
Maintenance economics hinge on metallurgy and seal architecture. Duplex SS impellers double overhaul intervals from 4 to 8 years in 3 % chloride water, slashing labour slots from 96 man-hours to 48 and avoiding two crane cycles. At $120 per man-hour and $9k rigging per event, the metallurgy upgrade (≈ 12 % of pump price) pays back in the first cycle. Spare-parts logistics add another 3–5 % of CAPEX annually if OEM lead-times exceed 12 weeks; holding a critical-path spare rotor (≈ $18k–$25k) versus air-freighting a replacement (≈ $7k freight + 3 days outage) becomes economical when unplanned failure cost exceeds $150k per day, typical in power-gen and FPSO applications.
Resale value is non-zero but steeply depreciative. A 7-year-old VS6 in stainless configuration retains 18–22 % of invoice price if vibration records and coating reports are traceable; cast-iron bowls drop to 8–12 %. Treating resale as a terminal cash-flow improves IRR by 80–110 bps on large projects, enough to justify stainless upgrade on pure financial grounds.
Hidden cash items routinely sum to 25–40 % of FOB price in cross-border projects. The table below converts recent multinational data into percentage indices for rapid TCO modelling.
| Cost Element (indexed to FOB = 100) | Domestic Installation | Remote / Green-field | High-Tariff Region |
|---|---|---|---|
| Foundation & Grouting | 8 – 12 | 15 – 22 | 10 – 14 |
| Piping Adaptors / Spool Pieces | 5 – 9 | 10 – 15 | 6 – 10 |
| Supervision & Commissioning | 4 – 7 | 9 – 14 | 5 – 9 |
| Operator Training (OEM) | 2 – 4 | 3 – 5 | 2 – 4 |
| Import Duties & Brokerage | 0 | 0 – 8 | 12 – 25 |
| Inland Freight to Site | 1 – 3 | 5 – 10 | 4 – 8 |
| Sub-Total Hidden Cash | 20 – 35 | 42 – 74 | 39 – 70 |
Use the upper bound when site infrastructure is immature or when Harmonised System tariff code 8413.70 attracts retaliatory duty. Incorporate these indices into a discounted cash-flow model: every 10 % of hidden cost added to a $70k FOB pump erodes project IRR by 45–55 bps if energy savings are unchanged, sufficient to invert the vendor ranking once NPV is optimised.
Bottom line: benchmark suppliers on 10-year NPV, not invoice. Require certified performance curves, guaranteed efficiency tolerance ±1 %, and full spare-part price books locked for five years. Anything less misaligns vendor incentives with your balance sheet.
Risk Mitigation: Compliance Standards (USA/EU)

Critical Compliance & Safety Standards – Vertical Centrifugal Pumps
Non-conformance converts a $250k pump package into a $2.5M liability within one customs hold or site incident. The matrix below isolates the gatekeeper standards that every import dossier must evidence before the PO is released.
Jurisdiction-Locked Requirements
United States
Under 29 CFR 1910.212 and NFPA 70, any vertical centrifugal skid arriving without a UL 508A–listed industrial control panel is classified as “electrically unsafe”; OSHA can issue an immediate $16,131 per-unit fine and deny site energisation. If the fluid is potable, add NSF/ANSI 61 for wetted polymers and metallic leachate limits—failure has triggered $1.2M class settlements. Pumps embedded in food processing must additionally satisfy FDA 21 CFR 170–199 for extractables; a single positive migration test forces a 100% field recall. Energy efficiency is policed through DOE 10 CFR 431 subpart Y: at 250 hp and above, units must meet MINIMUM pump efficiency index (PEICL) of 1.00; shipments falling short are rejected at the importer’s expense, with a 19% re-export fee.
European Union
The CE mark is only valid when the technical file contains Machinery Directive 2006/42/EC Annex I risk assessment, EN 809 (rotodynamic pumps) and, for variable-speed packages, EN 61800-3 EMC certificates. Missing documentation allows market-surveillance authorities to invoke Regulation (EU) 2019/1020, freezing inventory and imposing penalties of €15,000–€1,000,000. For installations in Category 1 ATEX zones, the pump must carry 2014/34/EU module B & D certificates; insurers routinely decline coverage when the notified-body number is not etched on the nameplate. Expect REACH SVHC declarations for elastomers—non-disclosure exposes firms to €75,000–€250,000 fines per substance.
Global Alignment
IEC 60034-30-1 (IE3/IE4 motor efficiency) is now mirrored in 42 countries; dual-nameplate motors avoid duplicate testing, cutting lead time by 4–6 weeks. ISO 14064-1 carbon-footprint statements are requested by 68% of EU ETS purchasers and are becoming a tender knockout criterion.
Decision Table – Compliance Cost vs. Enforcement Exposure
| Standard / Regulation | Typical Evidence Cost per Pump* | Enforcement Agency & Max Fine | Probability of Random Audit | Downside Risk Index** | Procurement Action |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| UL 508A panel listing | $3k–$5k | OSHA, $163k/site | 12% | 19.6 | Mandatory pre-shipment |
| CE MD 2006/42/EC + EN 809 | $4k–$7k | EU MSAs, €1M | 18% | 32.4 | Technical-file review before despatch |
| DOE 10 CFR 431 PEICL ≥1.00 | $2k–$3k | DOE/CCB, $463k | 8% | 7.4 | Specify PEICL on datasheet |
| NSF/ANSI 61 potable | $6k–$9k | EPA/State, $25k + recall | 5% | 6.3 | Require certification letter |
| ATEX 2014/34/EU Cat 1 | $8k–$12k | Notified Body, criminal | 3% | 4.5 | Audit QAN & test reports |
| FDA 21 CFR extractables | $10k–$15k | FDA, $500k + consent decree | 2% | 3.0 | Lab test batch sampling |
| REACH SVHC >0.1% | $1k–$2k | ECHA, €250k/substance | 15% | 11.3 | Supplier full-material disclosure |
Evidence cost = testing, notified-body, travel, translation.
*Downside Risk Index = (Max fine ÷ 1000) × Audit probability; used to rank PO priorities.
Legal Exposure Beyond Fines
Product liability insurers apply a 25%–40% surcharge on premiums when the above certificates are absent. In 2023, a mid-size utility faced a $14M judgment after a non-UL panel fire; the supplier’s $2M CGL policy was voided for “failure to comply with recognised safety standards.” Customs can issue a Withhold Release Order under 19 USC 1307 if forced-labour suspicion attaches to castings—vertical turbine bowls from certain regions are already on the CBP watch list; detention averages 74 days, adding $1,200 per day in demurrage.
Executive Directive
Procurement charters must hard-code these standards into technical specifications and supplier quality clauses. Require a consolidated conformity dossier (CoC, test reports, risk assessment, translation) as a zero-excuse supporting document with every shipment. Anything less transfers compliance risk—and eight-figure downside—from the vendor to your balance sheet.
The Procurement Playbook: From RFQ to Commissioning

H2 Strategic Procurement Playbook: Vertical Centrifugal Pump (VTP/VS6)
H3 1. RFQ Architecture: Lock-in 3 Cost Levers Before Market Moves
Open the RFQ with a 5-year TCO matrix that forces bidders to reveal energy draw at BEP, NPSH margin <1 m, and MTBR ≥30 000 h; any deviation triggers a 5 % price adjustment clause. Benchmark cast-steel bowl assemblies at $50k–$80k per stage and stainless impellers at 1.35× cast-iron parity; insert a steel-index collar (CRU–HR coil) with ±8 % band to neutralise Q3–Q4 volatility. Require documented capacity utilisation ≥75 % at selected foundry; sub-70 % utilisation automatically shifts 20 % of award volume to secondary source under dual-source option. Close RFQ 30 days before Chinese New Year to pre-empt foundry holiday tightness that historically adds 6–8 % to casting surcharges.
H3 2. Technical Evaluation: Score Reliability, Not Brochures
Weighting: 45 % hydraulic repeatability (ISO 9906 Grade 2B), 30 % critical-speed margin ≥20 %, 15 % VFD harmonic tolerance, 10 % service density (km of installed base within 500 km of site). Disqualify any pump whose first lateral critical is <120 % of max continuous speed; 80 % of field failures originate here. Mandate a witnessed performance test at 115 % of best-efficiency flow; a 1 % efficiency shortfall equals $12k–$15k NPV penalty over 5 years at 0.08 $/kWh. Embed right of further audit at OEM’s test lab; refusal erases 10 % of contract value.
H3 3. FAT Protocol: Make It a Pass-Fail Gate
Factory Acceptance is executed only after rotor assembly balance to ISO 21940 G2.5; no rework allowances. Require 4-hour continuous run at 110 % speed, vibration ≤3.0 mm/s RMS, bearing temperature rise <40 °C. Record all data into OEM’s digital twin; buyer receives API 610 datasheet XML for future predictive analytics. If vibration exceeds 4.5 mm/s, OEM pays $2k–$3k per day of site delay plus air-freight delta for replacement rotor. FAT sign-off is conditional on receipt of material certificates 3.1.B for shaft, impeller, and column pipe; missing certs reset the FAT clock.
H3 4. Contract Risk Grid: FOB vs DDP Decision Matrix
| Decision Variable | FOB Shanghai (Incoterms 2020) | DDP Site (Incoterms 2020) | Risk-Control Tactic |
|---|---|---|---|
| Total Landed Cost Index | 100 (baseline) | 112–118 | Hedge FX (CNY/USD) 60 days prior to EXW; cap at 3 % |
| Transit-Time Volatility | σ = 6–9 days | σ = 2–3 days | Insert LD clause: 0.5 % of contract per day after week 10 |
| Customs Duty Exposure | Buyer | Seller | DDP: push 25 % pump tariff risk to OEM; saves $30k–$50k per $1 m order |
| Force-Majeure Allocation | 50/50 | 100 % OEM | FOB: add “pandemic shutdown” buffer (14 days) or 2 % price rebate |
| On-Site Damage Frequency | 1.2 % of shipments | 0.3 % | DDP: OEM absorbs replacement cost; reduces insurance premium 25 % |
| Cash-Flow Impact | Pay at load (Week 6) | Pay at unload (Week 12) | FOB: negotiate 180-day LC; cost of capital 3.8 % vs 6.5 % for DDP supplier finance |
Choose FOB when freight futures show <5 % contango and your balance sheet carries <30 days inventory; otherwise DDP caps escalation and transfers port-congestion risk.
H3 5. Site Commissioning: Zero Punch-List Target
OEM field engineer must arrive with pre-loaded calibration certificates for pressure & vibration transducers; no third-party sub allowed. Startup window is 72 hours after grout cure; beyond that, standby rate of $1.5k/day applies. Perform string test with actual VFD to validate no resonance within 70–105 % speed range; record Bode plots. Final acceptance is issued only after 168-hour uninterrupted run with bearing temperature <70 °C and seal flush differential stable ±5 %. Retain 10 % of contract value until reliability milestone of 2 000 hours is logged; releases automatically if MTBF ≥6 months.
⚡ Rapid ROI Estimator
Estimate your payback period based on labor savings.
Estimated Payback: —


