Aluminium Concertina Doors: The Ultimate 2025 Sourcing Guide
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for aluminium concertina doors
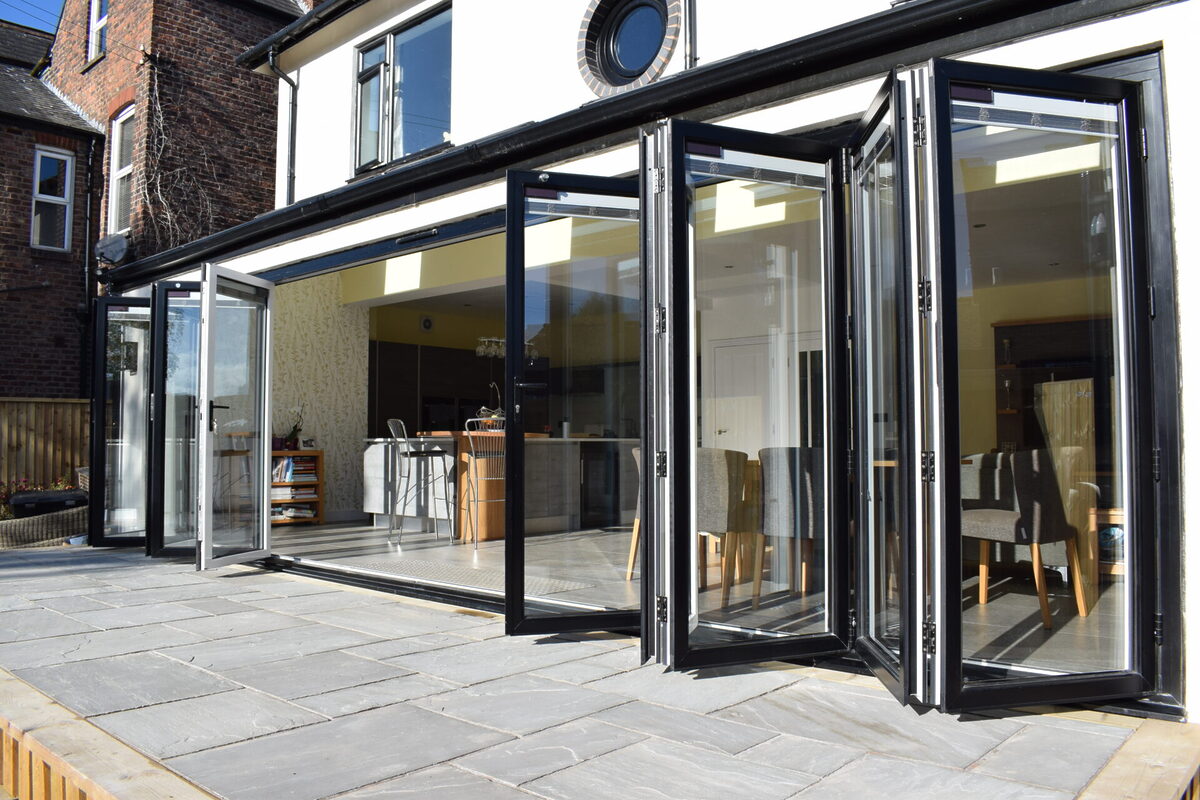
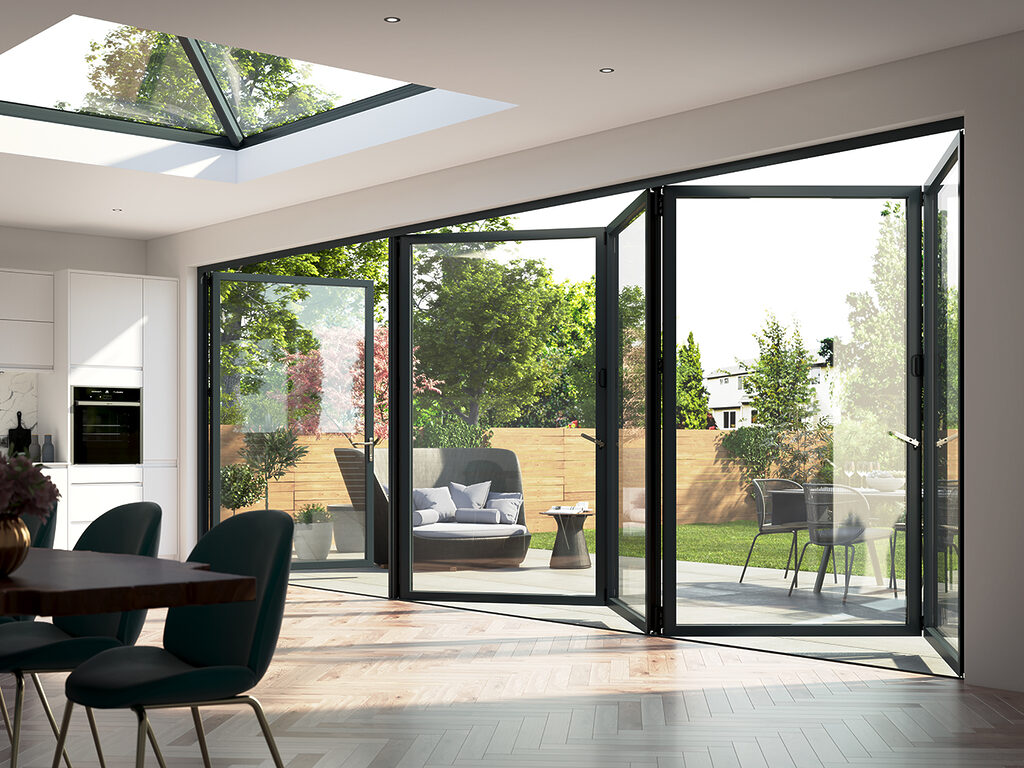
For commercial architects, developers, and project managers in the USA and Europe, aluminium concertina doors (folding, bi-fold, or multi-sliding systems) have become a strategic design choice: they deliver natural light, seamless indoor–outdoor flow, and strong operational performance. Yet sourcing them across regions introduces friction—confusing compliance, wide pricing bands, and inconsistent specifications.
Recent market signals show the split clearly. In North America, premium manufacturers such as LaCantina benchmark performance with energy efficiency, high-performance glass, and engineered hardware for exterior applications. In contrast, e-commerce suppliers like Innovz (Amazon) emphasize entry-level aluminium concertina doors with mesh, retractable screens, and compact sizes (44×80 in up to ~24×96 in), typically priced in the mid-hundreds. Shipping windows in the USA can be two to three weeks, with returnability limited to initial purchase windows (e.g., mid-2025 holiday purchases eligible until early 2026). These differences shape total cost of ownership (TCO): installation readiness, glazing quality, weather-seal durability, and lifecycle support matter as much as the sticker price.
This guide cuts through the complexity by helping you:
– Match specifications to code and climate across regions
– Decode compliance pathways (thermal, acoustic, weather performance, and project-specific standards)
– Scope true cost (hardware, glazing, delivery, installation, warranty)
– Evaluate suppliers using clear due-diligence criteria
– De-risk delivery and returns
Feature snapshot (performance vs. entry-level):
| Attribute | Premium Exterior Folding Systems | Entry-Level E-commerce Concertina |
|——————————–|———————————-|———————————–|
| Aluminium profile thickness | Engineered for rigidity and wind | Thick-frame focus; lightweight |
| Weather sealing | Multi-point compression seals | Basic seals; ventilation options |
| Glazing | High-performance, laminated/IG | Single-pane or budget IG |
| Screens | Integrated or retrofit options | Integrated retractable meshes |
| Burglary resistance | Hardened hardware and locks | Basic security enhancements |
| Acoustic performance | Enhanced ratings available | Limited isolation |
| Lead time (USA) | Weeks–months, factory orders | ~2–3 weeks for stocked sizes |
| Typical price (USA) | Quote-based (project-driven) | Mid-hundreds per set (example ~$556) |
| Returns | Project-specific | Amazon holiday returns allowed |
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Use this overview to set your evaluation criteria, then proceed with detailed spec checks, code mapping, and cost modeling.
Top 10 Aluminium Concertina Doors Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Origin – The USA’s Leading Manufacturer of Bi-fold Doors
Domain: originbifolds.com
Registered: 2013 (12 years)
Introduction: Origin are a global leader in the design and manufacture of custom aluminum bi-fold doors and windows. Combining a high grade aluminum with precision …Missing: top concertina…
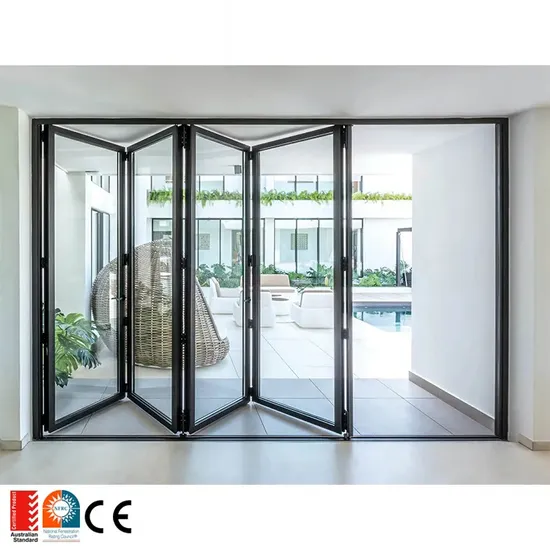

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
2. Buy Bifold Doors | Folding Patio Door – Eris Home Products
Domain: erishomeproducts.com
Registered: 2020 (5 years)
Introduction: Rating 4.8 (5,000) · Free delivery…
3. PA Folding Doors Leading Manufacturer with In-House Production
Domain: pa-window.com
Registered: 2023 (2 years)
Introduction: Experience the perfect blend of design and function with PA’s premium aluminum folding doors. As a trusted manufacturer with our own state-of-the-art …Missing: aluminium concertina suppliers…
4. Top 10 Bifold Door Manufacturers in the USA – George Furniture
Domain: georgefurniture.com
Registered: 2021 (4 years)
Introduction: Top 10 Bifold Door Manufacturers in the USA · 1. Centor · 2. Lanai Doors · 3. George Furniture · 4. LaCantina · 5. Andersen · 6. Aluk · 7. Origin · 8….
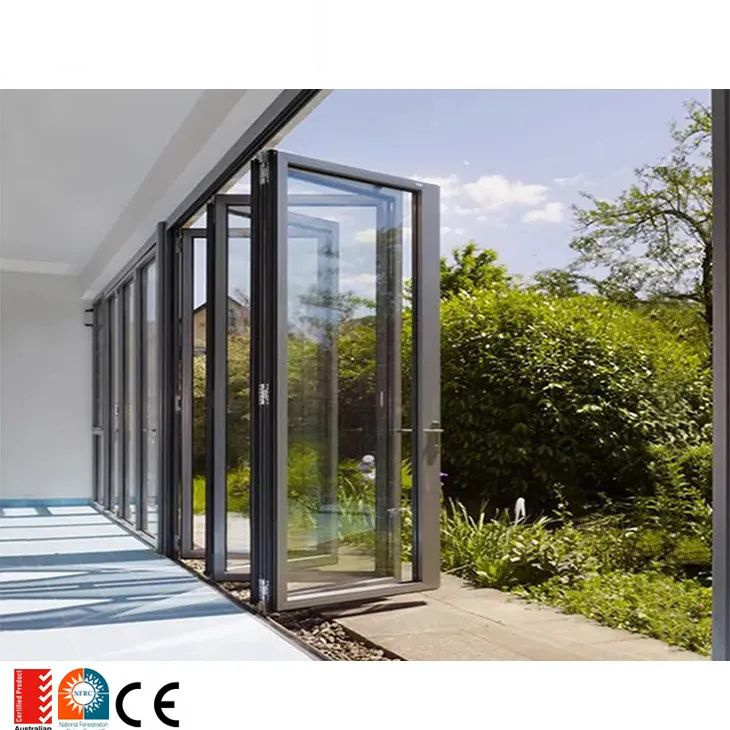
5. Lanai Doors Bi-folding Glass Walls and Folding Doors Systems …
Domain: lanaidoors.com
Registered: 2004 (21 years)
Introduction: Leading USA manufacturer of custom bi-folding glass walls & windows including radius, zero-post corner, door-window combo systems. We sell direct.Missing: top aluminium concertina…

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
6. Aluminum Bifold Sliding Glass Doors Manufacturers | Durable …
Domain: kenwindow.com
Registered: 2023 (2 years)
Introduction: Bifold Aluminum Sliding Glass Doors from us are made with top-grade rustproof aluminum for long-term durability and protection from harsh weather conditions….
7. China aluminium concertina doors Manufacturers Factory Suppliers
Domain: top-aluminium.com
Registered: 2018 (7 years)
Introduction: TOP ALUMINUM is one of the most professional aluminium doors manufacturers and suppliers in China, providing the best customized service….
8. APRO: Leading Manufacturer of Aluminum Doors & Windows
Domain: aprodoor.com
Registered: 2025 (0 years)
Introduction: APRO offers premium aluminum doors and windows, combining durability, style, and exceptional service for residential and commercial projects….
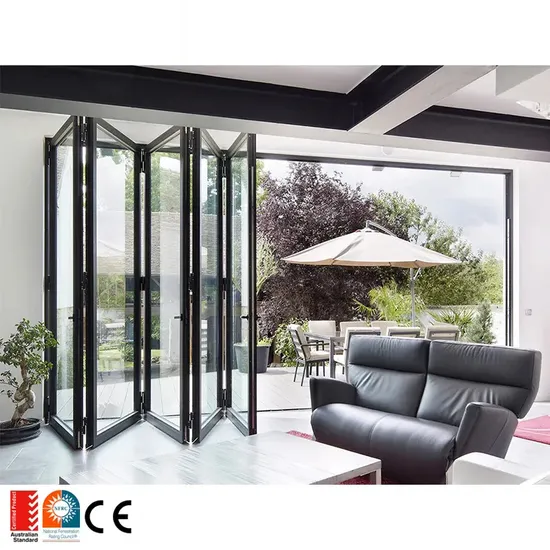
Understanding aluminium concertina doors Types and Variations
Understanding aluminium concertina doors: Types and Variations
Aluminium concertina doors (also called folding, bi-fold, or multi-slide doors) provide large clear openings while balancing structural, thermal, and security considerations. The right type depends on application, regulatory requirements, and performance goals (air/water/thermal). The table below contrasts the most common B2B variants.
| Type | Key Features | Typical Applications | Pros/Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| Exterior thermally broken (TB) multi-slide / bi-fold | Thermally broken frames; low‑U glazing; multi-point locks; adjustable tracks; sill options (flush/raised/threshold ramps); insect screens; multi-panel configurations | Residential/commercial patios, restaurants, hotels, residential/workspace expansions | Pros: Thermal control; large openings; scalable panel count; insect control options. Cons: Higher cost and coordination; sill planning needed; installation precision critical. |
| Narrow-stile commercial storefront folding | Thin profiles; minimal rail sightlines; exposed hardware; high traffic hardware; often butt-glazed | Retail fronts, offices, galleries, food service service windows | Pros: Clean aesthetics; high translucency; adaptable to storefront lines. Cons: Narrow profiles limit thermal performance; heavier handling; higher commercial hardware costs. |
| Fire-rated / egress-compatible folding | Fire-rated panel assemblies (e.g., tested to EN 16034 / UL 10C series) for specified durations; integrated egress leaf or tested egress performance in the folded stack; secure hardware; self-closing mechanisms | Schools, hospitals, corridors, commercial egress routes, mixed-use buildings | Pros: Code-compliant egress; controlled fire spread; flexible room layout. Cons: Heavier assemblies; higher installed cost; specialized detailing and testing documentation. |
| Integrated retractable screen folding (internal mesh concertina) | Retractable screen mesh; track options; burglar-deterrent framing; flexible panel widths; easy manual or spring-loaded operation; budget-forward finishes | Apartments, offices, healthcare, hospitality rooms, residential back-of-house | Pros: Air and insect control; security visibility; value-dense upgrade. Cons: Mesh visibility; cleaning/maintenance; limited thermal performance enhancement. |
| Pocket / folding pocket stacking (stacked in wall) | Panels nest into a concealed pocket; minimal floor space use; coordinated pocket door hardware; often integrated with sliding track; reduced swing clearance | Small spaces, restaurants, conference rooms, co-working areas, micro-units | Pros: Minimal floor intrusion; clean appearance. Cons: Pocket construction adds scope; limited maximum widths; complex trades coordination (framing, finishes). |
Exterior thermally broken multi-slide / bi-fold doors
- What it is: Multi-panel aluminium folding doors with thermally broken profiles designed for outdoor exposure and large openings.
- Why it matters: Thermal performance and seal integrity under wind and rain loads; operable large spans without column interruptions.
- Typical features:
- Low-E insulated glass (IGUs) with warm-edge spacers; low U-factor
- Multi-point locking hardware and reinforced panels for access control
- Adjustable tracks, cap rollers, and anti-rattle gaskets; adjustable thresholds (flush/raised/threshold ramps)
- Retractable insect screens; optional integral Venetian between panes
- 2–10+ panels per opening; bifold (paired) or multi-slide folding
- Applications: Patios, restaurants, hotels, co-working expansions, premium residential
- Standards and considerations: US—AAMA/WDMA performance, Egress (IBC/IFC) when applicable; EU—EN 12210/EN 12207/EN 12208/EN ISO 10077 for air/water/structural/thermal
- Pros: High thermal control and accessibility; scalable panel count; flexible finishes (Kynar/powder/anodized); low maintenance
- Cons: Higher installed cost; sill and drainage planning required; precise installation and trades coordination
- Procurement notes: Specify panel count, direction of travel, sill type, glazing, hardware, and performance class; plan for storage and staging during installation
Narrow-stile commercial storefront folding doors
- What it is: Folding door systems optimized for storefront and interior commercial spaces with thin stiles/rails and minimal visual obstruction.
- Why it matters: Maximizes daylight and storefront glazing lines while allowing flexible service openings.
- Typical features:
- Narrow sightlines and exposed hardware; butt-glazed options for continuous glazing
- High-cycle commercial hinges/rollers and locksets; reinforced panels for traffic loads
- Compatible with storefront framing and curtain-wall interfaces
- Powder coat and anodized finishes; specialty color matching
- Applications: Retail fronts, office atriums, galleries, quick-service food windows
- Standards and considerations: US—AAMA/WDMA storefront performance (air/water/structural), ADA where required; EU—relevant EN and National Building Code requirements
- Pros: Clean aesthetics; high translucency; integrates with existing storefront lines
- Cons: Narrow profiles can limit thermal performance; higher hardware costs for commercial duty; handling/transport of tall/large panels
- Procurement notes: Align with storefront perimeter framing; verify hardware rating for cycle count and accessibility; coordinate glazing type (tempered/laminated)
Fire-rated / egress-compatible folding doors
- What it is: Tested panel assemblies that provide fire resistance for a specified duration and maintain egress capability either through a dedicated leaf or tested performance when the door is in the folded configuration.
- Why it matters: Enables code-compliant openings in egress paths, corridors, and mixed-use applications without sacrificing flexibility.
- Typical features:
- Tested to EN 16034 or UL 10C-series standards (fire-resistive classification)
- Integrated egress leaf or approved egress performance in folded stack
- Intumescent seals; self-closing; positive latching; coordination of door closer, panic hardware, and hardware for rated assemblies
- Door and frame options with appropriate fire labels
- Applications: Schools, hospitals, hotels, corridors, assembly spaces
- Standards and considerations: US—IBC/IFC, NFPA 80, local authority approval; EU—EN 16034 and member-state approvals; ensure tested assemblies for both fire and egress
- Pros: Code compliance; flexible room layouts; controlled fire spread
- Cons: Higher installed cost; heavier panels; detailed installation documentation; specialized hardware costs
- Procurement notes: Order as a tested system; specify fire rating, egress type, hardware, finish, and required labels/inspections; coordinate with fire-stopping and adjacent construction
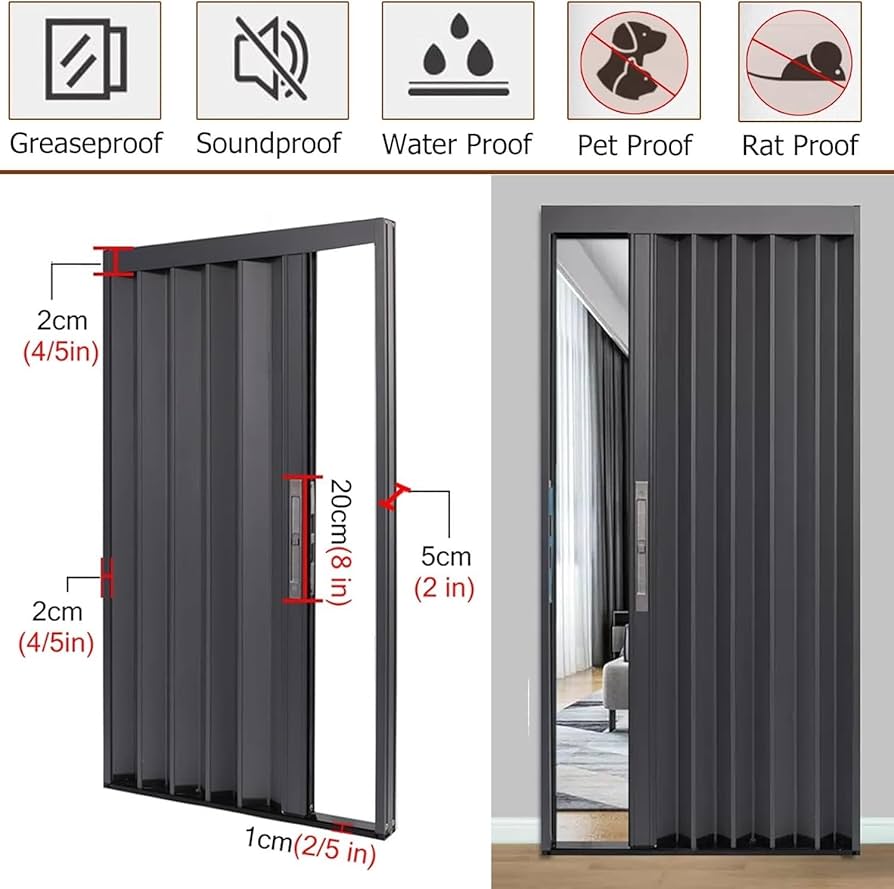
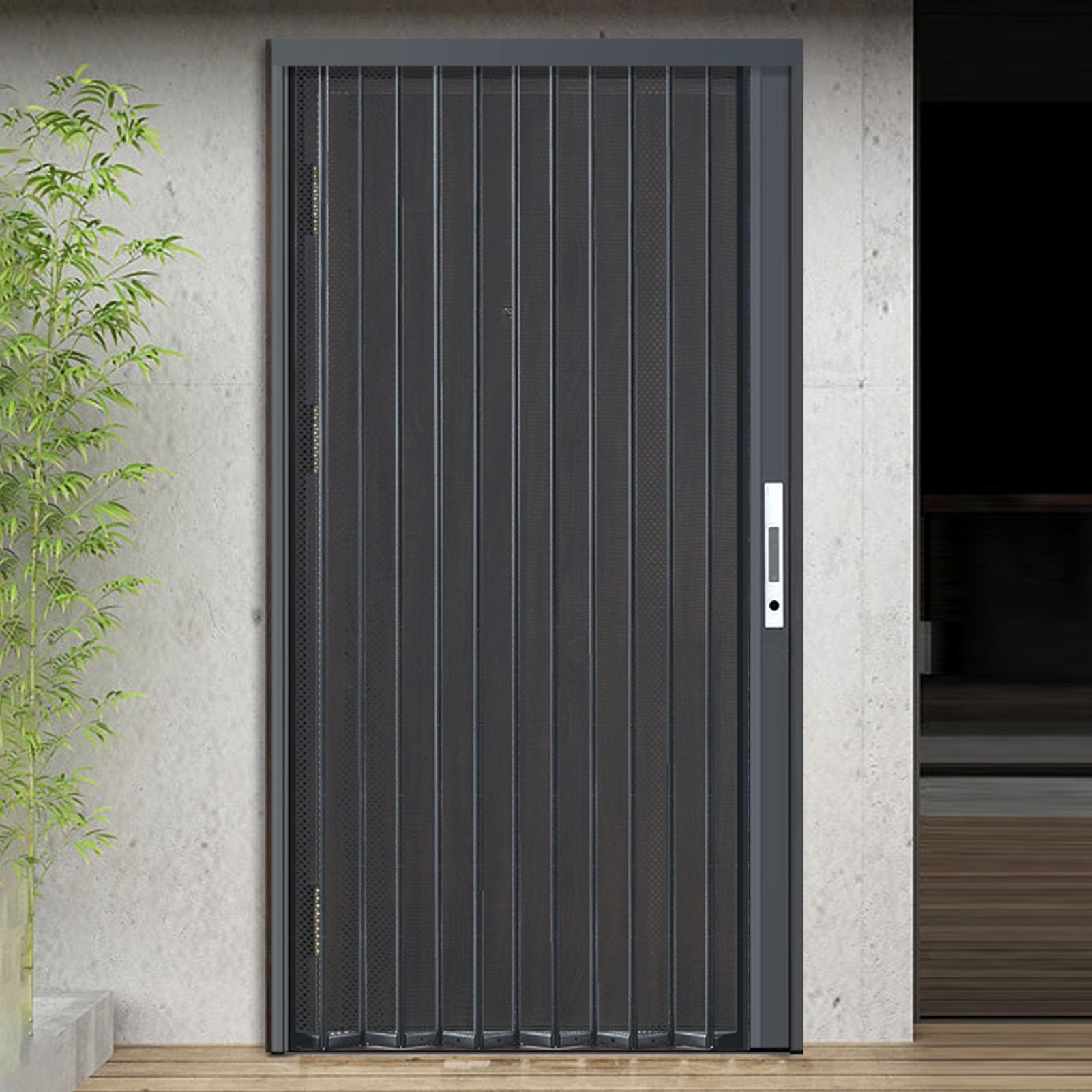
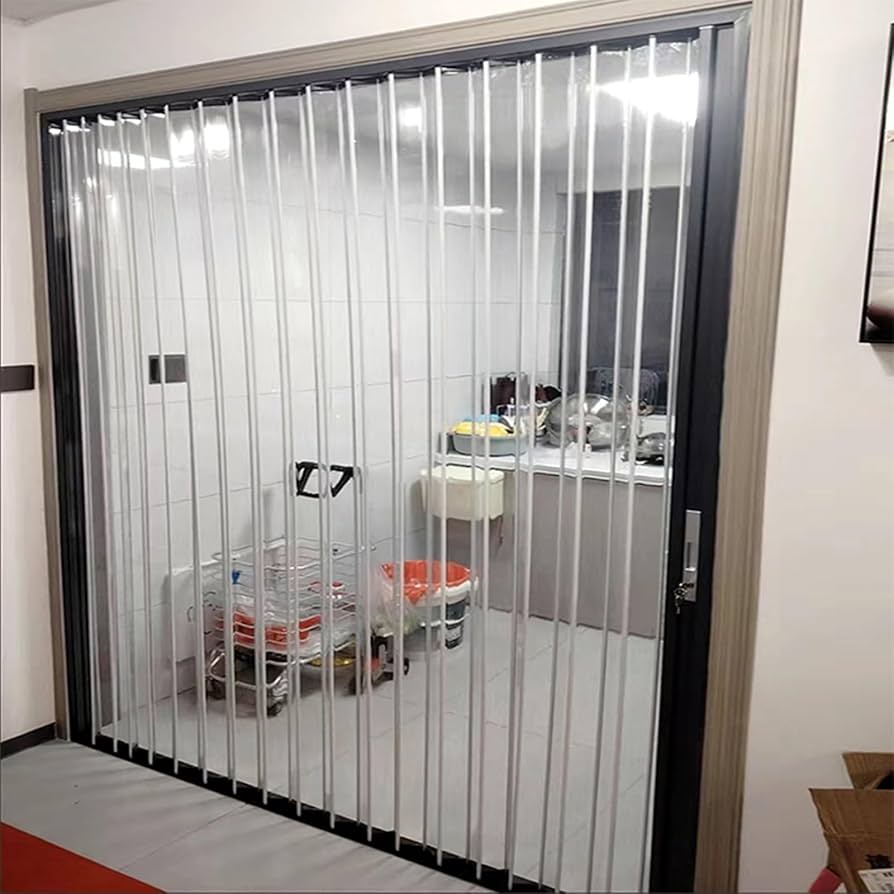
Integrated retractable screen folding (internal mesh concertina)
- What it is: Folding doors with integrated retractable insect/privacy mesh, often described as “internal concertina mesh,” intended for ventilation and basic security/deterrence.
- Why it matters: Adds airflow and pest control without heavy framing or complex tracks.
- Typical features:
- Retractable mesh with spring or manual roll-out; track integration
- Variable panel widths and common door sizes (e.g., 20×80, 22×96, 44×80 in);
- Burglar-deterrent frames; finishes suited for interior and semi-exterior use
- Lower cost than multi-pane thermal systems; often used in apartments, offices, and hospitality
- Applications: Apartments, offices, healthcare, hospitality rooms, residential back-of-house, interior partitions in mild climates
- Pros: Air and insect control; visibility with security; cost-effective add-on
- Cons: Mesh visibility and cleaning; limited thermal enhancement; lighter security compared to full door panels
- Procurement notes: Select mesh type (UV, privacy), track durability, and burglar-deterrent features; confirm dimensions and operating cycle rating
Pocket / folding pocket stacking (panels nest in wall)
- What it is: Folding doors whose panels slide and stack into a concealed wall pocket, minimizing floor space impact.
- Why it matters: Useful where clear floor area and swing paths are constrained.
- Typical features:
- Pocket construction (framed or pre-built) with concealed tracks and stops
- Paired or multi-panel folding; coordination of pocket door hardware
- Clean trim details and minimal sightlines
- Applications: Small offices, restaurant dining nooks, conference rooms, micro-apartments
- Standards and considerations: US/EU—building code for pocket construction, wall integrity, and egress; coordinate with architectural details and finishes
- Pros: Minimal floor intrusion; clear opening; aesthetic continuity
- Cons: Pocket build-out adds construction scope; limited span; track maintenance and access considerations
- Procurement notes: Verify pocket width/depth, panel weight, hardware cycle rating, and access for maintenance; coordinate with drywall, finish, and acoustic treatments
How to choose (quick checklist)
- Define application: exterior vs interior; occupancy; thermal and fire requirements.
- Confirm codes: egress, fire rating, storefront vs fenestration performance; local authority approvals.
- Set performance: specify air/water/structural classes (AAMA/WDMA or EN) and thermal targets (U-factor/SHGC).
- Panel strategy: count, direction of travel, stacking, pocket if needed.
- Hardware and lock sets: multi-point locking, commercial cycle ratings, ADA where applicable.
- Glazing: low-E IGUs, laminated where required, low-sightline options.
- Screens: integrated retractable or external mesh; consider maintenance and mesh replacement.
- Finishes and detailing: Kynar/powder/anodized; sill details and drainage; exterior/interior coordination.
- Procurement: order as tested assemblies; include submittals (shop drawings, hardware schedules, test data); plan for staging and installation sequencing.
Note on references: External manufacturers such as LaCantina illustrate exterior folding/multi-slide options, while “internal concertina” mesh kits provide integrated screening and basic security with light aluminium framing. Use these categories to align project goals with the right system type and specification pathway.
Key Industrial Applications of aluminium concertina doors
Key Industrial Applications of aluminium concertina doors
Aluminium concertina (folding) doors are engineered for high-cycle operation, large clear openings, and rapid evacuation. In regulated environments (USA/EU), their modular design supports fire, egress, accessibility, and sanitary integration while offering thermal, acoustic, and security performance. See “Design and Compliance Notes” for regional considerations.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
| Industry/Application | Detailed benefits |
|---|---|
| Manufacturing & Processing (wet/washdown, dust control) | Corrosion-resistant aluminium frames; integrated insect/bird mesh options for contamination control; seamless full-width cleaning; large opening for equipment moves and pallets; optional stainless hardware; gasketing systems resist particulates and cleaning agents. |
| Logistics & Warehousing (loading bays, dock areas) | Near-zero threshold for pallet jacks and fork trucks; high-cycle top-hung or bottom-rolling hardware; multi-point locking for perimeter security; optional steel-reinforced panels for impact resistance; retractable screens and mesh for pest mitigation; integrated fire shutters where required. |
| Food & Beverage (production, packaging, cold chain) | Hygienic surfaces and cleanability; optional mesh screens keep insects out; stainless fittings available for wet zones; large clear openings maintain throughput and visual supervision; anti-pinch hardware and high-cycle tracks for safety in busy areas. |
| Healthcare & Hospitals (operating suites, isolation, corridors) | Tight perimeter sealing for infection control; fast full-width access for stretcher movement and equipment; optional integrated insect/bird screens; compatible with antimicrobial finishes; large glazed panels for visibility and supervision. |
| Pharmaceutical & Laboratories | Fine-mesh variants help exclude insects/pests; large opening facilitates equipment installation; gasket systems minimize drafts and dust ingress; hardware supports high-cycle duty cycles; modular panels adapt to future reconfigurations. |
| Hospitality & Hotels (ballrooms, kitchens, service corridors) | Expansive openings for event setups; optional insect/bird screens for outdoor kitchens and pools; soft-close and anti-pinch hardware for guest safety; integrated security locks; finishes and hardware suitable for saline/coastal exposure. |
| Retail & Pop-up Spaces | Modular system allows rapid installation; security and insect/bird exclusion when paired with screens; clear openings maximize floor space and storefront sightlines; finishes align with brand aesthetics. |
| Education & University (multi-use halls, dining, labs) | Fire-rated variants support safe egress; insect/bird screens maintain hygiene in food prep and science areas; ADA-compliant hardware and thresholds; large panels enable flexible programming and frequent reconfiguration. |
| Government & Public Buildings | High-cycle egress solutions; perimeter security through multi-point locking; fire-rated options per opening; bird/insect exclusion with integrated screens; tamper-resistant hardware variants. |
| Utilities & Energy (water treatment, power, oil & gas) | Corrosion resistance and coastal compatibility; multi-point locking and reinforced panels for security; insect/bird screens for containment; large openings for equipment transfer; stainless hardware where required. |
| Marine & Coastal | Anodised/powder-coated aluminium resists saltwater corrosion; mesh screens resist sand ingress and pests; soft-close hardware limits slamming; coastal-grade finishes and stainless components for longevity. |
| Data Centers (cold aisle/hot aisle, security) | Seals reduce airflow leakage; insect/bird exclusion protects cleanrooms and server rooms; large openings for rack movement; multi-point locking for security; options for magnetic sensors and door status monitoring. |
| Transit/Aviation (concourse zones, cargo, catering) | Rapid full-width openings accelerate passenger boarding and material flows; high-cycle tracks and soft-close operation; insect/bird screens maintain hygiene; reinforced panels where impact resistance is needed. |
| Sports & Recreation (field houses, aquatic centers, courts) | Easy egress and crowd movement; insect/bird screens protect spectators and food service; corrosion-resistant finishes; large openings for maintenance equipment and event turnover. |
| Agriculture (greenhouses, processing, feed) | Mesh screens exclude insects, birds, and larger pests while allowing ventilation; aluminium resists moisture and ammonia exposure; large openings simplify bulk movements; stainless hardware for long service life. |
| Waste & Recycling (transfer stations, processing) | Reinforced panels resist abrasion; multi-point locking enhances perimeter security; insect/bird screens reduce vectors; near-zero threshold for loaders; corrosion-resistant finishes for harsh environments. |
Design and Compliance Notes
- Egress, fire, and accessibility: Consult project requirements for:
- USA: NFPA 101 (Life Safety Code), IBC/IFC for fire rating, NFPA 80 for fire doors, NFPA 1/Fire Code, ADA/ICC A117.1 for thresholds/operation.
- EU: CE marking (EN 16034, EN 14351-1), EN 15269 for fire/smoke testing, EN 16005 for security, EN 16005/EN 1125/EN 179 for escape routes, EN 16005/EN 1192 for durability class.
- Security and glazing: Specify laminated/impact-rated glazing where ballistic or impact performance is required.
- Thermal and acoustics: Pair panels with appropriate low‑E glazing and perimeter sealing to achieve target U‑factor and Rw/dB reduction.
- Hardware: Top‑hung tracks for long spans and reduced rolling resistance; bottom‑rolling for renovation or structural constraints. Provide soft‑close and anti‑pinch options in high‑traffic zones.
- Mesh and screens: Insect/bird screens should be integrated to maintain structural integrity and safe egress; ensure compatibility with fire/smoke specifications where applicable.
- Sanitary design: Smooth aluminium surfaces, sealed edges, and minimal pocket details support clean-in-place and frequent washdowns.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘aluminium concertina doors’ & Their Solutions
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘aluminium concertina doors’ & Their Solutions
Below are the top recurring pain points encountered by US and European buyers of aluminium concertina doors, with practical solutions and implementation steps to reduce risk, improve uptime, and protect margins.
Pain Point 1 — Installation complexity and integration risk
| Scenario | Problem | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| A mid-rise hospitality renovation in Chicago replaces old sliding doors with a 24-foot aluminium concertina system. Site reveals out-of-plumb openings, variable header levels, and an existing waterproofing membrane incompatible with the new threshold. | Misalignment and waterproofing details at threshold/head jambs cause rework; schedule slip; increased commissioning time. | 1) Pre-construction RFI set: verify rough opening, level, header deflection limits, flashing detail, and drainage plan. 2) Require dimensional tolerance drawings for site tolerance verification (e.g., deflection/settlement allowances). 3) Specify prefabricated head/ sill flashings and pre-cut sill pans; require coordination with waterproofing. 4) Mandate manufacturer’s install checklist and independent verification report. 5) Stage installation with mock-up panel; certify sealants and flashings before panel release. KPIs: site deflection ≤ L/300; on-time commissioning ≥ 95%; warranty claims ≤ 2% of panels. |
Pain Point 2 — Strength, sightline, and access control trade-offs
| Scenario | Problem | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| An office headquarters in Munich wants minimal sightlines for views, integrated insect screening, and increased security. The spec calls for “maximum strength with thin profile,” but typical thin aluminium frames flex and vibrate when screened or under wind load. | Excessive deflection under wind load; compromised insect-screen stability; uncertain resistance to forced entry; limited access control integration. | 1) Select engineered frames with reinforced stiles and interlocking profiles designed for screening and higher wind load zones. 2) Where insect resistance is needed, specify stainless-steel meshes with structural support tracks and corner alignment hardware; include impact-load testing for screen retention. 3) Validate security through third-party testing (e.g., PAS 24/Security Class, ASTM testing) and document results; avoid overpromising ratings not proven by test data. 4) Pre-coordinate hardware: multi-point locks, sensors, access control strikes, and concealed magnetic contacts in stiles/ heads. KPIs: screen sag ≤ 1 mm across panel; wind-load deflection ≤ L/180 at design pressure; hardware integration time ≤ 30 minutes per panel. |
Pain Point 3 — Lead times, logistics, and delivery uncertainty
| Scenario | Problem | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| A university campus in the Bay Area needs phased delivery (teaching break). Freight costs are volatile and delivery windows uncertain (e.g., long windows from 3rd-party retailers). | Missed teaching windows; site storage constraints; high demurrage; cost overruns. | 1) Require line-item lead times per system: panels, hardware, screens, glazing, flashing, finishes. 2) Lock schedules with contractual milestone deliverables; define demurrage and site-storage caps. 3) Pack and ship in staged sub-kits by elevation; verify packaging for UV/moisture protection; stage partial shipments (e.g., frames first, screens later) to reduce on-site risk. 4) Use a single logistics partner with guaranteed delivery windows; include delivery tracking and QA gates. 5) Build 10–15% contingency on freight; negotiate liquidated damages for late delivery. KPIs: lead-time variance ≤ 10%; delivered-in-full ≥ 98%; demurrage ≤ 2% of shipments. |
Notes:
– Reference context for integration: thick aluminium frames with integrated screens are common when strength and insect control are required (e.g., mesh concertina/screen options on retail channels).
– Reference context for delivery: extended delivery windows for bulky folding/screening systems can be 10–14 days or more; phase planning mitigates campus/tenant disruption.
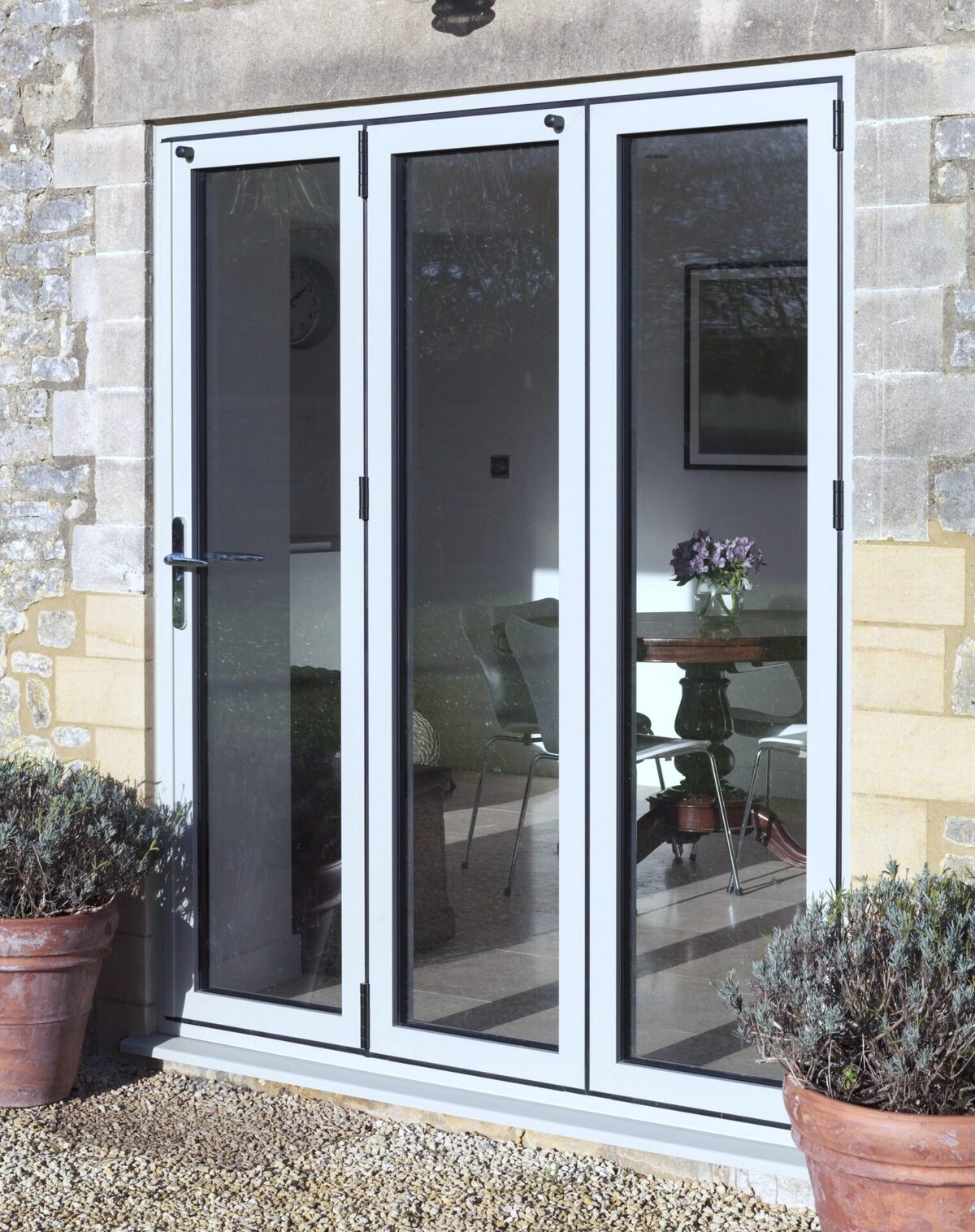
Strategic Material Selection Guide for aluminium concertina doors
Strategic Material Selection Guide for Aluminium Concertina Doors
Aluminium concertina doors are multi-panel folding systems that stack or “concertina” to clear large openings. Selecting the right materials is a direct lever on lifecycle cost, compliance, and user experience. Below is a practical guide focused on the decisions that matter for USA/Europe projects.
Frame alloy selection
| Alloy family | Typical temper | Strength and stiffness | Corrosion resistance | Machinability/weldability | Notes (USA/Europe) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6063 | T5/T6 | Moderate strength, good stiffness | Good, suitable for anodized/finish | Excellent extrudability; good weldability | The workhorse for architectural extrusions in residential/commercial folding doors. |
| 6005A | T5/T6 | Higher strength and stiffness than 6063 | Good | Extrudes less readily than 6063; good weldability | Favored for larger spans, heavy doors, or where deeper/stronger profiles are needed. |
| 6082 | T6 | Comparable or higher strength than 6005A | Good | Good machining; weldable with care | Less common for door extrusions but found in some structural hardware components. |
| 6061 | T6 | High strength | Adequate, but more prone to pitting; better when anodized | Machinability excellent; weldable with specific techniques | Typically used for load-bearing hardware (handles, brackets), not main frames. |
Recommendation: Use 6063-T5/T6 as the default frame alloy. Step up to 6005A-T5/T6 when spanning wider openings, carrying heavier glazing, or designing with deeper profiles.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Profile design and thickness
- Multi-wall/hollow profiles provide excellent stiffness at lower weight compared to solid sections. Deeper profiles also boost bending resistance for larger spans.
- Typical wall thicknesses range from ~2.0 mm (0.080 in) to 3.0 mm (0.118 in). Use thicker walls for:
- Heavy glazing (laminated/impact, triple-pane).
- Long panel spans (e.g., >2.4 m (8 ft) widths).
- High-traffic or commercial installations.
- Incorporate integrated thermal barriers (polyamide or polyurethane) for condensation control and improved thermal performance.
Finishes and coatings
| Finish | Corrosion resistance | Color options | UV/weather stability | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Clear anodized (Class I) | High (coastal capable) | Natural metallic | Excellent | Choose anodized for longevity and minimal maintenance in coastal/inland environments. |
| Color anodized | High | Wide range (satin to deep tones) | Excellent | Maintain color fastness; suitable for aggressive environments. |
| Polyester powder coat | Moderate–High | Extensive | Good | Lower cost; adequate inland; ensure proper pretreatment. |
| PVDF (Kynar) | Very High | Wide | Excellent | Superior UV/chemical resistance; premium choice. |
| E-coat/electrophoretic | High (primer) | Neutral | Good as primer | Often used as primer beneath top coats for corrosion “belt and suspenders.” |
Recommendation:
– USA/Europe coastal or polluted environments: Class I anodized or PVDF top coats over E-coat.
– Inland commercial: Class II anodized or high-quality powder coat.
– Interior or budget-focused internal systems: powder coat or electrocoat.
Glazing
- Low‑E IGU (Insulated Glass Unit) improves energy efficiency and occupant comfort.
- Laminated or laminated/impact glass for safety, burglary resistance, and hurricane-exposed projects.
- Tempered or laminated tempered for balance of safety, sound, and weight.
- Choose IGU cavity gases (argon/krypton) for enhanced thermal performance where climate/building energy targets demand it.
- Match glazing to hardware weight capacity. Heavier stacks may require thicker profiles, stiffer alloys, or stronger hardware.
Screens and insect control
| Screen type | Mesh | Visibility | Durability | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Standard fiberglass | Standard | Good | Good | Common on residential systems; adequate for most interiors. |
| Pet mesh (polyester) | Reinforced | Moderate | High | Resist pets, abrasion; ideal for high-traffic interior doors. |
| Retractable screens | Similar to above | Excellent when stowed | Good if quality hardware | Convenient for interiors and bi-parting openings; track/hardware quality matters. |
Screens do not replace burglar‑resistant glazing or hardware. For security intent, use laminated glass, multi‑point locking, and appropriate hardware.
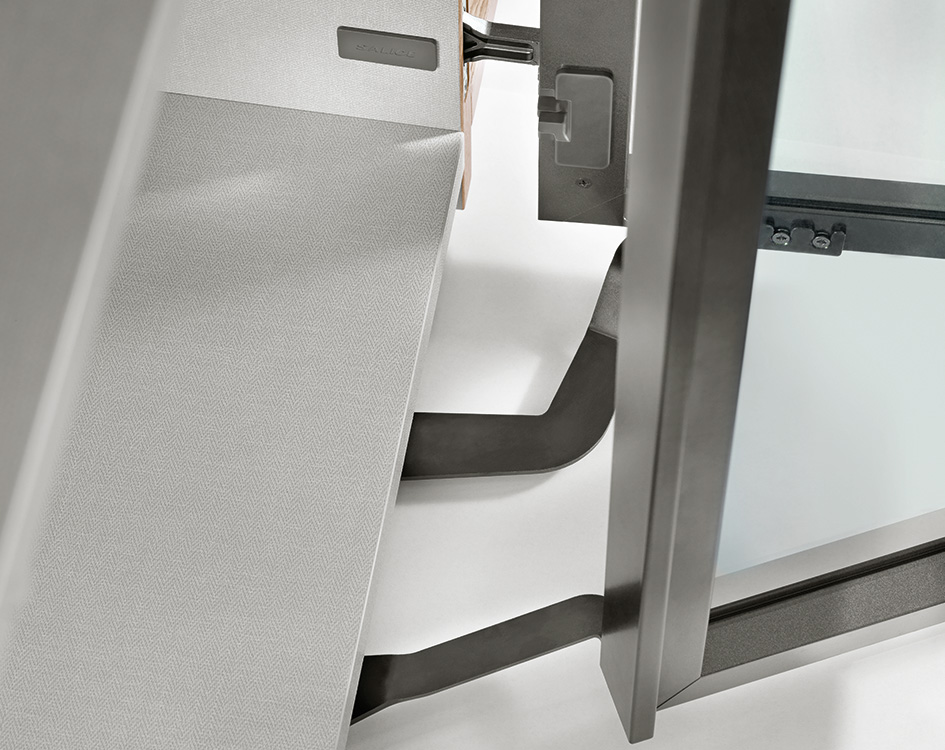
Hardware materials and selection
| Hardware element | Recommended material | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Hinges/pins/stainless components | 316L stainless (coastal) or 304 stainless (inland) | 316L offers superior corrosion resistance in marine/coastal climates. |
| Rollers/cam track systems | Hardened stainless or high‑grade anodized aluminium with stainless bearings | Smooth operation; rated for door panel weight. |
| Handles/latches/anchors | 316L stainless or high‑grade anodized aluminium with stainless fasteners | Provide smooth feel, durability; powder‑coat over aluminium acceptable inland. |
| Multi‑point locks | Stainless components; plated steel acceptable inland with protection | Critical to air, water, and security performance. |
Material choice affects noise, wear, and service life. Budget‑grade zinc die‑cast parts degrade faster and may sag over time.
Seals and gaskets
- EPDM: good compression set and UV resistance for exterior seals.
- Silicone: superior heat/UV stability; often used where high temperatures or long life are required.
- Polymeric TPE/TPV: good flexibility; suitable for interior or moderate climates.
Use dual seals (e.g., primary bulb and secondary fin) for better air/water performance.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Thermal performance levers
- Structural thermal breaks with polyamide or polyurethane reduce heat flow and condensation risk.
- Optimized sightlines and glazing geometry influence thermal performance and energy codes.
- IGU spacers: choose thermally improved spacers for lower U‑factors.
Use-case recommendations
| Use case | Alloy | Finish | Hardware | Glazing | Screens | Key notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Inland temperate (USA/Europe) | 6063‑T5/T6 | Class II anodized or powder coat | 304 stainless or high‑grade aluminium | Low‑E IGU, tempered | Standard or retractable | Balanced cost/perf; meet regional energy codes. |
| Coastal exposure (USA Atlantic/Gulf, EU coasts) | 6005A or 6063 | Class I anodized or PVDF | 316L stainless | Laminated/impact glass (where needed) | Retractable; corrosion‑resistant | Prioritize 316L hardware and high‑resistance finishes. |
| High-traffic commercial/interior | 6005A (stiffer profiles) | Powder coat or anodized | 304/316 stainless; reinforced rollers | Laminated glass for durability | Pet mesh optional | Emphasize hardware durability and large‑panel stiffness. |
| Budget/internal applications (interior bi‑fold/concertina) | 6063 | Powder coat | Zinc/steel with protection or aluminium | Clear or tempered | Basic mesh | Confirm use conditions; not for exterior wind/water ingress. |
Standards and certifications (typical references)
- Structural: ASTM E1886/E1996, ASTM E330 (USA); EN 1991 (wind load), product-specific CE marking where required (EU).
- Air/water/structural performance: ASTM E283/E331/E547 or ASTM E2357 (systems testing).
- Thermal: NFRC/energy compliance in USA; EN ISO 10077 (thermal performance), local energy codes in EU.
Note: Specific performance values depend on the panel system configuration and project design; verify with manufacturer test reports and calculations.
Notes on market examples
- High‑end systems (e.g., LaCantina Doors) typically offer robust aluminium profiles, multi‑point hardware, and extensive finish/glazing options suitable for exterior openings.
- Budget/internal concertina or folding screen products (e.g., a 44×80 in aluminium frame with retractable mesh) emphasize cost‑effective finishes and basic screens; confirm suitability for exterior exposure and security intent.
Comparison: Aluminium alloys and typical door uses
| Alloy | Temper | Best use in doors | Why it fits |
|---|---|---|---|
| 6063 | T5/T6 | Standard exterior/interior frames | Good extrudability, corrosion resistance, finish adhesion; cost‑effective. |
| 6005A | T5/T6 | Larger spans, heavy glazing, commercial | Higher stiffness/strength than 6063; supports deeper profiles. |
| 6082 | T6 | Structural hardware | High strength; less common in frames, suitable for robust hardware. |
| 6061 | T6 | Hardware components | Very strong; good machinability; typical for brackets/rods, not main extrusions. |
Key decision checklist
- Verify alloy+temper and profile thickness against span, glazing weight, and performance criteria.
- Choose finish per environment and maintenance expectations (coastal = Class I anodized or PVDF; inland = Class II anodized or high‑quality powder).
- Specify 316L stainless hardware in coastal or corrosive environments; confirm load ratings.
- Match glazing to safety/security and energy code; confirm IGU configuration.
- Select gasket materials suited to exterior temperatures/UV; specify dual seals for better performance.
- Align with regional standards and obtain system-level test reports from the manufacturer.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for aluminium concertina doors
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for Aluminium Concertina Doors
What, why, and how: the essentials for consistent, compliant production
- What is an aluminium concertina door system? A stackable, high-traffic folding opening comprising perimeter frames, interlocking panels, tracks/guides, seals, hardware, and glazing. The design prioritizes large clear openings, tight stack-backs, weatherproofing, and smooth operation.
- Why do manufacturing processes matter? Concertina doors concentrate cyclic stresses at hinges, tracks, and seals. Consistent alloy selection, dimensional control, finish performance, and verified hardware systems directly affect service life, safety, and compliance with market standards.
- How do leading B2B manufacturers ensure quality? They implement an ISO 9001 QMS; apply alloy-specific standards for raw materials; use calibrated CNC for precision; conduct incoming, in-process, and final inspections; perform lab and field performance testing; and maintain traceability across lots and batches.
Manufacturing steps (from alloy to installed system)
| Step | Purpose | Key Process Controls | Typical Defects Prevented | Common Tools/Equipment |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1) Material intake (aluminum profiles, glass, hardware, seals) | Verify specification and lot traceability | Mill certificates (alloy/temper), ASTM B209/B221, EN 573/755 checks; coating test reports; hardware lot tracking | Wrong alloy/temper, non-conforming coatings, missing documentation | Calipers, CMM, mill cert database, barcode/RFID scanning |
| 2) Extrusion & fabrication prep | Achieve dimensional stability | Cut lengths verified; burrs removed; hole patterns checked to prints | Incorrect panel height/width, burr damage, misaligned hardware prep | Precision saws, CNC machining centers, deburring tools |
| 3) Thermal break assembly (if applicable) | Maintain structural integrity across insulated profiles | Adhesive compatibility and cure profiles monitored; bond-line AQL verified | Adhesive voids, peel/rupture under cycling | Specialized thermal-break adhesives, hydraulic presses, cure ovens |
| 4) Finishing (anodizing, PVDF/powder coat) | Corrosion resistance and color control | Pre-treatment per finish spec; film thickness (e.g., AA10C44A for anodizing); adhesion cross-hatch; gloss/color variance limits | Flaking, corrosion, color drift | Pretreatment lines, anodizing baths, coating booths, DFT gauges |
| 5) Track/header fabrication | Ensure straightness and gliding tolerance | Runout straightness; track slot alignment; bearing/bushing fit | Binding, rattles, high friction during stack | Bench straighteners, millers, EDM slotting |
| 6) Panel assembly and glazing | Weatherproof, structurally sound panel units | Structural glazing to spec; EPDM/PVC gasket fit; glazing wedge accuracy; glass edge setting; safety glazing compliance | Air/water leakage, seal overcompression, glass edge stress | Automated gasket cutters, glazing tables, glass setters |
| 7) Hardware installation | Load-path reliability and smooth operation | Hinge/pivot bearing preloads; latch/center locks alignment; roller height adjust; track-bridge fit | Premature wear, panel sag, misalignment | Torque-controlled drivers, height/alignment jigs, gauge pins |
| 8) Panel-to-panel sealing and staging | Continuity of weatherproofing and stack integrity | Corner and hinge seals compression verified; interlocking fit checked | drafts, squeaks, dust ingress | Compression gauges, trial-assembly staging |
| 9) Final QC and packaging | Confirm dimensional and functional conformance | Functional cycling (open/close/fasten); sealing at test pressures; finish damage checks; hardware security | DOAs, finish chips, field rework | Test rigs, calibrated torque tools, protective packaging |
Quality assurance: standards and verification framework
| Domain | Standards/References | Typical Verification | Acceptance Cues (qualitative) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Quality management system | ISO 9001 | Process-based control, supplier evaluation, internal audits | Documented procedures, corrective actions tracked |
| Materials – sheet | ASTM B209 (US), EN 485/131 (EU) | Mill certs, alloy/temper checks | Correct tempers, no soft spots |
| Materials – extrusions | ASTM B221 (US), EN 755/12020 (EU) | Dimensional checks, mechanicals | Meets spec dimensions and yield |
| Structural glazing/glass | ANSI Z97.1, CPSC 16 CFR 1201 (US) | Edge support, glazing method verification | Compliant glazing method, no unsafe edges |
| Hardware/hinges/rollers | Manufacturer test data; corrosion classes e.g., EN 1993-1-4 corrosion categories | Hardware fit and torque; roller-to-track interference tests | Smooth action, no excess play |
| Weather & thermal performance | AAMA/EWA protocols (US); EN 14351-1, EN 12211/12210/12207/12208 (EU) | Air infiltration, water penetration, wind load testing | Meets project specification criteria |
| Energy rating (thermal) | NFRC procedures (US); local EU thermal transmittance | NFRC label; U-value calculations | Labeled U/SHGC values; no anomalies |
| Health & safety in production | ISO 45001 (workplace safety), ISO 14001 (environmental) | PPE, chemical handling, emissions | No incidents; waste minimized |
| Finish performance | ASTM B244/B487/B499/B571 (US) for anodizing; EN 573/12373 for anodizing; ASTM D4541/D4542/D3359 for coatings | Adhesion, abrasion, humidity, salt spray | No delamination, pass corrosion per spec |
How verification is executed in practice
| Inspection Stage | What is checked | Instruments/Conditions | Why it matters |
|---|---|---|---|
| Incoming | Mill certs; alloy/temper; coating thickness; hardware lots | CMM, DFT, calipers, documentation | Prevents wrong or non-compliant material entering production |
| In-process (machining) | Hole locations; cut lengths; burr control; hardware prep | CNC programs, go/no-go gauges | Maintains precision for hinge/pivot alignment and glazing fit |
| Pre-assembly (seals/finish) | Gasket compression; finish adhesion; surface integrity | Cross-hatch knife; surface inspection; gloss/color pass | Reduces air/water leaks and corrosion risk |
| Assembly | Panel squareness; hinge preload; track fit; glazing | Torque wrenches; angle/height jigs; glazing fixtures | Eliminates binding/sag and glazing stress |
| Functional test | Cycles open/close; latch engagement; interlocking fit; operating effort | Lab rigs with specified cycles | Predicts service performance and premature wear |
| Final | Weather tests to spec; finish damage; labeling/packaging | Test chambers; packaging standards; barcode scan | Ensures compliance and safe delivery |
Compliance across USA and Europe
- USA: Align material and glazing conformance with ASTM/ANSI/CPSC and AAMA/EWA testing protocols; meet NFRC labeling requirements for thermal performance.
- Europe: Align with EN standards for doors and performance testing; meet REACH and RoHS for coatings and hardware; apply relevant construction product standards.
Where the process typically fails—and how it’s controlled
- Misaligned hardware prep causes binding: prevented with CNC programs and calibration, verified on pre-assembly jig.
- Stack-back clearance errors produce panel interference: avoided via header/track dimension checks and functional staging.
- Seal overcompression from improper glazing wedge results: controlled via wedge sizing, gasket AQL, and compression verification.
- Finish corrosion and adhesion failures: controlled with validated pre-treatment and finish-process parameters, plus random batch testing.
- Hardware premature wear: controlled with load-path design, torque specifications, and validated hardware suppliers.
Practical guidance for B2B specification and procurement
- Insist on ISO 9001 and, ideally, ISO 14001 and ISO 45001 from the manufacturer.
- Require material traceability to alloy/temper and finish lots; request mill certs.
- Verify that glazing method and safety glazing conform to US (ANSI Z97.1/CPSC) and EU standards.
- Confirm that hardware, tracks, and hinge systems are specified for the project’s frequency of use and corrosion class.
- Validate performance testing to the appropriate AAMA/EWA (US) or EN (EU) methods aligned to your specification.
By following these manufacturing and QA fundamentals—material compliance, precision forming, calibrated assembly, and rigorous functional/performance verification—aluminium concertina door systems can achieve consistent operation, long service life, and reliable compliance across the USA and Europe.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘aluminium concertina doors’
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for Aluminium Concertina Doors
Product landscape at a glance
Aluminium concertina doors fall into distinct performance and sourcing classes. Align the system to your use case first.
- Heavy-duty commercial (stacking, lift-and-slide, bifold/concertina): high traffic, large spans, engineered to regional codes; typically supplied by national/regional manufacturers and specialists. Example: LaCantina Doors (premium folding systems for exterior use, including commercial).
- Mid-range domestic/interior renovations: integrated screens, moderate spans, limited load/safety requirements. Example: Amazon listing with aluminium frame and mesh concertina door at ~$556 (44×80 in).
Sourcing models and trade-offs
| Vendor type | Typical use case | Price level | Lead time | Warranty | Screen options | Certification/Code compliance support |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Premium manufacturers (e.g., LaCantina) | Commercial, high-end residential, large spans, harsh weather | High (custom) | 8–14 wks | 5–10 yrs (system specific) | Integrated retractable screens common | Strong (NFRC/Thermal/Performance for USA; CE/Structural for EU) |
| Regional specialists | Mid-market to premium, local service | Mid–High | 6–10 wks | 3–7 yrs | Often available | Variable; can provide stamped calculations |
| Import direct (Amazon or marketplaces) | Interior/light-use, price-sensitive, quick fill-in | Low | 2–4 wks | 1–2 yrs typical (seller-specific) | Often included as bundle | Limited; user-supplied compliance docs, may not meet wind-load codes |
| Local fabricators | Small shops, custom finishes, rapid local service | Mid | 4–8 wks | 1–5 yrs | Integrated per budget | Mixed; may depend on third-party suppliers |
Selection matrix: must decide before RFQ
| Parameter | Decision to make | Typical range or requirement | Note |
|---|---|---|---|
| Operation | Lift-and-slide vs bifold/concertina | Bifold: panel-by-panel fold; Lift-slide: gliding with lift hardware | Larger spans and heavy panels often favor lift-slide |
| Panel size | Width/height, number of panels | 24–48 in panel width; 96–120 in height common | Larger = thicker profiles, stronger tracks |
| Glazing | Glass type, thickness, sealed units | 1–1.25 in IGU; tempered/laminated by code | Thermal-break frames recommended |
| Thermal/Acoustics | Climate/performance targets | U-factor, SHGC, STC/Rw | USA: NFRC labels; EU: thermal/acoustic EN standards |
| Air/water/structural | Local code/climate | Air infiltration (cfm/ft²), water penetration (psf), structural (psf) | Confirm wind/snow loads for site |
| Hardware & locking | Multi-point locks, hinges, rollers | Deadbolts + latch guards; commercial-grade rollers | Higher security: multi-point locks + sash reinforcement |
| Screening | Integrated or external screens | Insect, blackout, UV, pet-resistant | Some suppliers bundle low-cost screens; verify durability |
| Finish | Anodized vs powder coat | AAMA 2603/2604/2605; 5–10 yr coastal | Coastal zones require better corrosion protection |
| Compliance | USA/EU code alignment | USA: IBC/IRC/FBC/TI/Title 24; EU: CE (CPR) | Expect manufacturer documentation |
| Logistics | Packaging, freight, lead time | Palletized/crated; FOB/FCA/DAP terms | Large panels need specialized freight |
Step-by-step sourcing checklist
1) Align requirements to use case
– Define site conditions (wind load, water exposure, acoustics).
– Choose operation type and panel configuration.
– Confirm compliance region (USA vs EU) and required certifications.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
2) Pre-qualify suppliers
– Screen for sector experience, warranty, and service coverage.
– Validate testing data and code compliance capability.
– Confirm lead time, logistics model, and installation support.
3) Prepare RFQ package (include:)
| Item | Details to include | Why it matters |
|---|---|---|
| Dimensions | Rough opening, panel width/height, stack-back clearances | Impacts hardware selection and pricing |
| Operation | Bifold vs lift-slide; traffic pattern | Determines hardware/stiffness |
| Glazing | Glass type, thickness, SHGC/U-factor, lamination/tempering | Performance and safety |
| Performance targets | Air/water/structural, thermal/acoustic ratings | Code compliance and comfort |
| Finishes | Anodized/powder coat, color, coastal exposure | Durability and aesthetics |
| Hardware/locking | Handle styles, multi-point locks, ADA compliance | Security and accessibility |
| Screens | Integrated/external, mesh type, pet resistance | User experience and maintenance |
| Compliance docs | Region, building code references, NFRC/CE | Avoids failed inspections |
| Logistics | Incoterms, delivery dates, packaging/crating | Controls cost and risk |
| Warranty | Term, coverage, exclusions | Lifecycle risk and service |
| Installation | Installer capability, attachment details | Real-world performance |
| Spares | Replacement rollers, seals, keys | Ongoing maintenance |
4) Technical review
– Confirm panel thickness, profiles, and track capacity for span.
– Verify hardware ratings (cycles, lock points) match duty cycle.
– Check drainage and weather sealing details.
5) Pilot/sample order
– Order one panel or small set for fit and finish review.
– Conduct site mock-up if critical; verify clearances and stack-back.
– Check screen integration and locking operation.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
6) Commercial and logistics
– Lock pricing, lead time, and delivery windows.
– Specify packaging and insurance; plan for liftgate or dock.
– Ensure installation method is compatible with existing structure.
7) QA and inspection
– On delivery: verify dimensions, finish, glazing, hardware counts.
– Check against RFQ and sample; document any deviations.
– Confirm compliance labels and test reports.
8) Installation and handover
– Verify installer follows manufacturer method.
– Commission locks, seals, and tracks; confirm operation.
– Provide O&M guidance and spares list to end user.
Compliance notes by region
- USA: Confirm structural performance, NFRC labeling for thermal, local code adoptions (IBC/IRC/FBC/Title 24). Expect manufacturer-stamped calculations for larger spans.
- EU (EU/EEA): CE marking under the Construction Products Regulation; ensure CE Declaration of Performance and applicable standards (structural, thermal, safety).
Pricing and lead-time context
- Entry-level internal concertina doors with aluminium frames and integrated screens may be available around ~$556 in consumer marketplaces; these are typically suited to light-use interiors and are unlikely to meet commercial wind-load or large-span requirements.
- Project-grade systems (premium manufacturers like LaCantina) are custom-quoted, with longer lead times and higher performance specifications aligned to commercial codes.
Quality and inspection checklist (summary)
- Verify dimensions and panel configuration match RFQ.
- Inspect finishes for uniformity, anodizing/powder thickness, and corrosion protection.
- Confirm glass type and safety compliance (tempered/laminated).
- Test hardware: rollers, hinges, multi-point locks, handle ergonomics.
- Check weather sealing continuity and drainage paths.
- Confirm screen mesh quality and attachment system.
- Review documentation: warranty terms, test reports, compliance labels.
Common pitfalls to avoid
- Underspecifying wind load and panel stiffness, leading to deflection or failures.
- Ignoring stack-back clearance and site serviceability.
- Overreliance on bundled low-cost screens that degrade under commercial use.
- Mismatched compliance (USA vs EU) and lack of documented calculations.
Action next: finalize your use case, select two vendor archetypes (premium manufacturer and regional/import alternative), and issue RFQs using the table above to ensure apples-to-apples comparison.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for aluminium concertina doors Sourcing
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for Sourcing Aluminum Concertina Doors
Market context and price anchors
- USA/EU retail anchors show a wide spectrum. A compact internal concertina (44×80 in) with aluminum frame and retractable screen lists at roughly $556 on Amazon (Innovz). [^1]
- Premium North American folding door brands (e.g., LaCantina) price at the top end for engineered systems, high-spec hardware, glazing, and services; typical pricing exceeds mid-market offerings by 50–200% depending on configuration. [^2]
Typical cost breakdown for a 6–8 ft tall concertina set (2–5 panels)
For budgeting, assume a European single-pane thermal-break set sized ~2.4 m high with intermediate hardware. Figures are indicative ranges for wholesale procurement, excluding taxes, duties, and installation unless noted.
- Materials and components
- Extrusions and frame: $450–$2,100 per set
- Hardware and hinges: $250–$1,800 per set
- Glazing and seals: $200–$900 per set
- Logistics (per set)
- Domestic/regional (US/EU): $100–$400
- Cross-border (within Europe): $200–$700
- Intercontinental to US/EU: $600–$1,500
- Installation labor
- US per unit: $800–$2,500 (typical residential, 2–4-person crew for a day or more)
- EU per unit: €300–€1,500 (country and region vary; complexity matters)
- Duties/taxes (when relevant; confirm for your shipment)
- US (e.g., HS 7610.10): 5.8% duty
- EU (typical category; subject to product specifics): 10.8% duty
Illustration: mid-spec set (US)
– Extrusions/hardware/glazing: ~$900–$1,300
– US domestic shipping: ~$300–$400
– US duty (if applicable): ~$70–$100
– Installed: add ~$1,400–$2,100 labor
Illustration: mid-spec set (EU)
– Extrusions/hardware/glazing: ~€600–€1,100
– EU cross-border freight: ~€200–€500
– EU duty (if applicable): ~€86–€173
– Installed: add ~€600–€1,100 labor
Retail example (internal compact concertina)
For a 44×80 in (1.12×2.03 m) internal folding door with aluminum frame, mesh, and retractable screen (single-pane), the Amazon listing is $556.08. This illustrates:
– Low-cost, light-duty hardware and frame
– Simplified glazing or mesh
– Economy retail fulfillment (no site survey, limited structural support)

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Small/compact single-pane internal units are not directly comparable to exterior thermal-break systems, but can validate the bottom end of the market for compact applications. [^1]
Premium segment benchmark (high-end US folding systems)
Brands like LaCantina represent the premium tier for engineered aluminum folding doors—typically with thermally improved frames, advanced hardware, larger spans, and performance glazing. Expect a significant price premium versus mid-market offerings due to engineered performance, testing, engineering services, and local distribution. [^2]
Material drivers (what moves the price)
- Alloy and finish
- 6063-T5 vs 6061 for load-bearing members (6061 can be costlier but stronger)
- Powder coating vs anodizing; PVDF for harsh/coastal environments adds cost
- Finish color complexity and thickness impact price
- Profile geometry and wall thickness
- Thermal-break quality (polyamide width), multi-chamber profiles, thicker walls
- Hardware
- Hinge type and capacity, stainless vs carbon hardware, corrosion protection
- Multi-point locks vs standard latch/lever sets
- Track and rollers: sealed bearings vs open rollers; heavy-duty systems cost more
- Glazing
- Single vs double; Low-E, acoustic, laminated vs tempered; spacer and IGU construction
- Seals and screening
- Quality and density of brush seals; integrated retractable or fixed screens add material/labor
Logistics drivers
- Dimensions and weight: per panel, oversize surcharges escalate quickly
- Freight mode: parcel (small units), LTL freight (multiple panels), FTL (large projects)
- Palletization and crating: robust crating for large-span panels protects against damage and claims
Duties and value-added tax (VAT)
- The HS classification (e.g., 7610) and origin rules determine duty; examples:
- USA: 5.8% duty (typical category; confirm exact code for your product)
- EU: 10.8% duty (typical category; confirm exact code and preferential origin)
- Incoterms
- DDP removes downstream cost surprises; DAP/EXW put freight, duties, and VAT on the buyer
- VAT in the EU is payable on the duty-paid value; the US does not have VAT but may have state/local sales tax
Tiered price framing (comparative anchors)
- Budget economy (retail/internal mesh)
- Example: compact internal with retractable screen listed at ~$556 for ~1.12×2.03 m (indicative retail anchor)
- Features: light-duty hardware, simple frame, single pane or mesh
- Mid-spec (thermal-break sets, regional freight)
- US/EU wholesale examples
- Materials/components: ~$900–$2,200 per set (config-dependent)
- Freight: US domestic ~$300–$400; EU cross-border ~€200–€500
- Installed: US ~$1,400–$2,100; EU ~€600–$1,100
- Premium (engineered systems)
- LaCantina-tier products carry higher prices driven by engineering, hardware, glazing, and services
- Price uplift typically 50–200% over mid-market, depending on spans, specs, and finishes
- Notes: ranges reflect general budgeting; confirm final quotes with suppliers and carriers
Tips to save cost without compromising reliability
- Standardize sizes and options; avoid bespoke widths where possible
- Design to nominal panel widths that maximize pack density and reduce freight surcharges
- Choose a proven thermal-break system with sufficient thickness and hardware rating for your climate/span
- Bundle orders for mixed SKUs to achieve FTL or better LTL rates
- Negotiate Incoterms; prefer DDP for predictable landed cost or verify VAT handling under DAP
- Align certification targets with regional codes; over-specification adds cost without benefit
- Limit premium finishes (e.g., PVDF) to exposed/exterior elevations where needed
- Request knocked-down components or partial assembly to reduce volume and freight
Supplier selection and quality checkpoints
- Verify hardware capacity (hinge ratings, roller load capacity) for your spans
- Check frame dimensions and thermal-break quality; request cut samples and test certificates
- Confirm gasket design, compression, and weather sealing details
- Review warranty terms (finish, hardware, glazing), RMA policies, and returns windows
- Request pilot orders or a sample unit to validate fit, finish, and installation requirements
Quick landed-cost checklists
- Confirm HS code, origin, duty, and VAT/VAT handling under your chosen Incoterm
- Request freight quotes with detailed surcharge policies (oversize, residential delivery, liftgate)
- Validate packaging (palletization, crating) and insurance coverage limits
- Plan installation scope (rough opening preparation, structural support, trim/finish) with local trades
Bottom line
- Budget/internal: small single-pane or mesh units can be sourced from ~$500 retail up, depending on size and options. [^1]
- Mid-spec thermal-break sets for typical spans commonly fall around ~$900–$2,200 in components, plus freight and installation. Freight and labor can be similar in magnitude to components, so project budgeting must include both.
- Premium engineered systems trade materially higher due to engineering, hardware, glazing, and services; plan accordingly. [^2]
- Manage cost volatility by standardizing sizes, bundling freight, and aligning specs with true performance needs.
References
[^1]: Thick Aluminum Frame & Mesh Folding Doors (44×80 in). Amazon listing. https://www.amazon.com/Aluminum-Folding-Internal-Concertina-Screens/dp/B09T5GQLN8/
[^2]: Aluminum Folding Doors | Exterior & More – LaCantina Doors. https://lacantinadoors.com/doors/aluminum-folding-doors/
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing aluminium concertina doors With Other Solutions
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing aluminium concertina doors with other solutions
For large residential and light commercial openings, aluminium concertina (stacking) doors are often benchmarked against sliding patio doors and timber/uPVC bifold doors. The three solutions differ materially in how they open, how much opening they deliver, and how they impact structural, accessibility, and aesthetic considerations.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
To ground the comparison, this analysis references general, well-known characteristics of premium aluminium folding door systems (e.g., large-panel, perimeter-sealed folding doors similar to those offered by brands such as LaCantina Doors) alongside widely recognized behaviors of sliding and bifold systems.
At-a-glance comparison
| Aspect | Aluminium Concertina (Stacking) Doors | Sliding Patio Doors | Timber/UPVC Bifold Doors |
|---|---|---|---|
| Typical panel size | Large; thin profiles with multi-point locking and perimeter seals | Medium-to-large; fixed + 2–3 panels; sealed perimeter | Smaller increments; many panels; perimeter seals |
| Max clear opening | Very large openings achievable; panel count determines max clear width | Limited by number of panels; can be substantial but typically less than a fully stacked concertina for the same bay | Very large openings; increases required stacking space on one or both sides |
| Stacking depth | Panels stack side-by-side; total width roughly equals leaf width per stack | Minimal; panels slide in fixed tracks; no large stack | Significant; cumulative panel width must be accommodated |
| Operation | Lift-and-slide; panels stack without folding | Linear sliding; no folding | Folding; panels hinge and stack via pivot sets and tracks |
| Accessibility | Low threshold options available; track exposure minimized by design | Low threshold possible; track present | Low threshold possible; multiple tracks/rollers can complicate door-level transitions |
| Security | Multi-point locks and aluminum framing with perimeter sealing | Multi-point locks common on premium systems | Variable; depends on hardware, profile, and frame anchoring |
| Thermal/airtightness | Premium systems use perimeter gaskets, thermal breaks; continuous seals at interlocks | Continuous interlocks and gaskets standard in premium products | Gaskets and interlocks; performance varies with profile and installation quality |
| Site tolerance | High; perimeter gaskets and adjustment accommodate structural movement | Moderate; precise framing tolerances benefit operation and sealing | Moderate-to-high; multiple adjustments on hinges/rollers help compensate |
| Maintenance | Low; rollers and seals inspected periodically | Low; rollers and seals periodically maintained | Moderate; multiple hinges/rollers require periodic adjustment |
| Glazing | Large panes; structural glazing options in some systems | Large panes; similar handling to folding systems | Pane size constrained by panel dimensions; more joints |
| Installation complexity | Moderate; careful planning for stack zones, head track support, and thresholds | Moderate; precise opening alignment critical | Higher; more panels, more hardware, and precise head/track alignment |
| Cost | Higher capital cost; total project value driven by size, finish, and hardware | Moderate capital cost; scaling largely by opening size | Lower-to-moderate capital cost; rises with panel count and finish |
What the differences mean for projects
-
Maximizing the opening: Concertina systems and multi-panel bifolds deliver the largest clear openings. Sliding doors can approach this with large panels, but the stacking depth and track layout of concertina systems are often advantageous where side room is available.
-
Stack space and sightlines: Where space for stacking is constrained, sliding doors excel since panels move along a track rather than stacking. Concertina doors need a defined stacking zone. Bifold doors require the most stack area for a given opening size.
-
Access and thresholds: Modern concertina systems and premium sliding products both offer low-threshold solutions. Bifold systems can be low-threshold but introduce more transition points where tracks and hinges sit.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
-
Buildability and tolerances: Concertina and bifold systems benefit from robust head support and careful track alignment. Sliding doors are sensitive to framing square and plumbness. All three require attention to level thresholds for smooth operation.
-
Thermal and airtightness: Perimeter gaskets, multi-point locks, and interlocking profiles are common to premium solutions in all categories. Concertina systems often combine these with larger panes and fewer panel breaks, aiding continuity of the envelope (though outcomes depend on specification and build).
-
Maintenance: Sliding and concertina systems typically require less ongoing adjustment than bifolds, where multiple hinges and roller sets need periodic tuning as the building settles or seals age.
-
Cost: For a given opening size, concertina systems generally carry a higher upfront investment driven by panel area, hardware, and finish. Sliding doors usually fall in the middle. Bifold doors tend to cost less per opening, with cost scaling strongly with panel count and finish.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
When to choose which option
- Choose concertina (stacking) doors when:
- You need near-complete panel stacking for maximum clear width and the stacking zone is planned and available.
- Large panes and minimal profile lines are desired for visibility and continuity with the facade.
-
Perimeter sealing, low threshold, and strong multi-point security are priorities.
-
Choose sliding patio doors when:
- Limited side room dictates minimal stacking footprint.
- Projects prefer simpler track-based operation with fewer moving parts.
-
Cost and maintainability over time are key considerations without sacrificing performance.
-
Choose timber/UPVC bifold doors when:
- Maximizing opening size is paramount and side space for stacking is available.
- Budget control is important; panel count can be tailored to opening width and budget.
- You can accept more hardware and slightly higher maintenance associated with multiple pivot points.
Final assessment
Aluminium concertina doors excel where maximum opening, large panes, and a low threshold are primary drivers and the stacking zone can be designed into the project. Sliding patio doors are optimal when space and simplicity are prioritized. Timber/uPVC bifolds offer scalability and cost control for large openings but trade off in stack depth and maintenance burden. Align your choice to building typology, usable side space, performance expectations, and lifecycle costs.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for aluminium concertina doors
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for Aluminium Concertina Doors
Note: Always verify project-specific requirements and model-specific data with the manufacturer. Performance varies by configuration, hardware, glazing, size, and site conditions.
Core technical properties and performance metrics
| Metric | What it means | Common test method | Typical industry range | Primary standards (US/EU) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| U-factor/U-value | Heat flow per unit area (thermal transmittance); lower is better | Lab testing on whole unit | ~0.8–2.6 Btu·ft/(h·ft²·°F) or ~0.5–1.5 W/(m²·K) | US: NFRC 100; EU: EN 14351-1 (reported value under EU standards) | Glazing, thermal break, spacer, and air gap drive U-value. |
| SHGC | Solar heat gain coefficient | NFRC 200 | ~0.20–0.60 | US: NFRC 200 | Lower SHGC in hot climates; higher for passive solar in colder climates. |
| Airtightness | Leakage of air at specified pressure differential | ASTM E283 | ~0.3–0.6 cfm/ft² at 6.24 psf (typical marketed values) | US: E283; EU: EN 12207 Class | Multi-point seals and compression affect class; request class rating per EN 12207. |
| Water infiltration | Resistance to water penetration at pressure | ASTM E331 | ≥0 psf static pressure performance | US: E331; EU: EN 12208 | Drainage paths, gaskets, and sealing critical. |
| Structural performance | Deflection and load resistance | ASTM E330 | Meet code deflection limit at specified pressure | US: E330; EU: EN 12210 | Larger openings require stiffer panels/track. |
| Durability (weather) | Cyclic testing for tightness | ASTM E2268 | Varies by product class | US: E2268; EU: EN 12210 | Required for wind load ratings and door classifications. |
| Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) door | Not applicable; ABS is a plastic not used in robust multi-panel concertina doors | N/A | N/A | N/A | Ignore—appears only in product listings, not structural door classes. |
| Glazing | Unitized glass used in panels | ASTM E2188/E2189 | N/A | US: ASTM; EU: EN 1279 (IGUs) | Ensure compatibility of glass thickness and weight. |
| Acoustic | Airborne noise reduction | ASTM E90/E413 | ~30–45 dB Rw or STC | US: ASTM E90/E413 | Dependent on panel mass, seals, glass, and gaps. |
| Max panel dimensions | Largest single panel supported by hardware | Manufacturer spec | Height typically 2.7–3.6 m; width up to ~1.2 m (model-dependent) | N/A | Larger panels increase weight and structural requirements. |
| Max leaf width | Supported opening width per panel | Manufacturer spec | Commonly ~900–1200 mm | N/A | Affects stacking depth and stacking space planning. |
| Stacking depth | Total depth when panels are fully stacked | Model dependent | 120–180 mm typical | N/A | Influences reveal clearances and sightlines. |
| Track | System accommodating folding motion | Model dependent | Bottom, top, or combination track systems | N/A | Floor vs ceiling loading, slope tolerance, and levelness impact performance. |
| Threshold height | Height of the bottom track/door line | Model dependent | Low-profile to full-height | N/A | Thermal breaks and ADA compliance considerations for commercial builds. |
| Panel material | Structural aluminum sections | N/A | 6000-series alloys common | N/A | Verify grade, thickness, and structural adequacy for wind loads. |
| Finish | Surface treatment durability | AAMA/WDMA industry practice | Anodized or organic coated | US: AAMA 2603/2604; EU: EN 12206-1 (paints) | Coastal/dilapidated sites need high-durability finish. |
| Finish warranty | Coverage period for coating | Manufacturer policy | 10–25 years | N/A | Confirm warranty for USA and EU separately. |
| Hardware warranty | Hinges, tracks, locks | Manufacturer policy | 2–10 years | N/A | Specify hardware pack and corrosion class. |
| Warranty (general) | Overall product coverage | Manufacturer policy | 5–10 years common | N/A | Include exclusions and maintenance conditions. |
Performance classes (use in specifications)
- Air leakage (EN 12207): Classes 1–4 (4 is tightest).
- Water tightness (EN 12208): Classes 0–E (E is highest).
- Wind load (EN 12210): Classes 0–5; deflection limits per product specification.
- Thermal classification (EN ISO 10077): Thermal break presence and overall window/door performance classification.
- Fire/smoke egress: Verify local code for fire ratings and emergency egress requirements.
Trade terminology and commercial conditions
| Term | Definition | How to apply in a B2B RFQ |
|---|---|---|
| MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity) | Smallest order size the supplier can accept | Ask MOQ by series/configuration; some factories require 1 panel minimum, others a full set. |
| Lead time (ETD) | Days/weeks from PO to shipment | Request standard lead time and expedited options. |
| Tooling (NRE) | Non-recurring engineering costs for unique profiles or dies | Request costs for custom extrusions, dies, or fixtures. |
| Samples | Small items to evaluate finish, hardware, and fit | Ask for sample swatches (finish) and sample panel/track. |
| Packaging | Crate/wood frame protection; palletization | Request crate type, bracing, corner protection, and stretch wrap. |
| FOB / EXW / CIF / DDP | Incoterms for delivery responsibility | Specify term and location; clarify responsibilities for loading and duties. |
| Warranty | Coverage scope and term | Specify coating, hardware, and moving components separately. |
| RMA (Returns/Repairs) | Policy for defect/returns | Request RMA terms and timeline; include photo evidence. |
| Compliance | Code and standard conformance | Reference US and EU standards in the RFQ. |
| Customization/OEM | Private-label, finishes, hardware, branding | Ask for custom anodized/painted finishes and brand stamping options. |
Measurement and quotation checklist
- Opening rough opening: width (W) × height (H); note out-of-plumb/level.
- Stacking space: width reserved for folded panels (stacking depth × number of panels).
- Track option: floor vs ceiling; thresholds: low-profile, flush, or ADA-compliant.
- Glazing: type (low-E, laminated), thickness, and IGU spacer/seal.
- Hardware set: multi-point lock, hinge type, soft-close, accessories.
- Finish: anodized vs powder coat; AAMA class and color code; finish warranty term.
- Performance targets: U-factor/SHGC, air/water/wind classes, acoustic goal.
- Delivery: incoterms, location, and desired lead time.
- Certification targets: US ENERGY STAR, NFRC labeling; EU DoP/CE under CPR and UKCA where applicable.
Certifications and declarations by region (summaries)
| Region | Mark/Declaration | What it covers | What to request in specs |
|---|---|---|---|
| USA | NFRC label (U-factor, SHGC, VT) | Energy performance label | Require NFRC label per product size/configuration. |
| USA | Florida Product Approval / TX Product Approval | Regional approval for wind loads/water | Provide approval ID and conditions of use if in Florida/Texas. |
| USA | ASTM test reports (E283, E331, E330, E2268, E90) | Air, water, structural, durability, acoustic | Request latest reports for the exact configuration. |
| USA | Building codes (IBC, IRC, local) | Fire, egress, accessibility | Cross-check egress hardware, fire ratings, and ADA thresholds. |
| EU | CE marking + DoP (CPR 2011/305/EU) | Product conformity and declared performance | Require CE marking and product-specific DoP/DoC. |
| EU | UKCA (UK) | Conformity for construction products | Request UKCA marking where applicable. |
| EU | Declaration of Conformity and safety information | PPE or accessory compliance | Include accessories and safety labeling where required. |
Sourcing notes and cautions
- Performance is configuration-specific: hardware, panel count, glazing type, and stack space influence U-values, air/water/wind ratings, and acoustic performance. Provide floor plans and elevation details.
- Stacking planning: ensure clear space behind the fully opened stack for maintenance and safe egress.
- Thresholds and slope: tolerances for floor levelness and slope affect water management and sealing.
- Thermal bridging: without a robust thermal break, dew point and condensation risks rise; select appropriate profiles and gaskets.
- Accessibility and egress: review local code for hardware ADA requirements and emergency egress widths.
- Warranty and service: define maintenance requirements (cleaning seals, lubricants) and response time for replacements.
- Shipping method: confirm crate strength, palletization, corner protection, and wrapping for your local port and storage conditions.
- Avoid generic listings: treat product marketplace descriptions (e.g., Amazon) as illustrative; specify performance with test-backed data.
When you are ready, share your target opening sizes, stack preferences, glazing targets, and desired performance classes so I can help you finalize a concise RFQ and a vendor shortlist.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the aluminium concertina doors Sector
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the aluminium concertina doors Sector
Why the market matters now
- Demand is driven by open-plan layouts, light-filled spaces, and retrofit programs that need minimal structural disruption; large-panelled aluminium concertina doors deliver wide openings with slim sightlines and strong thermal performance.
- Regulatory pressure and energy costs are raising the bar on U-factor, SHGC, acoustic separation, and whole-project embodied carbon; product selection is increasingly driven by verified performance (NFRC/EN test data, ASTM codes in the US, CE/UKCA in Europe).
- Supply chains are still normalizing after post-pandemic volatility; aluminium prices and freight remain sensitive, and specification-level compliance (codes, hurricane/impact, fire) is a gating factor for approvals.
Aluminium pricing and supply signals
- LME aluminium pricing is cyclical and macro-sensitive; 2022–2023 saw elevated averages, followed by mid-2024 declines, with USMCA producers and diversified suppliers helping to balance regional variability. Expect periodic spikes tied to energy costs and primary smelting capacity.
- Logistics capacity has improved versus 2021–2022, but ocean schedules and inland transport remain variable at regional nodes; buffer lead times for glazing and specialty hardware help avoid site delays.
- Panelization and glazing capacity are capacity-bound in high-demand markets; coordinating test schedules, glass orders, and freight is essential to meet installation windows.
Demand drivers by region
- US commercial: hospitality and multi-family conversions favor large-opening systems with acoustic ratings and accessibility-friendly track transitions.
- US residential: high-end single-family and mid-rise want hurricane/impact compliance in coastal markets and ADA-compliant low-threshold tracks in hospitality and public-facing spaces.
- Europe: strict building regulations and retrofit programs favor low-U and high Solar Heat Gain Control (SHGC) tuning; acoustic comfort and CE-marked performance data drive specifications.
Sustainability and circularity in aluminium concertina doors
- Recycled content is a practical lever: systems can incorporate substantial post-consumer recycled aluminium without compromising performance.
- Cradle-to-Cradle and Environmental Product Declarations (EPDs) are becoming standard in tenders; specifying EPD-backed aluminium and low-VOC finishes supports LEED/BREEAM and local sustainability frameworks.
- Powder coating vs. anodizing: powder coating offers broad color options, strong corrosion resistance, and energy-friendly curing; anodizing delivers superior wear resistance but has higher energy intensity. Verify local VOC regulations and finish lifecycle impacts in both US and EU.
- End-of-life value is high: aluminium has strong recyclability; designing for disassembly (DfD) makes panel and hardware recycling feasible and improves project circularity metrics.
Certification and compliance snapshot (US vs Europe)
| Region | Compliance focus | Typical evidence required | Notes for specifiers |
|---|---|---|---|
| USA | NFRC energy labeling; ASTM E283, E331/E330 (air/water/structural); ASTM E2357 (panel frame); Florida Product Approval; hurricane impact (large missile/ small missile) in coastal zones; ADA-compliant thresholds for accessible applications | Third-party test reports; Florida Product Approval IDs; NFRC labels; code compliance summaries | Confirm local AHJ requirements early; impact glazing and attachments (sunscreens/shutters) can alter SHGC and frame thermal response. |
| Europe | EN 12210 (wind), EN 1026 (air), EN 1027 (water), CE/UKCA marking; EN 12208/12209 (air/water); Reaction to fire classification (EN 13501) where applicable; Acoustic rating per EN ISO 10140 | CE/UKCA DoC; declared performance to EN 14351-1; NFRC-equivalent energy performance per EN ISO 10077; acoustic test data | Performance declaration drives procurement; energy and acoustic targets should align with national regulations and project briefs. |
Sourcing models and trade-offs
| Option | Strengths | Watch-outs | Typical lead time impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| US/Canada domestic supply (e.g., brands comparable to LaCantina Doors) | Faster approvals and code integration; localized installation and warranty support; familiarity with regional glazing schedules | Unit pricing typically higher; capacity constraints on premium sizes/finishes | Shorter overall; aligns with local permitting cycles |
| EU manufacturing (e.g., EU-based premium brands) | Strong CE compliance; design variety; advanced thermal/acoustic solutions | Shipping to US increases lead times and costs; US code harmonization requires coordination | Medium-to-long; customs clearance and glazing alignment can extend timelines |
| Turkey | Competitive price-performance; scalable capacity; growing CE penetration | Import documentation; regional freight variability; service depth may vary by supplier | Medium; manageable with early QA and logistics planning |
| China | Broad supplier ecosystem; cost competitiveness; flexible customization | Variable quality; extensive US/EU compliance diligence required; longer transit | Long; extended QA, documentation, and logistics cycles |
| Domestic/regional fabricators (non-brand proprietary) | Flexible configurations; value-engineered solutions | Inconsistent test data; warranty and parts support can be limited | Medium; delivery depends on material procurement and QA capacity |
Key specifications to anchor procurement
- Panels and sightlines: specify panel widths/heights and maximum panel weights; state desired sightline width and thermal break quality.
- Thermal performance: align target U-factor/SHGC with NFRC labels (US) or EN 10077-1/2 and project energy model (EU).
- Air, water, structural ratings: cite relevant ASTM/EN standards and test results; request independent third-party lab reports.
- Acoustic performance: target Rw/Ctr (EU) or STC (US), and ensure glazing assemblies match the door system rating.
- Hardware: heavy-duty tracks, anti-slam mechanisms, multi-point locks, weather seals, drainage details; confirm corrosion class.
- Finishes: specify corrosion class (e.g., C3/C4 per ISO 12944), VOC-compliant coating, and finish warranties.
Quality assurance and compliance roadmap
- Verify brand or supplier credentials (ISO 9001/14001), test reports, and third-party certifications.
- Request project-specific submittals: elevation drawings, section details, anchor methods, glazing specs, finish schedules, installation instructions.
- Confirm performance continuity: panel-to-frame tests (ASTM E2357 or EN equivalent) reflect real installations better than component-level tests.
- Schedule inspections: on-site QA for frame alignment, anchoring, drainage, and glazing quality; retain mock-ups where performance is critical.
Logistics and lead time planning
- Critical path items: specialty glazing (laminated, low-e, acoustic), hurricane/impact assemblies, and custom finishes.
- Buffer planning: include 4–8 weeks contingency on transatlantic shipments; secure dock appointments and customs brokers early.
- Incoterms and risk: clarify DDP vs FOB terms; US tariffs, EU anti-dumping duties (where applicable), and VAT/duties drive landed cost. Select Incoterms aligned with your risk appetite and installation readiness.
Practical actions for procurement teams
- Build a specification-first pipeline: lock target performance (U-factor, SHGC, acoustic, air/water/wind) before price shopping; verified performance avoids change orders.
- Dual-source panelization or glazing where feasible to reduce regional logistics risk and maintain schedule.
- Use recycled-content targets and EPD-backed aluminium to satisfy sustainability requirements without sacrificing performance.
- Run a lead-time gap analysis: material supply, testing, glazing, logistics, and installation; stage orders to avoid bottlenecks.
- Codify compliance: maintain a library of NFRC/EU EN test summaries, product approvals, and installation checklists.
Cost and timeline scenarios (indicative ranges)
| Scenario | Typical US unit cost band (retail-like listings suggest $500–$3,000+ per standard-size configuration; your project range may differ based on size/performance) | Lead time to site (incl. glazing/logistics) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Basic residential, moderate size | US mid-market and value-tier systems | 10–16 weeks | Limited customization; standard finishes; single-glazing more common |
| High-performance residential/commercial | Premium systems with better thermal/acoustic ratings | 12–20 weeks | Multi-point locking, large formats, custom finishes; glazing coordination critical |
| Hurricane/impact coastal | Impact-rated panels, tested air/water/structural | 16–24 weeks | Florida Product Approval plus full system impact testing; may require engineered anchoring |
Risk register (procurement-level)
- Energy and freight volatility: price shifts and schedule slippage; mitigation via locked quotes and flexible lead buffers.
- Substandard compliance documentation: rejected submittals; mitigation via upfront QA, third-party tests, and clear AHJ coordination.
- Glazing supply delays: bottleneck on laminated/low-e variants; mitigation via early glazing orders and regional backup suppliers.
- Finish failures or corrosion: warranty disputes; mitigation via corrosion class specs and accelerated testing for aggressive environments.
What to ask your suppliers up front
- “What is your NFRC/EN thermal performance with specified glazing, and can you provide labeled values?”
- “Which specific ASTM/EN tests support the declared air/water/structural and panel-frame performance?”
- “Do you have Florida Product Approval (US) or CE/UKCA declarations (EU) for our geometry and anchoring methods?”
- “What are your acoustic ratings and test assemblies, including glazing coupling?”
- “What are your corrosion class, finish warranty, and DfD options for end-of-life recycling?”
When performance and logistics must align
In high-end residential and hospitality, a hybrid approach often works best: domestic supply for approvals and faster installation, paired with EU/Eastern European manufacturing for premium thermal/acoustic and design detail. In commercial retrofits and multi-family projects, prioritize systems with proven NFRC/EU performance and robust hurricane/impact testing to minimize change orders and site rework.
Done right, aluminium concertina door procurement is a balance of verified performance, compliant documentation, and logistics discipline. Anchor your specs to recognized test standards, plan for glass and impact sub-assemblies, and lock in sustainability metrics with EPD-backed aluminium. That combination minimizes risk and keeps installation timelines intact across the USA and Europe.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of aluminium concertina doors
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of Aluminium Concertina Doors
1) What is a “concertina door” and how does it differ from a standard bifold?
A concertina door is a multi-panel aluminum folding system designed to fully open and stack in a compact “accordion” configuration. Compared to a conventional bifold, concertina systems often emphasize narrow sightlines, superior panel alignment, and high-cycle hardware to support frequent openings in high-traffic, commercial environments.
| Attribute | Concertina (aluminium) | Conventional bifold |
|---|---|---|
| Panel count/stacking | Many panels; full-stack “accordion” at one or both sides | Pair or small set; hinges on a track with pivot points |
| Track/rail profile | Heavy-duty top track with guided bottom option; precise alignment | Top track and bottom pivot rail; panel gaps can be larger |
| Sightlines | Narrower stiles/rails typical for premium systems | Varies; typically wider stiles on standard systems |
| Hardware | High-cycle rollers, hinges, multi-point locksets | Standard bifold hardware; durability varies |
| Weather-sealing | Continuous perimeter seals; engineered for larger openings | Perimeter seals present; performance varies by product |
| Typical use | Retail/office frontages, restaurants, hotels, high-frequency openings | Residential/rear doors; moderate frequency openings |
Premium manufacturers such as LaCantina Doors produce commercial-grade aluminum folding systems that are widely specified by architects and contractors for exterior applications. Budget or retail systems (e.g., thin-frame products with mesh intended for interior use, like certain Amazon listings) offer cost-effective options but are not intended for exterior storefront or high-security use.
2) What dimensions and panel layouts are possible?
Concertina systems are configurable in width, height, and panel count. Panels can open to the left, right, or both sides, and configurations include pairs, “telegraph” panels that set the stack width, and “trailing” panels that fold against the stack.
| Dimension | Typical considerations | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Width | Determined by number and width of panels (e.g., panels ~300–600 mm wide are common in commercial systems) | Wider spans require reinforced hardware and additional rollers/track support |
| Height | Height-limited by hardware ratings and site geometry | Taller stacks often need guided bottom track for alignment |
| Panels | Many panels possible; each adds stack width and seal lines | Balance opening width, stacking depth, and traffic flow |
| Stacking | One-sided or two-sided stacks | Two-sided stacks provide even load distribution and symmetry |
| Thresholds | Low-profile or ADA-style options | Specify slope and drainage to avoid trip hazards and water ingress |
Coordinate site measurements early with the supplier; panel dimensions and stack width drive track design and installation complexity.
3) What glazing and thermal performance options are available?
Premium commercial concertina systems support a range of glazing options. Architects typically select glazing to meet performance, code, and project objectives.
| Category | Options | Use cases |
|---|---|---|
| Glass types | Annealed, tempered, heat-strengthened; laminated; low-e coated; insulated glass units (IGUs) | Security, impact resistance, acoustics, thermal performance |
| Safety/security | Tempered or laminated; ballistic glazing variants; secure locking hardware | Front-of-house, schools, healthcare, high-value retail |
| Impact/weather | Impact-resistant glazing; gaskets and weatherproofing details | Regions with windstorm/seismic or vandalism risk |
| Thermal | Low-e IGUs; multi-cavity glass; thermal breaks in aluminum frames | Energy-efficient exterior openings and interior climate control |
| Appearance | Tinted, fritted, or reflective finishes for solar control and privacy | Retail branding, daylighting strategy, glare management |
Coordinate with the supplier for U-factor, SHGC, and acoustic ratings consistent with local energy and building codes.
4) What hardware and locking/security features are standard or available?
Commercial-grade hardware prioritizes durability, alignment, and security. Locking hardware and access control can be integrated with the frame.
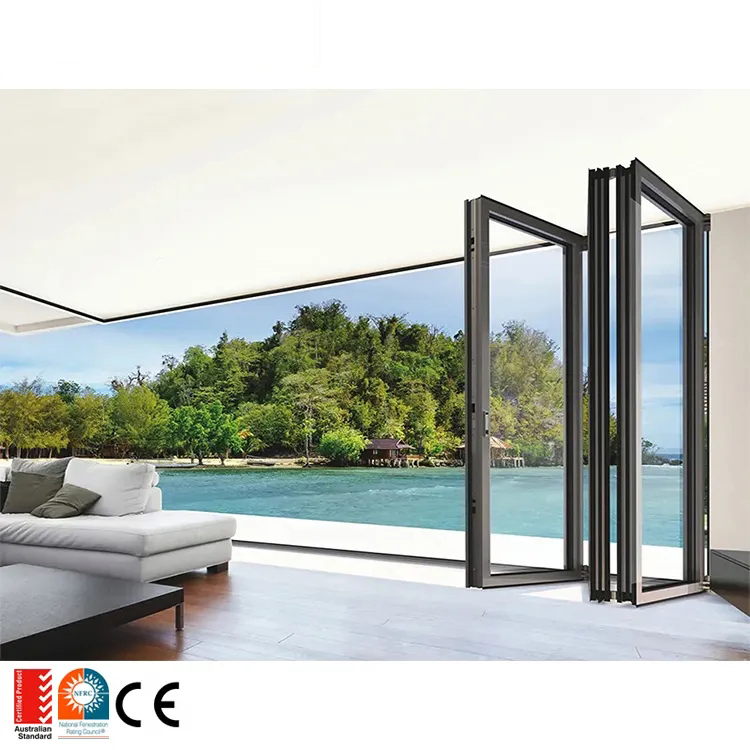

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
| Category | Standard | Options/upgrades |
|---|---|---|
| Tracks/rollers | Top track with heavy-duty rollers; optional guided bottom track | Low-profile tracks, anti-sag adjustments |
| Hinges/panels | Reinforced panel joints for commercial cycles | Security hinges, tamper-resistant fasteners |
| Locks/multi-point | Keyed lever handles; multi-point locking available | Magnetic locks, electric strikes, card readers, remote locks |
| Perimeter sealing | Continuous weather seals | Pressure seals, acoustic seals, brush seals |
| Accessibility | ADA-compliant handles and clearances | Integrated door operators for hands-free use |
Ensure alignment and tolerances meet supplier specifications; incorrect tracks, rollers, or fasteners can compromise performance and security.
5) What finishes and colors are available?
Aluminum concertina doors accept durable finishes suited for commercial environments. Surface treatments include anodizing, PVDF, polyester, or powder coatings.
| Finish | Typical attributes | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Anodizing | Corrosion-resistant; integral color | Avoid contact with cementitious products |
| PVDF (Kynar) | Excellent UV and chalk/fade resistance | Favor for high-UV exposures |
| Powder coat | Broad color range; textured or smooth options | Specify AAMA/Qualicoat performance class |
| Woodgrain/textured | Aesthetic finishes with protective coatings | Check abrasion and UV stability |
| Specialty | Metallic, antimicrobial, or conductive finishes | Verify lead times and cost implications |
Coordinate finish schedules across adjacent storefront systems to maintain visual continuity.
6) What are typical lead times and how should we plan scheduling?
Lead time depends on custom dimensions, finish, glazing, and market conditions.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
| Scope element | Typical lead-time considerations | Planning guidance |
|---|---|---|
| Dimensions/config | Longer for custom widths/heights and complex panel counts | Early submittals prevent delays |
| Finishes | Standard colors typically shorter lead; custom and specialty finishes longer | Lock color early to avoid rework |
| Glazing | Tempered/laminated and low-e IGUs add time; impact-rated longer | Coordinate shop drawings with glazing supplier |
| Hardware/security | Multi-point and access control integration increases lead time | Finalize access control specs early |
| Certification/testing | Impact, wind load, or acoustic testing extends schedules | Build testing windows into master schedule |
| Freight | Overseas freight subject to port congestion and customs | Include buffer for international shipments |
Use a phased procurement approach: approve shop drawings and glazing details before release to manufacture, confirm freight windows, and allow site-access inspection before shipment.
7) How is the product installed, and what site preparation is required?
Installation quality determines long-term performance. Expect a staged process: coordination, framing, installation, testing, and commissioning.
| Step | Required activities | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Structural support | Verified rough opening dimensions; head/jamb support; deflection limits | Avoid cutting tracks or frame to fit; fabricate to opening |
| Track alignment | Top track level and square; guided bottom track if specified | Precision alignment prevents binding and seal failure |
| Perimeter sealing | Install continuous gaskets; specify drainage paths | Provide sill slope and weep locations |
| Hardware | Secure rollers/hinges to frame; torque fasteners to spec | Use manufacturer-approved fasteners and anchors |
| Glazing | Install glazing per approved detail; check clearance and setting blocks | Verify glass type and performance match spec |
| Testing & commissioning | Operate panels through full cycle; verify locks, alignment, weather sealing | Document QA checklists and punch list items |
| Training | Site training for maintenance cycles and troubleshooting | Include access control integrations if applicable |
Specify installation tolerances, anchor types, and clearances per supplier requirements; verify local code for weatherproofing and egress.
8) Are these systems sustainable and compliant?
Aluminum frames are inherently recyclable and long-lived. Finish and glazing strategies can contribute to building sustainability objectives.
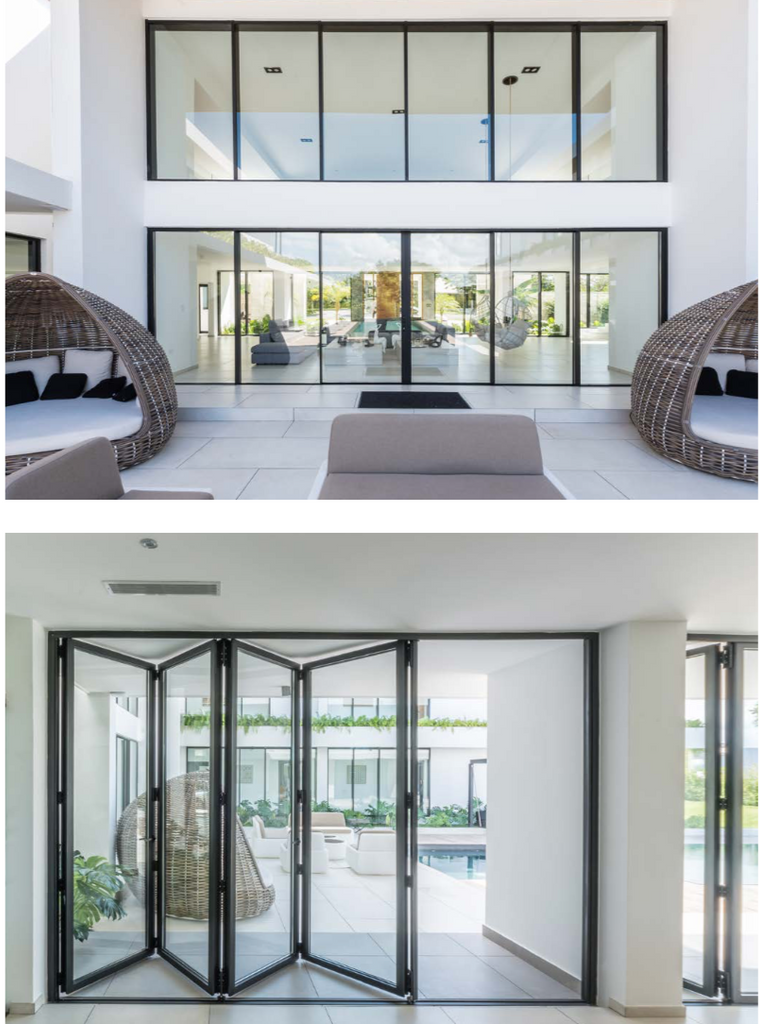

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
| Aspect | Consideration | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Recyclability | Aluminum is widely recyclable | Confirm recycled content and end-of-life recovery plans |
| Finishes | Low-VOC options available; specify durable finishes to minimize maintenance | Verify AAMA/Qualicoat compliance where applicable |
| Glazing | Energy-efficient IGUs and low-e coatings | Coordinate U-factor/SHGC targets with project energy model |
| Certifications | Products may carry or be compatible with NFRC, CE marking, EPDs | Request manufacturer documentation per region |
| Maintenance | Long service intervals when properly specified and installed | Plan annual inspections and replacement of seals/rollers |
| Responsible sourcing | Factory audits and chain-of-custody for materials | Ask for certificates of compliance and traceability |
Integrate concertina doors into the project’s daylighting, ventilation, and operational strategy; align with regional codes and sustainability certifications.
Notes for buyers:
– Specify performance targets—glazing, hardware, and finishes—up front to avoid late-cycle changes.
– Confirm installation tolerances and access control integrations with suppliers and contractors.
– For budget or retail options (e.g., thin-frame mesh products listed on consumer marketplaces), verify suitability for your environment; these are typically interior solutions and not intended for high-security or exterior commercial applications.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for aluminium concertina doors
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for aluminium concertina doors
Aluminium concertina doors deliver long-term value across commercial and premium residential segments in the USA and Europe: they combine durability, low maintenance, smooth operation, and contemporary aesthetics. For procurement, prioritize suppliers offering robust hardware stacks, high‑performance glazing, superior weather sealing, and multi‑point locking with documented performance, service, and warranty coverage.
Quality-to-price spectrum is clearly segmented:
– Entry-tier options: thick aluminium frames and mesh, typical price point around $556 (e.g., Innovz Amazon listing). Fit for budget-conscious projects where performance basics suffice. [Innovz]
– Premium-tier brands: engineered for exterior applications, advanced thermal/acoustic ratings, and tailored configurations, represented by leading suppliers like LaCantina. [LaCantina]
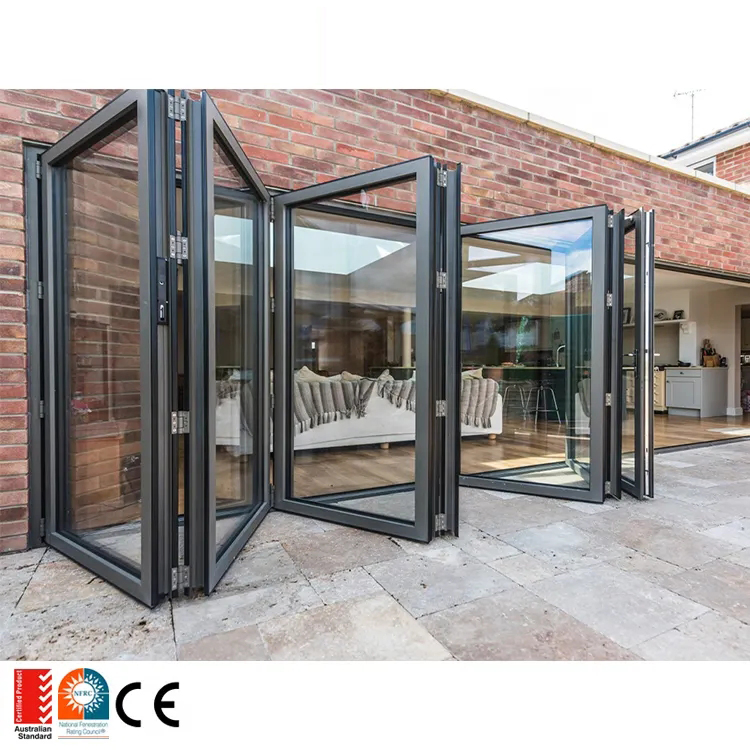

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Outlook: increasing demand for higher thermal and acoustic performance, ESG-driven specifications, and energy-saving solutions will shape 2025–2027 programs. Expect tighter documentation, sustainability disclosures, and lifecycle guarantees.
Next steps:
– Define performance specs and compliance requirements (safety, air/water/structural, accessibility).
– Shortlist vendors with proven after-sales service, documented testing, and regional support.
– Pilot installations or sample approvals; benchmark hardware life and seal durability.
Action: issue an RFP tied to measurable KPIs (durability, maintenance, energy, service SLAs). Begin sourcing with a short-list aligned to project priorities.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided is for informational purposes only. B2B buyers must conduct their own due diligence.