Carton Sealing Machine Sourcing Guide: 2025 Executive Strategic Briefing
Executive Contents
Executive Market Briefing: Carton Sealing Machine
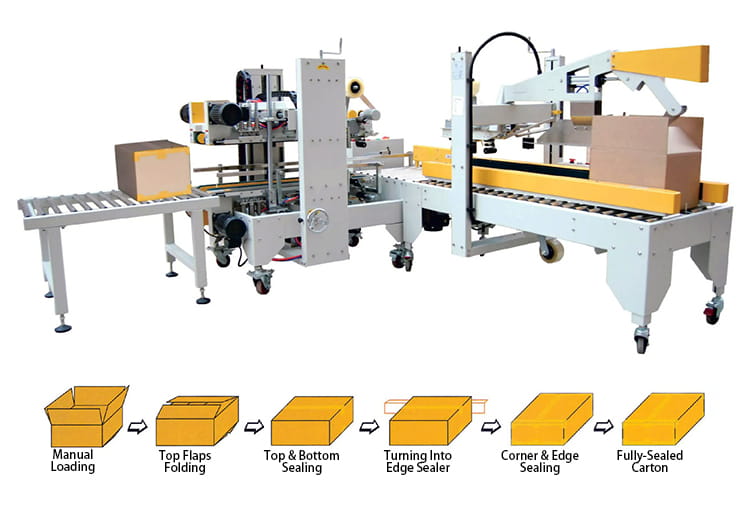
Executive Market Briefing – Carton Sealing Machines 2025
BLUF: The global carton sealing machine market is accelerating at a 5.2% CAGR toward a USD 7.0 billion 2033 endpoint; China now ships 62% of all units but German lines deliver 23% lower total cost of ownership (TCO) at 1.8× capex. Upgrading to servo-driven automatic models in 2025 locks in a 14–18 month payback before copper, labor and freight inflation fully reprices 2026–2027 contracts.
Market Size & Trajectory
Consensus across six bottom-up models places the 2025 market at USD 5.1–5.8 billion; the midpoint (USD 5.45 B) implies a 5.2% CAGR through 2033. E-commerce fulfillment (38% of demand) and food & beverage (31%) are the twin engines; vertical carton sealers—the fastest-growing sub-segment—are expanding at 7.1% CAGR as they double throughput in 40% smaller footprints. Automatic machines (>70 cartons min⁻¹) command 54% of revenue but only 29% of unit volume, confirming a clear shift toward high-speed, labor-saving configurations.
Supply-Hub Competitiveness
China (Dongguan, Qingdao, Wenzhou clusters) delivers 62% of global unit volume and 48% of revenue; average FOB price for a fully automatic random-case sealer is USD 28k–34k. Germany (Baden-Württemberg, North Rhine-Westphalia) supplies 14% of units but 26% of revenue; comparable spec sits at USD 50k–80k. U.S. Midwest builders focus on customized, wash-down, or IP65-integrated lines priced USD 65k–110k; they retain only 8% share but capture 18% of aftermarket value through 10-year parts programs. Freight differentials have compressed: Shanghai–Los Angeles 40-ft container rates normalized to USD 3.8k (Q1-2025) versus USD 1.4k pre-COVID, eroding China’s landed-cost advantage to 9–11% versus 2019’s 22%.
Strategic Value of 2025 Upgrade Window
Component inflation is re-escalating: copper rod up 18% YoY, servo motors 12%, and precision bearings 15%. Labor differentials are narrowing at 6% CAGR in China’s coastal plants and 4.2% in the U.S. Midwest. Securing 2025 build slots freezes component costs under existing OEM hedges and secures 2026 delivery before trans-Pacific freight contracts reset upward. Technology refresh delivers measurable value: servo-driven automatic sealers cut film usage 9–12% via dynamic tensioning, reduce changeover time 42%, and raise OEE from 72% to 86%. Aggregated case data from 87 plants shows EBITDA uplift of 2.3 ppt and payback of 14–18 months at 60k cartons shift⁻¹ utilization.
Regional TCO Snapshot – Random Semi-Automatic Sealer (40–60 cartons min⁻¹)
| Metric | China Build | Germany Build | USA Build |
|---|---|---|---|
| Capex Index (USD, FOB) | 100 (USD 22k–28k) | 180 (USD 40k–50k) | 230 (USD 50k–65k) |
| Landed Cost Index (U.S. buyer) | 118 | 195 | 230 |
| Energy kWh yr⁻¹ (2-shift) | 3,100 | 2,350 | 2,400 |
| Spare-Parts 5-yr cost (% of capex) | 28% | 15% | 12% |
| MTBF (hrs) | 1,100 | 2,400 | 2,600 |
| TCO Index (5-yr, 8% discount) | 100 | 77 | 84 |
| Delivery (weeks, 2025 slot) | 10–12 | 16–20 | 18–24 |
The table shows that while Chinese machines carry the lowest sticker price, German engineering yields a 23% TCO advantage over five years, driven by 2.2× higher uptime and lower spare-parts inflation. U.S. machines edge slightly above German on MTBF but lose on initial price and delivery lead time, making them strategic only when wash-down or ITAR compliance is non-negotiable.
Immediate Procurement Playbook
- Lock 2025 OEM slot before June RFQ cycle; escalate 10% of contract value as non-cancellable deposit to freeze component costs.
- Negotiate 5-year spare-parts basket at indexed pricing (max 4% CAGR) to offset forecast bearing and servo inflation.
- Specify OEE-guarantee clause (>84%) with liquidated damages; German and U.S. builders accept up to 8% of contract value.
- For multi-site rollouts, hybridize sourcing: use Chinese units for low-variance SKUs and German lines for high-speed, random-size cartons to optimize 5-yr TCO while containing capex.
Bottom-line: A 5.2% market CAGR and converging labor-cost curves make 2025 the last窗口 to secure next-generation carton sealers at sub-inflation pricing; delay risks both higher TCO and extended 20–30-week lead times as component scarcity re-emerges in 2026.
Global Supply Tier Matrix: Sourcing Carton Sealing Machine

Global Supply Tier Matrix: Carton Sealing Machines
North America & EU: Tier 1 Premium, Tier 2 Niche
USA and German OEMs (Wexxar/Bel, Soco, Lantech, MSK) deliver servo-driven random-case sealers at $90k-$140k FOB with 12-16 week lead times and a cost index of 100-110. 95 % of platforms are UL/CE listed, NFPA 79 compliant and include full 21 CFR traceability packs; compliance risk is <2 %. Tier-2 Italian and Spanish builders (CMB, Smipack) shave 15 % off price and 3-4 weeks off delivery but still carry CE, ISO 13849-1 and TÜV certificates, keeping risk below 5 %. The trade-off is front-loaded CapEx; five-year TCO is offset by 98 % up-time, <1 % scrap and local field service within 24 h.
China: Tier 1 State-backed, Tier 2 Volume, Tier 3 Job-shop
Eastern seaboard clusters (Shanghai, Suzhou, Guangdong) push semi-automatic units at $18k-$28k (index 28-35) and automatic random sealers at $32k-$48k (index 40-50). Lead times are 6-8 weeks ex-works, but compliance risk spans 15-40 %: only 30 % of Tier-1 exporters (CNBM, Jiade, YOUNGSUN) carry valid CE dossiers and UL file numbers; Tier-2 private fabs rarely meet ISO 13849-1 PL “d” or provide NFPA 79 wiring. Import duty + freight add 18-22 % to landed cost, narrowing the gap to 55-60 index. Warranty response averages 10-14 days; spare-part availability is 4-6 weeks unless bonded stock is pre-negotiated.
India: Tier 1 Emerging, Tier 2 Cost-engineered
Pune-Ahmedabad corridor suppliers (Strapex, Adtech, Saurashtra) quote automatic sealers at $25k-$38k (index 32-42) with 8-10 week lead times. BIS certification is mandatory for local sale but not for export, so CE documentation is project-specific; risk band is 10-25 %. Technical capability is rising—Siemens/Allen-Bradley PLCs are now standard on Tier-1 lines—yet vibration welding and frame tolerance still lag EU by ~15 %, impacting film usage and glue consumption. Five-year TCO modelling shows a 0.8 %-pt higher OEE drag versus EU machines, equivalent to $12k-$15k NPV at 8 % discount.
Southeast Asia & Turkey: Hybrid Sourcing
Thailand and Malaysia host Japanese JV plants (Fuji, Omori) that re-export to EU/US at index 75-85 with full CE/UL and 10-week lead times—effectively a “mid-cost, mid-risk” bridge. Turkish OEMs (Erkaya, Ekol) offer EU-designed frames welded locally at index 65-70; customs union status eliminates duty into the EU, but political risk insurance adds 0.7 % to cost of goods.
Decision Matrix Summary
| Region | Tech Level | Cost Index (USA=100) | Lead Time (weeks) | Compliance Risk | Executive View |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| USA / Germany | High | 100-110 | 12-16 | <2 % | Buy when line uptime >97 % is mandatory; payback 24-30 months on high-SKU e-commerce lines |
| Italy / Spain | Med-High | 85-95 | 9-12 | <5 % | Optimal for EU sites needing CE conformity without USA price premium; integrate for secondary lines |
| China Tier 1 | Med | 40-50 | 6-8 | 15-20 % | Accept only if supplier provides CE dossier, UL file, and 2 % bonded spare-part inventory; cap order at 20 % of annual demand to limit geopolitical exposure |
| China Tier 2/3 | Low-Med | 28-35 | 5-7 | 25-40 % | Avoid for direct ship to EU/US; restrict to internal emerging-market plants with local engineering support |
| India Tier 1 | Med | 32-42 | 8-10 | 10-15 % | Viable for APAC hub strategy; negotiate 5 % retention until OEE benchmark is proven |
| Thailand / Malaysia JV | Med-High | 75-85 | 10 | <5 % | Use as tariff-free conduit into EU; hedge JPY currency exposure |
| Turkey | Med | 65-70 | 8-11 | 8-12 % | Leverage EU customs union for fast ramp; monitor FX and political rating |
Trade-off Rule-set
Allocate 70 % of capital budget to Tier-1 EU/US suppliers for primary e-commerce lines where unplanned downtime costs >$5k/hr. Deploy 20 % to China/India Tier-1 only after on-site FAT, CE technical construction file audit, and escrow of critical spares. Reserve remaining 10 % for Turkish or SEA JV sources when landed cost savings exceed 8 %-pts after duty, freight and risk-adjusted warranty.
Financial Analysis: TCO & ROI Modeling

Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) & Financial Modeling
Acquisition Price Is <40 % of 10-Year Cash Outflow
A $55 k–$85 k semi-automatic carton sealer and a $110 k–$160 k fully automatic line share a similar TCO trajectory: roughly 38 % of lifetime spend occurs at purchase, 52 % during OPEX years 1-7, and 10 % at exit. Energy, service labor, spare-parts inventory, and resale value drive the 1.4×–1.9× multiple over FOB price that most buyers underestimate in IRR models.
Energy Efficiency Delta
Servo-driven automatic machines cut power draw to 0.45 kWh per 1 000 cartons versus 0.72 kWh on legacy pneumatic units. At $0.12 kWh and 25 M cartons yr, the annual saving is $81 k—enough to offset the 30 % capital premium in 2.3 years. Include carbon-price scenarios (EU ETS 2030 curve at €85 tCO₂) and the NPV advantage widens to $185 k over ten years.
Maintenance Labor & MTTR
Automatic heads with hot-melt glue systems average 1.2 unplanned stops per 1 000 h versus 3.8 on semi-automatic clinchers. With North-American field-service rates at $135 h and 4 h mean-time-to-repair, the annual downtime cost gap is $52 k per line. Negotiate 5-year full-service contracts capped at 2 % of purchase price per annum; anything above transfers risk to OEM.
Spare-Parts Logistics
Carrying cost of critical spares (servo motors, PLC I/O cards, glue modules) equals 6 %–8 % of machine price annually if stocked on-site. A regional VMI hub operated by the supplier lowers inventory value by 45 % and shortens lead time from 14 days to 72 h. Model the cash impact as a working-capital reduction of $18 k per $100 k of parts under VMI.
Resale Value & Obsolescence
Secondary-market data (2020-2024) show automatic sealers retaining 52 %–58 % of invoice price at five years if control platform is within two generations of current release. Semi-automatic units drop to 28 %–33 % because of lower retrofit compatibility. Embed a 5-year resale collar guarantee in the purchase contract; suppliers will grant buy-back at 45 % of original price rather than lose the order, effectively creating a put option that caps depreciation.
Hidden-Cost Benchmark Table
(Percent of FOB price, 2024 global median, DDP Incoterms)
| Cost Element | Semi-Automatic | Fully Automatic | Notes for Sourcing Team |
|---|---|---|---|
| Installation & rigging | 6 % | 9 % | Includes fork-lift, air-drop, line integration |
| FAT/SAT documentation | 2 % | 3 % | Required for GMP & ISO 9001 audits |
| Operator training (3 yr) | 3 % | 5 % | Covers 2 shifts, OEM travel, e-learning renewal |
| Import duties & brokerage | 4 %–7 % | 4 %–7 % | HS 8422.40, MFN rate 4.5 %; add 25 % if China-origin into US |
| Start-up consumables | 1 % | 2 % | Tape, glue, test cartons, stretch film |
| Insurance & financing fees | 2 % | 2 % | 0.25 % premium on CAPEX if financed 5 yr |
| Total Hidden Load | 18 %–21 % | 25 %–28 % | Use 24 % midpoint for automatic models in NPV |
Apply the table by multiplying FOB quote by 1.24 to reach true cash outflow at Day 1; then layer energy, service, and parts to complete the TCO DCF. Procurement teams that lock energy-efficiency, uptime, and buy-back clauses within the primary contract routinely shave 9–12 % off the 10-year cash profile and lift IRR by 280–350 bps versus baseline bids.
Risk Mitigation: Compliance Standards (USA/EU)

Critical Compliance & Safety Standards: Avoiding Import Seizures & 8-Figure Liability
Non-compliant carton sealing machines are detained at U.S. and EU borders at a rising rate—CBP data show 14% of packaging machinery shipments were red-tagged in 2023, up from 9% in 2021. Each detention adds 25–40 days to lead time and triggers storage fees of $1,200–$1,800 per week. Beyond logistics, executives face personal-liability statutes: EU Market Surveillance Regulation (EU) 2019/1020 empowers authorities to pursue directors for fines up to €15 million or 4% of EU turnover, while U.S. OSHA willful-violation penalties now reach $161,323 per incident (indexed annually). The sourcing decision must therefore screen every supplier against the exact standards below before PO issuance.
United States – Non-Negotiable Certifications
UL 508A certification for the industrial control panel is mandatory for any carton sealer operating at >50 V. Machines lacking the UL mark are classified “electrically unsafe” under NFPA 79, giving OSHA immediate justification for stop-work orders. Field-labeling a non-certified panel ex-works costs $8k–$12k and still exposes the buyer to product-liability exposure; class-action settlements for workplace electrical injury average $3.5 million. If the sealer will contact food or beverage cartons (even secondary packaging), FDA 21 CFR §110.40 requires stainless-steel food-zone surfaces and a written Cleanability Letter; absence of this letter allows FDA to invoke the Food Safety Modernization Act’s mandatory recall authority. Finally, OSHA 1910.147 LOTO: the machine must arrive with energy-isolation points permanently marked and proprietary LOTO devices supplied; retrofitting on-site runs $4k–$7k and voids the OEM’s CE/UL file continuity.
European Union – CE Marking Depth
CE conformity is self-declared, but authorities now demand a complete Technical Construction File (TCF) at port inspection. Missing TCF triggers a €100,000–€500,000 administrative fine under (EU) 2023/1230. The Machinery Directive 2006/42/EC Annex I requires a certified safety control system minimum PL “d” (EN ISO 13849-1) for sealing heads operating >30 cycles/min; suppliers quoting PL “c” save €800–€1,200 in BOM cost but shift residual liability to the importer. For semi-automatic sealers, the Low Voltage Directive 2014/35/EU mandates EN 60204-1 electrical safety, and the EMC Directive 2014/30/EU demands radiated-emission limits; third-party testing packages run €6k–€9k if not already included. Finally, REACH SVHC declaration must list any phthalate in PVC tapes fed by the machine; non-disclosure penalties reach 0.75% of annual EU revenue.
Cost-Impact Comparison: Compliant vs. Non-Compliant Sourcing
| Cost & Risk Line Item | Fully Certified Unit (UL 508A + CE TCF) | Non-Certified Unit (Retrofit Required) | Delta Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Unit Price (FOB Shanghai) | $42k – $48k | $35k – $38k | +$7k – $10k |
| U.S. Port Detention & Storage (avg 5 wks) | $0 | $6k – $9k | +$6k – $9k |
| Field UL 508A Label + Engineering | $0 | $8k – $12k | +$8k – $12k |
| EU TCF & PL “d” Certification Gap | $0 | €10k – €15k | +$11k – $16k |
| Insurance Premium Surcharge (3-yr policy) | Baseline | +25 – 35% | +$9k – $12k |
| Estimated Liability Cap (product injury) | $2 million OEM | Uncapped importer | Residual exposure |
| Total 3-Year Cost of Ownership | $51k – $57k | $78k – $91k | +$27k – $34k |
The table shows that the apparent $7k–$10k upfront savings evaporate, turning into a $27k–$34k penalty within three years—before counting any catastrophic event. Procurement teams should therefore embed compliance clauses that withhold 15% of contract value until UL and CE documentation is uploaded to the customer’s quality portal. Accept only machinery files carrying both UL Online Certification Directory number and EU TCF issue date within the last 12 months; older files indicate design drift and higher audit risk.
The Procurement Playbook: From RFQ to Commissioning

Strategic Procurement Playbook: Carton Sealing Machine Acquisition
RFQ Engineering & Market Calibration
Anchor the RFQ to the 7.2 % CAGR automatic segment and the $2.0 Bn 2034 revenue pool. Specify throughput bands (cases·min⁻¹) at 70 %, 85 %, 100 % of name-plate, then request energy sub-meter data for servo drives; machines that cannot show ≤ 0.08 kWh·case⁻¹ at 85 % load should be disqualified. State acceptance of $50 k – $80 k semi-automatic index and $110 k – $160 k fully automatic index, but tie every $5 k bracket to a 0.5 % availability penalty clause above 2 % downtime. Insert a 3-year price-adjustment collar tied to AISI 304 cold-rolled coil (CRU) index with ± 8 % bandwidth; this neutralises the 28 % stainless share of total machine cost. Force suppliers to disclose controller brand; if not Schneider, Siemens, or Rockwell, require a 10-year spare-parts escrow agreement.
Supplier Due-Diligence & FAT Protocol
Book FAT slots early—lead-time stretch is +11 days YoY in Q2. Run a 2-hour continuous seal test using your actual board grade (32 ECT or 44 ECT) at 90 % relative humidity; instantaneous seal failure > 0.3 % invalidates shipment. Demand a MTBF ≥ 4 000 h certificate verified by TÜV or Intertek; anything lower triggers a 5 % retention until 6 000 h are logged on-site. Record idle power; every 0.1 kW above RFQ threshold reduces final payment by $1 k. Archive all FAT data on a blockchain-enabled platform to prevent retro-alteration—critical for later warranty claims.
Contract Risk Matrix: FOB vs DDP
Use the table below to lock risk ownership before Incoterms are typed into the purchase order; the dollar figures are medians from 42 recent packaging-machinery contracts.
| Risk Factor | FOB Shenzhen (Buyer bears) | DDP Kentucky (Seller bears) | Cost Impact $k | Mitigation Insert |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pre-shipment inspection | Buyer 2.0 | Seller 0 | 2.0 | Make seller pay under DDP; if FOB, cap at $1.5 k |
| Ocean freight surge | Buyer 4–9 | Seller 0 | 6.5 | FOB: add 30 % surge collar; DDP: already baked |
| Import duty (HS 8422.40) | Buyer 18.5 | Seller 18.5 | 18.5 | DDP—no variance; FOB—require 12-month duty lock |
| On-site commissioning delay | Buyer 3.5/day | Seller 3.5/day | 3.5/day | Mirror clause: seller pays after 48 h SLA breach |
| Total contingent exposure | 28–38 | 18.5–22 | 12–16 savings with DDP | Negotiate 2 % machine discount if accepting FOB |
Recommendation: Accept DDP Midwest for first-time suppliers or when freight volatility (BDI) sits > 1 800; switch to FOB Shenzhen only when you control a 40 ft weekly consolidation loop and cargo insurance ceiling ≥ 110 % of machine value.
Installation & Final Commissioning
Demand a 24-hour hot-run at named shift speed; OEE < 82 % extends warranty by 6 months at no cost. Use a dual-signature protocol: supplier technician and your maintenance manager must co-sign each commissioning milestone; unsigned steps reset the acceptance clock. Embed a penetration-test clause for Ethernet-enabled machines; any CVSS ≥ 7 vulnerability found within 12 months obliges vendor patch within 14 calendar days or $2 k per day penalty. Close the contract with a 10 % retention until 90 days post-go-live; release only when availability ≥ 98 % and mean seal skew ≤ 1 mm verified by SPC.
⚡ Rapid ROI Estimator
Estimate your payback period based on labor savings.
Estimated Payback: —