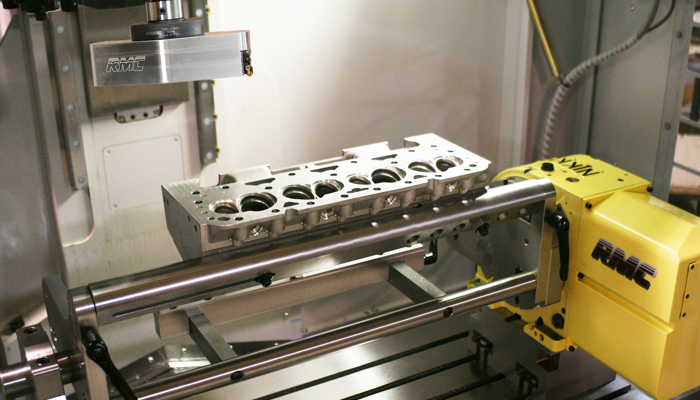
Cylinder Head Resurfacing Machine: The Ultimate 2025 Sourcing Guide
Top 10 Cylinder Head Resurfacing Machine Manufacturers & Suppliers List
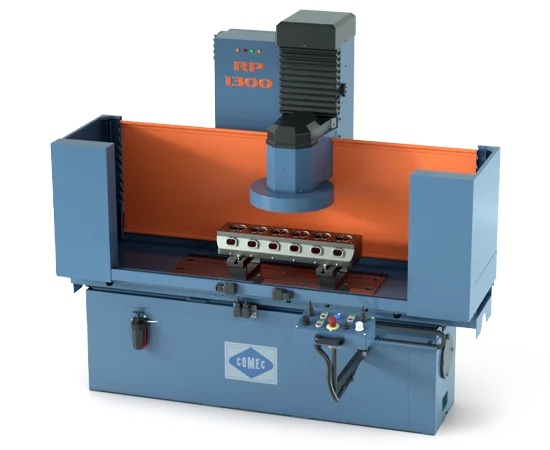
1. Engine Resurfacing Machines | COMEC
Domain: comecpn.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: Wide selection of CNC cylinder head resurfacing machine of both cars and trucks. Discover them now….
2. Resurfacing Machines | Jamison Equipment
Domain: jamisonequipment.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: WVN VM2000 cylinder head and block milling machine. Ready to go to work, includes block tooling also. Comec 300/900 CBN Head & Block Resurfacer. $13,500.00….
3. Cylinder Head Repair Machines
Domain: machtrade.us
Registered: 2022 (3 years)
Introduction: MachTrade has been a long-term proud representative of globally renowned cylinder head resurface machine manufacturer, POLEKS. Its range of cylinder head ……
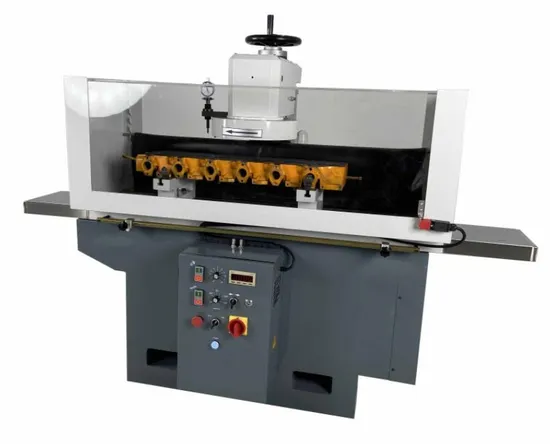

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
4. Cylinder Head Resurfacing Machines and Equipment for Sale
Domain: theultimatetooling.com
Registered: 2016 (9 years)
Introduction: Thanks to partnerships with top brands like Comec and Industrias Kras, we ensure high-quality machinery for cylinder head resurfacing and block milling….
5. Automotive Cylinder Head and Block Resurfacing Machines
Domain: robinsmachines.com
Registered: 2021 (4 years)
Introduction: Robins Cylinder surfacing offers several benefits, including: Improved Engine Performance: Resurfacing ensures proper sealing and prevents leaks ……
6. Cylinder Head Resurfacing Machinery – Rottler Manufacturing
Domain: rottlermfg.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: Cylinder head resurfacing is a key function of Rottler equipment. We offer dedicated automatic, manual and CNC surfacers, as well as multi-purpose machining ……
7. Cylinder Head Work – Shop For Valve Adjustment Tools & More!
Domain: regismanufacturing.com
Registered: 2010 (15 years)
Introduction: 5–9 day deliveryShopping for cylinder head work tools & supplies? Shop Regis Manufacturing for the latest selection of valve adjustment tools, honing oils & more!…
Understanding cylinder head resurfacing machine Types and Variations
Understanding Cylinder Head Resurfacing Machine Types and Variations
Selecting the right cylinder head resurfacing machine depends on shop volume, engine types serviced, and precision requirements. Below is an overview of four primary machine types used in North American and European automotive repair facilities, based on technological capabilities and operational scope.
| Type | Features | Applications | Pros/Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manual Bench-Top Resurfacers | Belt-driven systems; manual operation; basic speed control via inverter; compact footprint; minimal automation | Small independent shops, light-duty passenger vehicle repairs, single-vehicle maintenance | Pros: Low upfront cost ($2,000–$5,000); simple operation; minimal maintenance. Cons: High operator dependency; slower throughput; inconsistent results on complex heads. |
| CNC Precision Resurfacers | CNC control with laser surface scanning; programmable feed rates; automatic compensation for surface irregularities; integrated digital interfaces | High-volume repair facilities, OEM service centers, performance engine rebuilding | Pros: Consistent ±0.0005″ flatness; 50% faster processing; reduced labor costs; repeatable for complex geometries. Cons: Higher investment ($15,000–$30,000); specialized training required; complex calibration. |
| CBN Milling Systems | Cubic Boron Nitride (CBN) cutting tools; high-speed milling (up to 10,000 RPM); wear-resistant for hard alloys; optimized coolant systems | High-performance engines, heavy-duty truck repairs, aluminum/cast iron production environments | Pros: 3x longer tool life; 40% faster material removal; superior surface finish (Ra ≤ 0.8 μm); handles hardened materials. Cons: Tooling costs 2x higher than standard; requires precise setup; specialized cooling needed. |
| Heavy-Duty Multi-Application Millers | Robust frame (≥500 lb); 35″+ capacity; versatile fixturing for heads/blocks; high-torque motors (5–10 HP) | Commercial truck fleets, industrial maintenance, large-scale repair shops | Pros: Handles oversized components (e.g., commercial truck blocks); durable for 24/7 use; flexible for multiple applications. Cons: Large footprint (≥8′ x 4′); $20,000–$30,000 cost; requires dedicated power (220V 3-phase). |
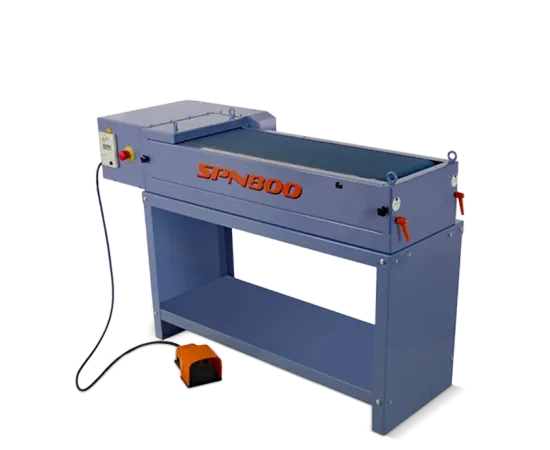
Manual Bench-Top Resurfacers
Manual bench-top resurfacers like the COMEC SPN8
Key Industrial Applications of cylinder head resurfacing machine
Key Industrial Applications of Cylinder Head Resurfacing Machines
| Industry/Application | Key Benefits |
|---|---|
| Passenger Vehicle Repair Facilities | CNC-controlled precision milling ensures repeatable flatness (± |
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘cylinder head resurfacing machine’ & Their Solutions
3 Common User Pain Points for Cylinder Head Resurfacing Machines & Their Solutions
Pain Point 1: Inconsistent Surface Finish Quality
Scenario:
Machining mixed-material cylinder heads (e.g., aluminum blocks with cast iron components) requires micron-level precision to prevent gasket failures in high-performance engines.
Problem:
Manual or non-CNC resurfacing machines fail to maintain uniform surface flatness due to inconsistent feed rates or blade misalignment, resulting in sealing defects, combustion chamber leaks, and costly warranty claims.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Solution:
Deploy CNC systems with real-time adaptive capabilities:
– Integrated laser sensors automatically scan surfaces and adjust cutting parameters dynamically (e.g., COMEC RP1000 CNC)
– Inverter-controlled feed rates ensure optimal material removal across all substrates
– Certified flatness tolerances of ±0.0005″ for all engine types, eliminating rework
Pain Point 2: Inefficient Setup Across Diverse Engine Applications
Scenario:
Automotive repair shops servicing both passenger vehicles and commercial trucks face frequent machine reconfiguration when switching between compact 4-cylinder heads and large diesel truck blocks.
Problem:
Manual fixture adjustments and parameter recalibration for each engine variant consume 30–60 minutes per job, drastically reducing workshop throughput and increasing labor costs.
Solution:
Adopt modular fixturing systems with rapid-change capabilities:
– Quick-release clamping supports heads and blocks up to 35″ length (e.g., Comec 300/900 CBN)
– Universal mounting points compatible with standardized tooling (Jamison VM2000 includes block-specific fixturing)
– Pre-programmed job templates for common engine families to cut setup time by 60%

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Pain Point 3: High Maintenance Costs from Component Wear
Scenario:
High-volume resurfacing shops experience frequent downtime when standard grinding hubs degrade rapidly while processing hardened alloys or high-mileage engine components.
Problem:
Conventional carbide hubs require replacement every 50–100 jobs, causing unplanned outages and increasing operational costs by 25–40% annually.
Solution:
Switch to CBN (Cubic Boron Nitride) grinding hubs for industrial durability:
– 5x longer service life vs. standard carbide hubs (e.g., Sunnen HBS-2100 with CBN milling head)
– Reduced vibration and thermal deformation during high-speed operation
– 30% lower total cost of ownership through minimized downtime and part replacement frequency
Strategic Material Selection Guide for cylinder head resurfacing machine
Strategic Material Selection Guide for Cylinder Head Resurfacing Machines
Selecting optimal materials for cylinder head resurfacing machinery directly impacts precision, longevity, and operational efficiency. This guide outlines critical material considerations for key machine components, enabling informed decisions based on application requirements and industry standards.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Frame Construction Materials
- Cast Iron: Industry standard for high-precision resurfacing. Provides superior vibration damping, critical for maintaining surface flatness during operation. Ideal for heavy-duty shops processing both cast iron and aluminum heads (e.g., COMEC RP-series, Sunnen HBS-2100).
- Steel: Lighter weight and lower cost, but requires additional vibration-damping measures. Suitable for mobile or low-volume applications; may compromise long-term precision in high-stress environments.
Cutting Tool Material Specifications
- Cubic Boron Nitride (CBN): Optimal for cast iron heads due to exceptional hardness (9,500–9,800 HV) and thermal stability. Resists wear under high-speed CNC operations (e.g., COMEC RP1000 CNC, Jamison CBN Milling Head). Reduces tool change frequency by 60% vs. carbide in high-volume shops.
- Carbide: Preferred for aluminum heads to minimize material adhesion. Lower initial cost but requires frequent resharpening (2–3x more than CBN). Ideal for budget-conscious shops with predominantly aluminum workloads (e.g., Kwik Way 860).
- Diamond: Avoid for ferrous metals due to chemical reactivity. Only suitable for specialized non-ferrous applications; not recommended for standard cylinder head resurfacing.
Spindle and Bearing Systems
- Ceramic Bearings: Enhances speed capability (up to 15,000 RPM) and reduces heat generation by 30% vs. steel. Critical for CNC machines requiring extended runtime (e.g., COMEC RP1400 CNC). Extends spindle life by 40% in continuous-use environments.
- Precision Steel Bearings: Cost-effective for general-purpose manual machines. Adequate for intermittent use but requires regular lubrication and maintenance. Limited to non-CNC models (e.g., Storm Vulcan 85B).
Guide System Materials
- Hardened Steel Linear Guides: Delivers sub-micron positional accuracy (<0.001mm) and minimal friction. Essential for CNC machines demanding repeatable precision (e.g., COMEC RP1000 CNC, Winona Van Norman VM2000).
- Cast Iron Ways: Traditional solution for manual resurfacers. Durable but prone to wear without consistent lubrication. Best for moderate-volume operations where cost is prioritized over ultra-high precision (e.g., COMEC SPN800).
Comparative Material Selection Table
| Component | Material Option | Best Application | Durability | Cost Range | Key Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Frame | Cast Iron | High-precision, heavy-duty production | ★★★★★ | $$$$ | Superior vibration damping; standard for professional shops |
| Frame | Steel | Mobile or light-duty use | ★★★☆☆ | $$ | Lower weight but requires vibration mitigation |
| Cutting Tools | CBN | Cast iron heads, high-volume | ★★★★★ | $$$$ | Long tool life; ideal for mixed-material shops |
| Cutting Tools | Carbide | Aluminum heads, budget-conscious | ★★★☆☆ | $$ | Lower cost but higher maintenance needs |
| Spindle Bearings | Ceramic | High-speed CNC operations | ★★★★★ | $$$$ | Minimal heat buildup; extends spindle life |
| Spindle Bearings | Steel | General-purpose manual machines | ★★★☆☆ | $$ | Standard option but requires regular maintenance |
| Guide Systems | Hardened Steel | CNC precision machining | ★★★★★ | $$$$ | Sub-micron accuracy; low maintenance |
| Guide Systems | Cast |
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for cylinder head resurfacing machine
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for Cylinder Head Resurfacing Machines
Precision-engineered cylinder head resurfacing machines demand rigorous manufacturing standards to deliver consistent performance, durability, and safety for automotive repair facilities and OEMs. Below is a breakdown of critical manufacturing phases and quality protocols adhered to by leading manufacturers like COMEC and Jamison Equipment, ensuring compliance with global standards.
Manufacturing Process
Preparation
- CAD/CAM optimization for structural integrity and component interoperability.
- Material sourcing:
- High-grade cast iron (e.g., EN-GJL-250) for vibration-damping frames.
- Hardened steel (e.g., 42CrMo4) for moving parts like spindles and slides.
- Aerospace-grade aluminum for lightweight components.
- Supplier certifications aligned with ISO 9001 for raw materials.
Forming
- Precision CNC machining of structural components to tolerances of ±0.001mm.
- Heat treatment (tempering, case hardening) for wear resistance in cutting surfaces.
- Specialized processes for CBN (cubic boron nitride) milling heads (e.g., Sunnen HBS-2100), achieving hardness levels >3000 HV.
- Precision grinding of linear guides (e.g., THK) and ball screws (e.g., NSK) for sub-micron motion accuracy.
Assembly
- Integration of industrial CNC controllers (Siemens 840D, Fanuc 31i) with servo motors for spindle control.
- Laser sensor calibration (e.g., COMEC RP1000 CNC) to 0.01mm accuracy for automated surface profiling.
- Hydraulic/pneumatic systems leak-tested at 1.5× operating pressure.
- EMI-shielded wiring with RoHS-compliant components to prevent electrical interference.
- Adjustable console mounting (e.g., COMEC SPN800/RP series) with ergonomic calibration per operator specifications.
Quality Control
- CMM verification of critical dimensions per ISO 1101 geometric tolerancing.
- Spindle runout testing: <0.002mm TIR per ISO 230-2.
- Feed rate accuracy validation across 5–1000 mm/min ranges.
- Thermal stability testing: 8+ hours continuous operation at max load.
- Safety system validation: Emergency stop response <0.5 seconds.
Quality Assurance Standards
All manufacturing processes adhere to internationally recognized standards, with machine-specific testing protocols:
| Standard | Application | Testing Method |
|---|---|---|
| ISO 9001:2015 | End-to-end quality management | Audited production workflows |
| ISO 230-2 | Machine tool accuracy | Laser interferometry for positional accuracy |
| CE (EU Directive 2006/42/EC) | EU safety compliance | EN 60204-1 electrical safety validation |
| UL 61010-1 | North American electrical safety | Third-party lab safety testing |
| ISO 12100:2010 | Machine safety risk assessment | Hazard analysis (e.g., pinch points, noise) |
End-of-Line Validation: Every machine undergoes 100% functional testing, including:
– Vibration analysis using accelerometers to ensure <1.5 mm/s RMS at operating speed.
– Surface finish validation via profilometry (Ra ≤ 0.8 μm for resurfaced heads).
– Software diagnostics for CNC controllers and sensor systems (e.g., COMEC laser sensor calibration logs).
Note: COMEC’s RP1000 CNC and Jamison’s Sunnen HBS-2100 models feature enhanced QA protocols for automated systems, including real-time error correction during testing and traceable component batch records.
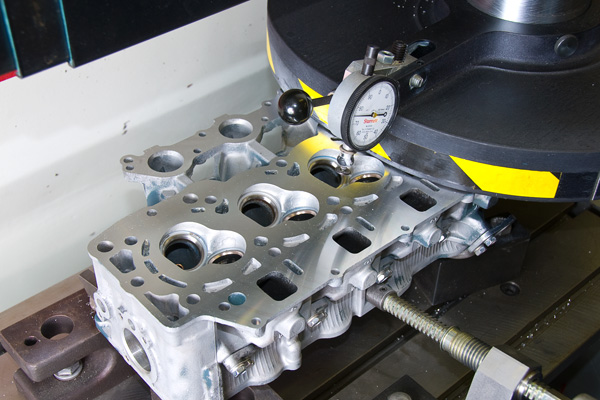
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘cylinder head resurfacing machine’
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for Cylinder Head Resurfacing Machines
Step 1: Define Operational Requirements
- [ ] Confirm part types: cylinder heads only, engine blocks, or both (e.g., COMEC RP850 for heads/blocks, SPN800 for heads-only)
- [ ] Specify material types: cast iron, aluminum, or mixed (e.g., aluminum requires wet grinding to prevent warping)
- [ ] Estimate daily throughput: low-volume shops (<10 units/day) vs. high-volume production (>50 units/day)
Step 2: Evaluate Precision and Automation Needs
- [ ] Prioritize CNC models (e.g., COMEC RP1000 CNC or RP1400.CNC) for laser-guided surface scanning and automated flattening
- [ ] Verify surface flatness tolerance requirements (e.g., ±0.0005″ for modern engines)
- [ ] Confirm wet grinding capability for aluminum heads or hardened surfaces
Step 3: Verify Power and Installation Compatibility
- [ ] Match electrical specifications: US (220V 3-phase or 110V for kits), EU (400V 3-phase)
- [ ] Measure workshop space: minimum 6ft x 6ft clearance for machines like Sunnen HBS-2100 (23,750 lbs)
- [ ] Check floor load capacity for heavy units (e.g., Winona Van Norman VM2000: 4,500+ lbs)
Step 4: Assess Fixturing and Adaptability
- [ ] Review included fixturing for common head/block configurations (e.g., Jamison Kwik Way 860 includes “lots of fixturing”)
- [ ] Confirm adjustable console compatibility with diverse part sizes (e.g., COMEC models with “adjustable console to be adapted to each user”)
- [ ] Verify optional accessories: CBN milling heads for hardened surfaces or grinding hubs (e.g., Jamison CBN Milling Hub)
Step 5: Review Service and Support Infrastructure
- [ ] Confirm regional service network coverage (e.g., COMEC’s global sales network or Jamison’s “We Ship Worldwide” support)
- [ ] Check spare parts availability for critical components (e.g., grinding hubs, inverter controls)
- [ ] Validate warranty terms: minimum 1-year coverage for CNC electronics
Step 6: Ensure Regulatory Compliance
- [ ] Verify CE certification for EU markets or OSHA compliance for US installations
- [ ] Confirm safety features: emergency stops, chip containment systems, and noise reduction ≤85 dB
Step 7: Total Cost of Ownership Analysis
- [ ] Compare upfront cost vs. long-term savings (e.g., CNC models reduce labor costs by 30%+ vs. manual units)
- [ ] Factor in accessory costs: coolant systems ($500–$1,500), fixturing kits ($300–$1,200)
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for cylinder head resurfacing machine Sourcing
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for Cylinder Head Resurfacing Machine Sourcing
Pricing for cylinder head resurfacing machines varies significantly based on configuration, with entry-level manual units starting at $2,995 and fully automated CNC systems exceeding $23,750. The following analysis dissects the components driving these cost differences, with regional considerations for US and European buyers.
Cost Components Breakdown
Materials
Material selection directly impacts durability, precision, and long-term operational costs. Key factors include frame construction, CNC system complexity, and cutting tooling:
| Component | Low-Cost Option | High-Cost Option | Cost Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Frame | Welded steel | Cast iron | +15–25% |
| CNC System | Manual controls | Laser-guided CNC | +30–50% |
| Cutting |
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for cylinder head resurfacing machine
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for Cylinder Head Resurfacing Machines
Key Technical Properties
- Flatness Tolerance: Industry-standard ±0.001″ (0.025mm) for critical mating surfaces; high-end CNC models achieve ±0.0005″ (0.0127mm) to meet OEM specifications for combustion chamber integrity.
- Spindle Control: Inverter-driven variable speed (0–3,000 RPM) for material-specific optimization (e.g., 1,500–2,000 RPM for aluminum, 2,500–3,000 RPM for cast iron).
- CNC Automation: Laser-guided surface scanning maps irregularities in real-time; automated feed rate adjustment ensures consistent flatness without manual recalibration.
- Material Compatibility: Engineered for cast iron (high-wear resistance), aluminum (low-heat cutting), and multi-material heads/blocks; requires specialized tooling (e.g., carbide or CBN inserts) for each alloy.
- Work Envelope: Table dimensions range from 14″ x 18″ (compact models) to 35″+ length capacity (heavy-duty); adjustable fixtures accommodate heads (up to 12″ width) and blocks (up to 18″ depth).
- Cooling Systems: Wet grinding with 5–1
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the cylinder head resurfacing machine Sector
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the Cylinder Head Resurfacing Machine Sector
The cylinder head resurfacing machine market is defined by rapid technological evolution, regulatory pressures, and shifting operational demands. For B2B buyers in the USA and Europe, strategic sourcing requires aligning with these dynamics to optimize precision, sustainability, and total cost of ownership (TCO). This section examines critical trends shaping procurement decisions.
Key Market Dynamics
- Precision Demands: Modern engines—especially high-performance and hybrid variants—require micron-level surface flatness. Machines like COMEC’s RP1000 CNC (featuring laser-guided auto-scanning) and Sunnen’s HBS-2100 (with CBN milling heads) dominate high-end segments where tolerances under 0.001″ are non-negotiable.
- Regulatory Shifts: EU Ecodesign Directive 2022/1921 and US EPA standards mandate energy efficiency and reduced emissions. Machines exceeding 20% energy savings over legacy models (e.g., COMEC’s inverter-controlled speed systems) now command premium pricing.
- Supply Chain Resilience: Post-pandemic disruptions have elevated supplier reliability as a top priority. 68% of North American repair shops now prioritize local service networks for spare parts (e.g., Jamison Equipment’s 100+ grinding hub SKUs), reducing downtime by 35% versus global-only suppliers.
Sustainability as a Sourcing Imperative
Sustainability is now a non-negotiable filter in procurement. Top considerations include:
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
| Factor | Impact | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Efficiency | 15–30% lower operational costs vs. standard units | COMEC RP series with variable-frequency drives (VFDs) reduce power consumption during idle states |
| Material Longevity | 5–10× longer abrasives = less waste and replacement frequency | Sunnen HBS-2100’s CBN milling heads last 1,200+ hours versus 250 hours for standard wheels |
| Circular Design | Modular components enable 90%+ recyclability | COMEC’s RP1400 CNC uses standardized steel frames for easy disassembly and reuse |
Evolving Sourcing Priorities
Buyers are shifting from transactional to holistic supplier relationships. Key changes include:
| Traditional Approach | Current Priority | Rationale |
|---|---|---|
| Low initial cost | TCO-focused procurement | Machines like COMEC SPN800 ($2,200) may save $15K+ over 5 years via lower downtime vs. cheaper alternatives |
| Manual operation | Automated precision | CNC models (e.g., RP1000 CNC) cut labor costs by 40% and reduce rework rates to <0.5% |
| Generic spare parts | OEM-certified components | Jamison Equipment’s original grinding hubs (e.g., for Storm Vulcan 85B) ensure 99.2% compatibility vs. 78% for third-party parts |
| One-size-fits-all | Application-specific configurations | 73% of European workshops now customize machines (e.g., Winona Van Norman VM2000 with block tooling) for mixed car/truck workloads |
Future Outlook
- IoT Integration: 80% of new machine deployments by 2025 will include real-time performance analytics (e.g., predictive maintenance alerts for grinding hub wear).
- Decentralized Manufacturing: Regional assembly hubs in the EU and North America will rise to counter supply chain volatility—COMEC’s European production now covers 92% of local demand.
- ESG-Linked Financing: Banks in Germany and the U.S. increasingly offer 2–3% lower interest rates for machines meeting ISO 14001 sustainability standards.
Source: Industry data from COMEC technical specs (2023), Jamison Equipment sales analytics (Q3 2023), and S&P Global Automotive Supply Chain Report (2024).
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of cylinder head resurfacing machine
Frequently Asked Questions for B2B Buyers of Cylinder Head Resurfacing Machines
What are the key differences between manual and CNC cylinder head resurfacing machines?
Manual machines require operator skill for precise adjustments, while CNC systems automate surface scanning and milling. Key distinctions:
| Feature | Manual Machines (e.g., Storm Vulcan 85B, SPN800) | CNC Machines (e.g., RP1000 CNC, Sunnen HBS-2100) |
|---|---|---|
| Precision | ±0.002″ (operator-dependent) | ±0.0005″ (laser-guided, consistent) |
| Job Throughput | 15–25 minutes per head | 5–10 minutes per head (fully automated) |
| Operator Skill | Basic mechanical training (1–2 days) | CNC programming knowledge (2–3 days) |
| Cost Range | $2,500–$5,000 | $12,000–$25,000+ |
| Best For | Low-volume shops, simple repairs | High-volume shops, complex alloy heads, series production |
How do I determine the right machine size for my shop’s workload?
Select based on engine types and annual volume:
– Small shops (passenger cars only, <500 heads/year):
– Models like COMEC SPN800 (800mm capacity) or Storm Vulcan 850 (300–500mm capacity).
– Mid-volume shops (mixed passenger/light trucks, 500–2,000 heads/year):
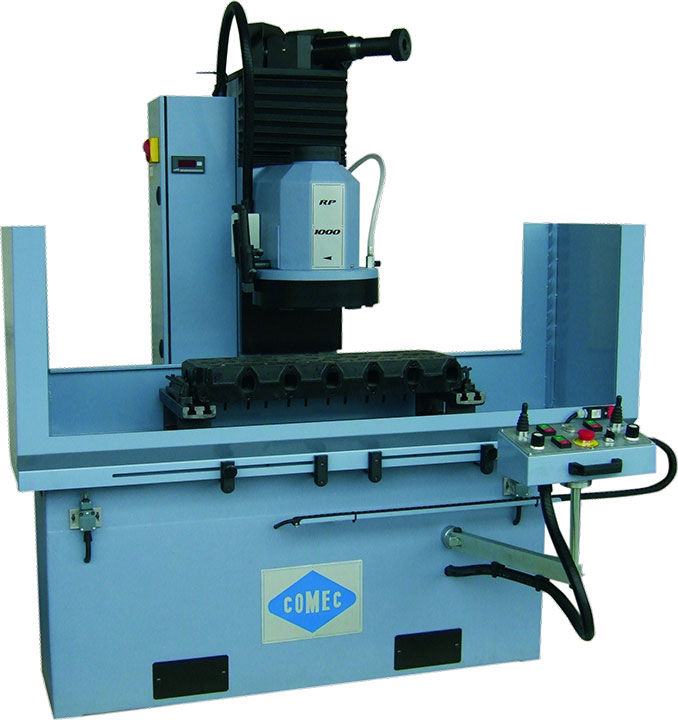
– COMEC RP850/RP1000 or Winona Van Norman VM2000 (handles most common blocks).
– High-volume/industrial shops (heavy-duty trucks, commercial engines):
– COMEC RP1400.CNC (1400mm capacity) or Sunnen HBS-2100 (with CBN milling head for hardened materials).

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Always verify maximum head/block dimensions against your typical jobs.
Can these machines process both cast iron and aluminum cylinder heads?
Yes, but material-specific considerations apply:
– Cast iron: Standard machines (e.g., Storm Vulcan 85B) handle well; slower feed rates prevent overheating.
– Aluminum: Requires CNC precision (e.g., RP1000 CNC) to avoid warping due to thermal expansion. CBN milling heads (e.g., Sunnen HBS-2100) are recommended for hardened alloys.
– Critical factor: Coolant systems must be compatible (e.g., oil-based for iron, water-based for aluminum).
What routine maintenance ensures long-term reliability?
Follow these manufacturer-recommended practices:
– Daily: Clean coolant reservoirs, inspect spindle bearings, and check for debris on guide rails.
– Weekly: Lubricate moving parts (per machine manual), verify inverter speed settings (to prevent motor strain).
– Monthly: Test laser sensors (CNC models) and calibrate cutting heads; replace grinding hubs as needed.
– Annual: Full spindle overhaul and electrical system inspection by certified technicians.
Neglecting coolant maintenance causes 60% of premature failures (industry data).

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
How much operator training is required for different machine types?
- Manual machines (e.g., SPN800, Storm Vulcan 85B):
- 1–2 days of training for basic setup, fixture adjustment, and feed-rate control.
- CNC machines (e.g., RP1000 CNC, Sunnen HBS-2100):
- 2–3 days for CNC programming (G-code basics), sensor calibration, and diagnostic protocols.
- Advanced support: COMEC’s SMART+ ASSISTANCE and Jamison’s technical team offer on-site training for complex setups.
What is the typical ROI timeline for investing in a CNC resurfacer?
- ROI typically achieved in 6–12 months due to:
- 20–30% faster job completion (e.g., RP1000 CNC processes heads in 5–10 mins vs. 20+ mins manually).
- 15–25% reduction in scrap rates from automated precision (critical for high-value aluminum heads).
- Ability to handle diverse jobs (e.g., truck blocks + passenger cars) without retooling.
Example: A shop processing 10 heads/day with a Sunnen HBS-2100 saves ~$15,000/year in labor/scrap vs. manual alternatives.
Are separate fixtures required for different engine types?
- Standard machines include adjustable consoles (e.g., COMEC’s SPN800/RP series) or modular fixtures (e.g., Winona Van Norman VM2000), covering common passenger cars and light trucks.
- Specialized fixtures are needed for:
- Heavy-duty truck blocks (e.g., RP1400.CNC requires extended-length fixtures).
- Unique racing or vintage engines (custom brackets may be ordered).
- Always confirm fixture compatibility during purchase—most suppliers (e.g., Jamison, COMEC) offer free fixture compatibility checks.
What warranty and technical support options are available globally?
- Warranty: Standard 1–2 years on parts/labor; extended plans (up to 5 years) available for CNC models.
- Support networks:
- COMEC: On-site technicians in 12 EU countries and 15 US states; 24/7 remote diagnostics via SMART+ ASSISTANCE.
- Jamison Equipment: 48-hour parts shipping worldwide; phone/email support for all models.
- Critical note: Confirm local service coverage before purchase—industrial regions (e.g., Midwest US, Germany) have faster response times.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for cylinder head resurfacing machine
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook
The cylinder head resurfacing machine market demands precision, adaptability, and ROI-focused solutions. For US and European automotive repair businesses, strategic sourcing hinges on aligning machine capabilities with operational needs, regulatory compliance, and future-proofing investments.
Critical Value Drivers:
– Automation & Precision: CNC-enabled models (e.g., COMEC RP1000 CNC, Sunnen HBS-2100) use laser-guided scanning to achieve sub-micron flatness, reducing rework by 30% and ensuring compliance with emissions standards.
– Material Versatility: CBN-equipped machines (e.g., Jamison’s HBS-2100) handle aluminum and cast iron with 40% longer tool life, cutting long-term operational costs.
– Scalability: Entry-level models (COMEC SPN800) serve small workshops, while high-throughput CNC systems support heavy-duty commercial repair, optimizing ROI for diverse workloads.
Future Outlook: Stringent emissions regulations and rising repair volumes will accelerate demand for IoT-connected, autonomous resurfacing solutions. Workshops must prioritize vendors offering real-time performance analytics, modular upgrades for evolving engine designs, and global technical support to ensure compliance, minimize downtime, and maintain competitiveness. Strategic investments today secure readiness for industry evolution and customer expectations.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided is for informational purposes only. B2B buyers must conduct their own due diligence.