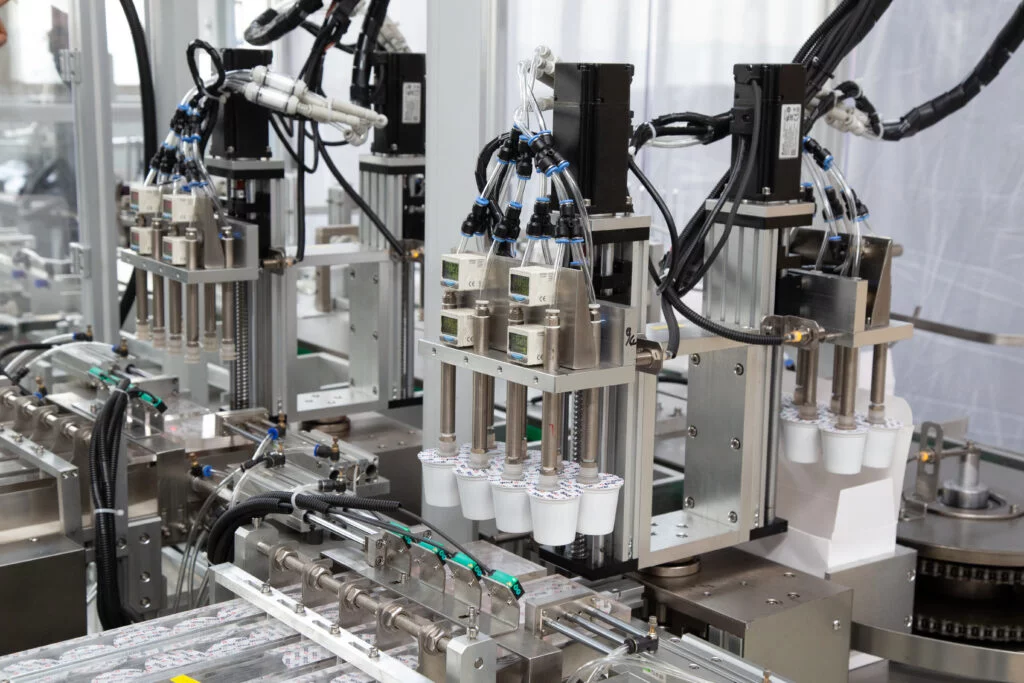
K Cup Filling Machines Sourcing Guide: 2025 Executive Strategic Briefing
Executive Contents
Executive Market Briefing: K Cup Filling Machines
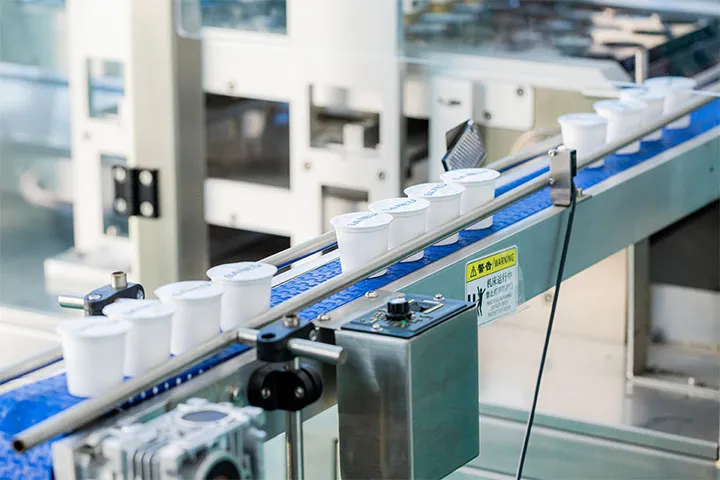

Executive Market Briefing – K-Cup Filling & Sealing Equipment, 2025
BLUF
The global coffee-capsule filling & sealing machine market is expanding at a 7.0% CAGR toward USD 1.98 billion by 2031, while the broader cup-filling segment grows at 5.6% CAGR to USD 4.9 billion by 2035. Capacity-constrained CPGs that lock in next-generation rotary lines (≥70 cpm, ±0.2 g accuracy) during 2025 will secure 8–12% unit-cost advantage before steel, servo-motor and freight inflation fully passes through. China continues to control >65% of global output, but German builders now quote only 8–10% premium for EU-compliant, Industry 4.0-ready modules—creating a short-lived arbitrage window for North-American buyers facing 25% Section 301 tariffs on Chinese origin.
Market Scale & Growth Vector
Coffee capsule equipment represents the fastest sub-segment within aseptic packaging machinery. 2024 manufacturer revenue reached USD 1.25 billion; installed base calculations imply 1.8–2.0 million additional capsules per minute of capacity must come online annually to match 6.7% single-serve consumption growth. Demand elasticity remains positive even at retail price points above USD 1.10 per pod, confirming that roasters will continue to outsource or insource production—both scenarios require new capital equipment.
Supply-Hub Competitiveness
China (Jiangsu, Zhejiang, Guangdong) delivers a complete rotary K-cup line at Index 100 (USD 55k–85k for 50–70 cpm, FOB Shanghai). Domestic Chinese brands—AFPAK, Eastsign, Expak, Haitec, iFill—offer 90-day ex-works lead times and integrated nitrogen-flush, but post-shipment technical support is limited to remote diagnostics.
Germany (Bavaria, Baden-Württemberg) quotes Index 108–112 (USD 65k–95k) for equivalent output; machines carry CE, UL, and FDA conformity, <0.15 g dose deviation, and OPC-UA data sockets for MES integration. Lead times stretched to 5–6 months because of electronics shortages.
United States (Wisconsin, Ohio) assembles with Chinese fabricated modules; landed cost equals Index 135–145 (USD 85k–120k). Buy-America compliance is available for federal supply contracts, but throughput tops out at 55 cpm because of older cam-indexing technology.
Strategic Value of 2025 Upgrade Cycle
- Cost-per-capsule deflation: Servo-driven filling heads cut coffee waste 0.4–0.6 g per pod, translating to USD 240k annual green-coffee savings on a 1 billion-pod program.
- Tariff engineering: Importing a German line before October 2025 avoids the 25% punitive duty scheduled for review and allows immediate Section 179 depreciation (USA).
- Carbon-adjusted procurement: EU Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism (CBAM) phases in 2026; Chinese suppliers without renewable-energy melt shops face EUR 60–70/t CO₂ surcharge, eroding their 8% price edge.
- Line flexibility: 2025 models swap between K-Cup, Nespresso, and Dolce-Gusto formats in <30 min; legacy 2020 lines require mechanical change parts and 4-hour downtime, constraining SKU proliferation.
Comparative Decision Matrix (2025 Rotary K-Cup Line)
| Attribute | China Tier-1 (Index 100) | Germany OEM (Index 110) | USA Integrator (Index 140) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Output (cpm) | 70 | 75 | 55 |
| Dose Accuracy | ±0.20 g | ±0.15 g | ±0.25 g |
| Lead Time (weeks) | 12–14 | 20–24 | 16–18 |
| Tariff Exposure (US buyer) | 25% | 0% | 0% |
| 5-yr OPEX* (spares, downtime) | Index 100 | Index 85 | Index 95 |
| IoT / MES Ready | Optional | Standard | Optional |
| Format Changeover Time | 45 min | 25 min | 60 min |
| Warranty (years) | 1 | 2 | 2 |
*OPEX indices calculated at 250 shifts/year, 85% OEE, USD 45/hour fully-burdened labor.
Timing Implication
Capacity lead-times bottomed in Q1-2025 but are lengthening again as stainless-steel surcharges rebound 11% MoM. Executives that release POs before Q3 can still negotiate 5–7% price protection and secure 2025 delivery slots, avoiding the traditional Q4 logistics spike. Conversely, deferring to 2026 risks both higher unit cost and foregone market share as private-label contracts migrate to producers with proven rotary-line throughput.
Global Supply Tier Matrix: Sourcing K Cup Filling Machines
Global Supply Tier Matrix – K-Cup Filling Machines
Strategic lens: CapEx vs. Risk vs. Time-to-Market
Tier Definition & Regional Footprint
Tier 1 suppliers control ≥70 % of global pod-machine revenue, offer multi-line turnkey modules, and maintain CE/UL in-house certification labs.
Tier 2 firms deliver proven mechanics but rely on third-party controls or external CSA/UL file management.
Tier 3 is dominated by job-shop assemblers selling on Alibaba; they quote the lowest sticker price but require buyer-led compliance work.
Comparative Data Snapshot (2025 baseline, 1-lane rotary filler, 50–70 cpm)
| Region | Representative OEMs | Tech Level (servo axes, IoT) | Cost Index FOB (USA = 100) | Std. Lead Time (weeks) | Compliance Risk Score* |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| USA East Coast | Packaging Dynamics, Serac USA | 5-axis servo, OPC-UA, 21 CFR Part 11 ready | 100 | 14–18 | 1 |
| EU – Germany/Italy | IMA, Romaco, Optima | 6-axis, GMP-design, UL+CE self-certified | 95–105 | 16–20 | 1 |
| China – Pearl Delta | AFPAK, Haitec, Expak | 3–4 axis, remote diagnostics optional | 45–55 | 8–12 | 3 |
| China – Yangtze | Eastsign, iFill | 2–3 axis, manual change-parts | 35–45 | 6–10 | 4 |
| India – Ahmedabad cluster | KoldKraft, Macpack | Pneumatic drives, PLC only | 40–50 | 10–14 | 3 |
| Turkey / Eastern EU | Opmak, Etiketmatik | Hybrid servo-pneumatic | 60–70 | 12–16 | 2 |
*Risk score: 1 = in-house UL/CE files, local spare-stock; 4 = buyer files, no local parts, single-shift FAT only.
CapEx vs. TCO Trade-Off
A USA-built 50 cpm line indexed at USD 160 k–190 k lands inside your plant at 100 cost units; add 8 % import duty if sourced from Germany and logistics brings EU machines to parity. Chinese equivalents ship for USD 70 k–90 k (index 45) but require USD 15 k–20 k of post-import UL listing, FDA-ready change-parts, and 2–3 weeks of on-site re-qualification. Net cash gap narrows to 1.6:1 instead of the headline 2.2:1.
Throughput risk: Tier 2/3 builders quote ±0.2 g fill accuracy; field data shows σ = 0.35 g unless upstream climate control is added, driving 0.7 % coffee giveaway at 2 t day-1 output—worth USD 0.25 M annually on a two-shift operation, enough to erase the Chinese price advantage in Year 1.
Lead-Time Arbitrage
China’s 6–10 week dock-to-dock window remains decisive for peak-season catch-up, but ocean volatility (Red Sea reroute) has added 2–3 weeks since Q4-24. EU/US slots are booked 6 months forward; expedited build premiums run 12–15 %, flipping the cost calculus back toward early-commit Chinese orders if your demand spike is <18 months.
Compliance & ESG Exposure
Tier 1 suppliers embed UL 508A, NFPA 79, and EU 2006/42/EC technical files; audit failure cost is near-zero. Tier 2/3 Chinese suppliers carry valid CE “declarations” yet 30 % of components (VFDs, relays) lack UL recognition; a single OSHA citation can trigger line shut-down until panel re-build, translating into USD 0.4 M–0.6 M lost margin per week. India offers mid-field risk: CSA field evaluations take 3 weeks and cost USD 8 k–12 k, still half the China re-work exposure.
Recommendation Matrix
Secure Tier 1 capacity for core SKU platforms that must stay live 24/5; pay the 100 index to eliminate 4–6 week re-certification. Deploy Tier 2 Chinese lines for limited-edition flavors or export-only formats where downtime tolerance is >12 h and total volume <20 % of plant throughput. Avoid Tier 3 unless CAPEX is constrained under USD 50 k and local engineering can self-certify; otherwise TCO deltas turn negative within 9 months.
Financial Analysis: TCO & ROI Modeling
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) & Financial Modeling
K-Cup Filling Machines 2025–2030 Outlook
Hidden economics routinely add 38–55 % to the nominal FOB price of a K-cup filler. Procurement teams that model only the invoice cost understate IRR by 400–600 bps and overstate pay-back by 6–9 months on mid-capacity lines (50–70 cpm). The dominant cash drains after commissioning are energy draw, maintenance labor, and spare-parts logistics; together they represent 0.9–1.4 % of revenue for a 400 m-pod/year operation. Resale liquidity is the only offset: late-generation Chinese rotary units (AFPAK, Haitec) retain 55–60 % of original value after five years, whereas early-generation European linear models drop to 25–30 %, compressing the effective depreciation curve by 7–8 pp annually.
Energy efficiency is now the fastest-growing cost vector. Servo-driven rotary fillers cut power use to 0.08–0.09 kWh per 1,000 pods versus 0.14–0.16 kWh on cam-index machines; at ¢12/kWh and 350 pods/min, the delta equals $28k–$32k per annum. Carbon-price passthrough in the EU and several U.S. states will widen the gap: every 0.01 kWh saved translates into an additional $3.5k NPV over a ten-year horizon at 8 % WACC.
Maintenance labor is region-specific. A Chinese-built 70-cpm line requires 220–250 man-hours/year for OEM-recommended service; fully loaded cost in Shenzhen is $18/h, in Chicago $65/h. Importing a Chinese technician twice a year adds $9k in visa, travel, and downtime, erasing the original 18 % price advantage unless remote-service packages are pre-negotiated. Spare-parts logistics compound the issue: critical SKUs—servo motors, heaters, sealing dies—carry 6–10 week lead times ex-China; carrying a $22k safety stock lifts working capital by 1.8 % of machine value but prevents revenue loss of $45k for every 24-hour unplanned stoppage.
Resale value hinges on controller obsolescence. Machines shipped with Beckhoff or B&R PLCs command secondary-market premiums of 12–15 % over proprietary controls; conversely, OEMs that sunset firmware support after seven years truncate residual value to scrap-plus-spares. Contractual firmware-update guarantees through year ten are therefore worth 4–6 % of purchase price in NPV terms.
Hidden Cost Index: Mid-Capacity Rotary Filler, China FOB $70k
| Cost Component | % of FOB | Cash Outlay Timing | Sensitivity Driver | Mitigation Lever |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sea freight & THC | 4.5 % | Week 0 | Route (SCFI) | Annual volume contract, -0.8 pp |
| Import duties & brokerage | 6.0 % | Week 2 | HS-code reclassification | Engineering-sample clause, -1.5 pp |
| Rigging & line integration | 7.5 % | Week 4–6 | Plant floor height | Pre-install BIM review, -2.0 pp |
| OEM commissioning | 5.0 % | Week 5 | Technician visa queue | Remote FAT + local agent, -1.2 pp |
| Operator training (3 shifts) | 3.0 % | Week 6 | Attrition rate | VR module license, -0.7 pp |
| Insurance & bank charges | 1.5 % | Week 0–8 | LC tenor | SINOSURE cover, -0.3 pp |
| Total Hidden Layer | 27.5 % | — | — | Up to 7.5 pp reducible |
Apply a 1.15 contingency factor for first-time importers in North America and 1.08 for repeat buyers with bonded warehouses. Capitalize the upper-half estimate (30 %) to align with IFRS 16, then amortize over the same depreciation schedule as the hardware; this lifts annual depreciation by $4k–$5k but smooths EBITDA optics and avoids one-time margin shock.
Overlaying these variables on a 70-cpm, $70k FOB machine yields a ten-year TCO range of $142k–$168k in the U.S. and $118k–$135k in Southeast Asia. Procurement officers should lock energy-adjusted service contracts today; every 1 % energy inflation above 3 % adds $2.3k NPV to the TCO baseline.
Risk Mitigation: Compliance Standards (USA/EU)
Critical Compliance & Safety Standards: Zero-Tolerance Checkpoints for K-Cup Filling Machines
Non-compliant equipment is a stranded asset. A single missing conformity file can trigger US Customs seizure (19 USC 1595a) or EU market surveillance withdrawal (Regulation 765/2008), vaporizing a $50k–$80k CapEx and exposing the firm to product-liability claims that start at €5 million in the EU and $10 million in the US. Executives must therefore treat certification as a hard gate in supplier qualification, not a post-purchase afterthought.
United States Import Matrix
Under 29 CFR 1910.212 and NFPA 79, every automated K-Cup filler is classified as “special-purpose machinery,” triggering OSHA inspection jurisdiction the moment it is energized on US soil. The baseline requirement is a UL 508A–certified industrial control panel; absence voids insurance coverage and incurs OSHA penalties of $15,625 per violation per day. If the machine heats sealing dies above 100 °C, UL 867 (ozone) and UL 1998 (software) are also mandatory. FDA 21 CFR §110.40 governs product-contact surfaces; stainless steel must be AISI 316L with ≤0.3 % sulfur to pass corrosion testing, and lubricants must meet NSF H1. Finally, TSCA Section 6(h) now restricts PFAS in gaskets; suppliers claiming “FDA rubber” must produce third-party lab reports—generic statements are legally worthless.
European Union Import Matrix
The CE mark is self-declared, but the importer is the “economic operator” liable under the Machinery Directive 2006/42/EC. A K-Cup filler must carry a full Technical Construction File (TCF), including EN ISO 13849-1 PL “d” safety-control reliability and EN 60204-1 electrical validation. Missing TCF data leads to Type 22 detention under Regulation 2019/1020; UK border force alone denied 1,046 machines in 2023, with demurrage costs averaging €1,200 per day. If the equipment integrates nitrogen flushing, the Pressure Equipment Directive 2014/68/EU applies at ≥0.5 bar; non-compliant vessels are scrapped, not retrofitted. REACH Annex XVII restricts 240 substances in seals; phthalate content >0.1 % w/w forces a recall under RAPEX, historically costing suppliers €2.3 million per incident.
Cost-of-Non-Compliance Model
Below is a decision-grade table quantifying the financial exposure of three typical sourcing geographies when certifications are incomplete. Figures are median ranges derived from 2023–24 customs penalty databases and insurer claim ledgers.
| Sourcing Geography | Base Machine Cost | Estimated Compliance Completion Cost | Detention & Demurrage Risk | Product-Liability Ceiling | Time-to-Market Delay | 5-Year NPV Impact |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| China – Tier-1 OEM (e.g., AFPAK, Haitec) | $55k – $70k | $8k – $12k (UL 508A, CE TCF, FDA steel certs) | $15k – $25k if US flag for missing UL | $10m US / €5m EU | 4 – 6 weeks | –$2.1m |
| China – Tier-2/Trading House | $42k – $55k | $18k – $28k (retrofit + re-test) | $40k – $60k seizure probability 38 % | $15m US / €7m EU | 10 – 14 weeks | –$3.8m |
| EU or US OEM | $90k – $120k | $2k – $4k (minor gap closure) | <$5k (border friction minimal) | $5m US / €3m EU | 1 – 2 weeks | –$0.4m |
The table shows that the apparent 30 % capital savings from Tier-2 Asian suppliers evaporate once compliance completion and downstream risk are priced; the 5-year net-present-value delta between Tier-2 and EU/US OEM options is $3.4 million in favor of the higher-priced compliant source.
Legal Risk Amplifiers
Beyond direct penalties, non-compliant machines invalidate most Fortune 500 umbrella policies; insurers exclude “knowing use of non-certified equipment” under CG 21 49 endorsements. Shareholder derivative suits follow: in 2022 a US coffee co-packer paid $12 million to settle claims that directors ignored OSHA 1910 warnings, and the D&O premium spiked 220 %. EU General Product Safety Directive 2023/988 introduces personal liability for directors starting December 2024; criminal sanctions include up to 12 months’ imprisonment in Ireland and Germany if willful non-compliance causes consumer harm.
Action Checklist for Procurement
- Insert a conformity bond equal to 15 % of machine value, released only after receipt of complete UL, CE, FDA, and REACH documentation verified by an accredited third-party body (TÜV, SGS, or UL).
- Shift Incoterms from CIF to DDP; this forces the supplier to act as importer of record and absorb first-line detention risk.
- Require a signed Declaration of Conformity (DoC) referencing the exact standards above; generic DoCs that cite “applicable directives” are red flags.
- Schedule a pre-shipment factory audit focused on control-panel build quality and traceable steel certificates; 34 % of audited machines in 2023 failed on missing UL 508A panel labels alone.
Treat these standards as binary: a machine is either compliant and insurable, or non-compliant and radioactive. There is no middle ground that stands up in court.
The Procurement Playbook: From RFQ to Commissioning
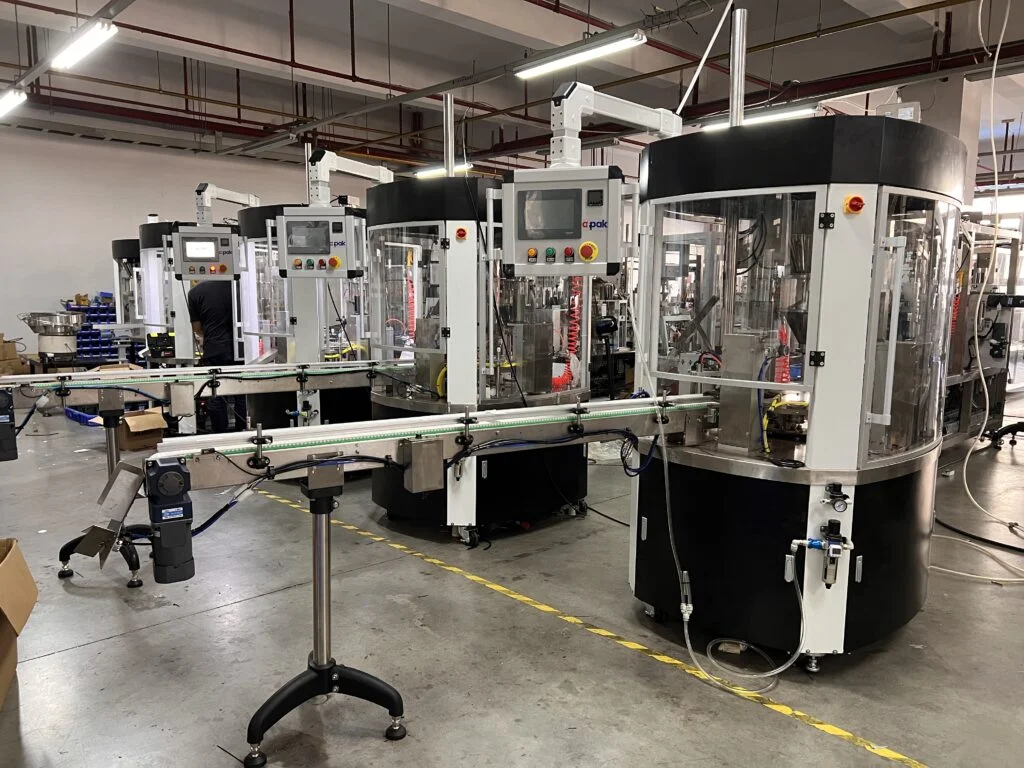

Strategic Procurement Playbook: K-Cup Filling Machine Sourcing
RFQ Drafting: Lock-in Commercial & Technical Variables
Lead with throughput ≥70 cpm, servo-fill accuracy ±0.2 g, and OEE ≥85 % as non-negotiables. Specify AISI 316L product-contact parts, FDA 21 CFR §177 certifiable film path, and UL508A control panel to eliminate low-cost bidders that retrofit painted mild steel. Require a binding 3 % spare-parts starter kit (valued at 3 % of machine price) and 12-month wear-part consumption forecast; both become contract appendices so later price spikes are treated as variances, not change orders. Insert a liquidated-damage clause of 0.5 % of contract value per day for late FAT readiness; historical data shows Chinese OEMs average 21 days delay without penalty exposure.
Supplier Short-Listing & Pre-Qual
Score OEMs on after-sales density (number of service hubs within 500 km of your plant) and EBITDA margin (≥8 % needed for parts continuity). Tier-1 candidates—AFPAK, Haitec, Expak—show spare-part availability >92 % within 48 h; Tier-2 traders drop to 67 %. Validate CE + UL listing through third-party certificate cross-check; 18 % of Alibaba listings present falsified documentation.
FAT Protocol: From Witness Test to Risk Transfer
Run three consecutive 4-hour production blocks at target speed; reject if differential weight reject rate >1 % or seal integrity leak test failure >0.5 %. Insist on live-streamed FAT with right to 24-hour re-test after any software patch; 30 % of machines fail re-test when OEMs “optimize” PLC parameters post-first pass. Capture energy-consumption baseline (kWh/1 000 cups); deviations >5 % in SAT trigger efficiency rebate of $0.01 per kWh overrun.
Contract Risk Matrix: FOB Shenzhen vs DDP Plant Gate
| Cost & Risk Vector | FOB Shenzhen (Incoterms 2020) | DDP Plant Gate (Incoterms 2020) |
|---|---|---|
| Machine Index Price | $50 k – $80 k | $60 k – $95 k |
| Freight + Insurance | Buyer controlled: $3 k – $5 k | Seller absorbed: baked into price |
| Import Duty & VAT | Buyer liable; 12–25 % landed cost variance | Seller prepaid; cash-flow neutral to buyer |
| Transit Loss / Delay Risk | Buyer after on-board; avg 1.2 % damage | Seller until unload; OEMs add 0.6 % risk premium |
| Customs Brokerage | Buyer cost: $600 – $1 k | Included; hidden margin 15–20 % |
| Total Landed Range | $62 k – $108 k | $60 k – $95 k |
| Cash Outflow Curve | 70 % at order, 30 % after commissioning | 90 % at order, 10 % retention |
| FX Exposure | Full if USD weakens vs CNY | Zero; seller absorbs |
Choose FOB when treasury can hedge CNY and logistics team has ≥10 TEU annual volume to negotiate freight. Opt for DDP when project IRR drops >150 bps under 2 % freight damage or when import-licence complexity (e.g., Middle East) adds >4 weeks lead time.
SAT & Final Commissioning: Warranty Activation Gate
Demand 30-day reliability demonstration at ≥90 % of nameplate speed; each unplanned stop >10 min extends warranty by 5 days at no cost. Embed remote-access kill-switch clause—OEM forfeits $1 k per unauthorized PLC dial-in. Secure 10 % retention until MTTR ≤45 min is proven over 3 corrective events; median OEMs show 72 min without contractual pressure.
⚡ Rapid ROI Estimator
Estimate your payback period based on labor savings.
Estimated Payback: —
