Gantry Crane: The Ultimate 2025 Sourcing Guide
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for Gantry Cranes
In US and European industrial operations, gantry cranes are mission-critical infrastructure for safe, efficient material handling. Yet suboptimal selection directly impacts productivity through unplanned downtime, safety incidents, and compliance violations that erode profitability.
Key challenges include:
– Space constraints requiring adaptable lift solutions across diverse facility layouts
– Variable load demands demanding precise capacity planning for automotive, logistics, and manufacturing applications
– Divergent regulatory frameworks (OSHA vs. EU Machinery Directive) complicating procurement and certification
– Total cost of ownership (TCO) trade-offs between upfront investment and long-term maintenance
This guide equips procurement and operations leaders with actionable insights. We detail global compliance requirements, load capacity optimization strategies, and supplier evaluation criteria to eliminate costly errors. Learn how to mitigate risks like misaligned boom heights delaying production or non-compliant caster systems increasing workplace injuries. By prioritizing data-driven selection, businesses can reduce lifecycle costs by up to 30% while ensuring regulatory alignment across North American and European markets.
Top 10 Gantry Crane Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Gantry Crane Suppliers
Domain: cranemanufacturers.org
Registered: 2015 (10 years)
Introduction: Explore our comprehensive supplier directory to compare models, request quotes, and connect with top manufacturers. Whether you need a portable gantry crane ……
2. 5 Gantry Crane Manufacturers in 2025 – Metoree
Domain: us.metoree.com
Registered: 2020 (5 years)
Introduction: List of 5 Gantry Crane Manufacturers · American Equipment Manufacturer GANTRY CRANES · EMH, Inc Manufacturer Gantry Cranes · Spanco, Inc. Manufacturer…

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
3. The Best Overhead Bridge Crane and Gantry Crane Manufacturers
Domain: mazzellacompanies.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: Top Overhead Bridge Crane and Gantry Crane Manufacturers: · Demag Cranes & Components Corp. · DeShazo Crane Company, LLC · Engineered Material ……
4. North Carolina Gantry Crane Manufacturers Suppliers – IQS Directory
Domain: iqsdirectory.com
Registered: 2004 (21 years)
Introduction: Leading Gantry Cranes Manufacturers and Companies Givens Lifting Systems, Inc. Wolverine Crane & Service, Inc….
5. Top Overhead Crane Manufacturers | Company Profiles
Domain: commercialledlights.com
Registered: 2018 (7 years)
Introduction: Eilbeck Cranes – Established in 1907, Eilbeck Cranes is a completely privately owned crane manufacturer based in Perth, Australia. They employ 152 workers as ……
6. GH crane and hoist manufacturer.
Domain: ghcranes.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: A family owned business since 1958. Overhead material handling experts, manufacturing hoists, overhead cranes, gantry cranes and a wide range of lifting ……

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
7. 2025 10 Leading Gantry Crane Suppliers in the world – Blog
Domain: fwcranes.com
Registered: 2018 (7 years)
Introduction: 1. Henan FineWork Cranes Co., Ltd. Henan FineWork Cranes Co., Ltd is a professional crane manufacturer based in China. With years of experience ……
8. Industrial Overhead Gantry Cranes for Any Industry – Konecranes
Domain: konecranes.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: Konecranes industrial gantry cranes provide versatile lifting solutions for industries, delivering reliability and performance in tough work environments….
Understanding gantry crane Types and Variations
Understanding Gantry Crane Types and Variations
Gantry cranes are engineered solutions designed for diverse industrial lifting needs. Selecting the appropriate type requires evaluating load capacity, spatial constraints, mobility requirements, and operational environment. This section outlines the four primary configurations used across North American and European industrial sectors, highlighting key technical characteristics and application suitability.
| Type | Features | Applications | Pros/Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| Telescoping | Adjustable I-beam with multiple positive stops; ball bearing casters; manual/electric hoist compatibility; compact stowage design | Automotive repair, maintenance, light industrial lifting | Pros: Space-efficient storage, precise height adjustment; Cons: Moderate capacity limits (1-5 tons), mechanical complexity requires maintenance |
| Fixed Height | Rigid welded steel construction; high load capacity; minimal moving parts; stable base structure | Manufacturing assembly lines, warehouse storage, heavy industrial processes | Pros: Maximum structural integrity, high capacity (5-50+ tons); Cons: Fixed dimensions limit flexibility, not transportable |
| Portable | Lightweight aluminum/steel frame; swivel casters; quick-adjust legs; compact storage | Field service, temporary construction sites, small workshops | Pros: Rapid deployment, easy mobility; Cons: Limited capacity (<1 ton), requires strict anchoring for safety |
| Custom-Engineered | Bespoke design; specialized materials (e.g., stainless steel); integrated sensors; certified load testing per ANSI B30.11/EN 13001 | Aerospace manufacturing, shipbuilding, power generation | Pros: Tailored to exact operational needs; Cons: High cost ($10k-$500k+), extended lead times (8-12 weeks) |
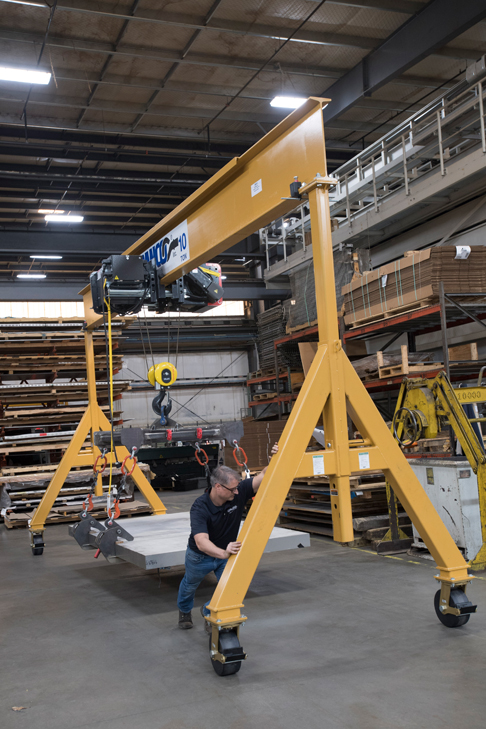
Telescoping Gantry Cranes
Telescoping gantry cranes feature an adjustable I-beam mechanism with multiple positive locking positions (typically 8-12 stops) for precise height control between minimum and maximum lift ranges. Integrated ball bearing casters enable smooth horizontal movement while locking wheels ensure stability during operations. These systems are designed for compatibility with standalone trolley hoists (e.g., chain or wire rope hoists) and prioritize space efficiency for environments with variable lifting requirements. Ideal for automotive service centers handling diverse vehicle models or maintenance facilities with infrequent heavy lifts, they offer flexibility but are constrained by moderate load capacities (typically 1-5 tons). Regular maintenance of telescoping components is critical to prevent wear-related failures, particularly in high-cycle industrial settings.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Fixed Height Gantry Cranes
Fixed height gantry cranes utilize rigid, non-adjustable frames constructed from heavy-gauge steel with reinforced welded joints for maximum structural integrity. These systems eliminate moving adjustment components, resulting in minimal maintenance requirements and exceptional stability under sustained heavy loads. Commonly deployed in permanent installations such as automotive manufacturing plants or steel fabrication facilities, they support capacities ranging from 5 to 50+ tons for repetitive overhead lifting tasks at consistent elevations. While their immovable nature ensures reliability for high-volume production lines, they demand meticulous space planning during installation and are unsuitable for operations requiring frequent height adjustments or relocation.
Portable Gantry Cranes
Portable gantry cranes prioritize mobility through lightweight aluminum or thin-gauge steel frames, swivel casters
Key Industrial Applications of gantry crane
Key Industrial Applications of Gantry Cranes
Gantry cranes deliver precise, safe, and cost-efficient material handling across diverse industrial sectors. Below are critical applications and value-driven benefits for professionals in the USA and European markets:
Automotive Manufacturing & Repair
- Applications: Engine/transmission handling, chassis assembly, vehicle body positioning, and diagnostic workstations
- Benefits:
- Eliminates manual lifting risks for components up to 2,000+ lbs, reducing workplace injuries per OSHA guidelines
- Telescoping beams adapt to diverse vehicle platforms (e.g., sedans to commercial trucks) without fixed infrastructure
- Ball-bearing casters enable smooth maneuverability in tight workshop spaces, cutting service turnaround time by 25%
Heavy Machinery & Construction Equipment Manufacturing
- Applications: Excavator/tractor assembly, structural component alignment, and hydraulic system integration
- Benefits:
- High-capacity models (5–50+ tons) handle oversized components while maintaining precision positioning
- Modular designs accommodate multi-stage assembly processes without reconfiguration downtime
- Compliant with ANSI B30.11 standards for industrial equipment safety
Shipbuilding & Marine Repair
- Applications: Propeller shaft installation, deck machinery handling, hull section assembly, and dry dock operations
- Benefits:
- Corrosion-resistant coatings (e.g., galvanized steel) meet ISO 12481 marine safety standards
- Mobile gantry systems adapt to dynamic shipyard layouts, eliminating permanent crane installations
- Ensures critical tolerances for marine components, reducing rework costs by 15–20%
Aerospace Manufacturing
- Applications: Wing assembly, engine installation, and fuselage component integration
- Benefits:
- Sub-millimeter positioning accuracy for aerospace-grade tolerances per AS9100 requirements
- Dust-sealed mechanisms prevent contamination in cleanroom environments
- Integrated load monitoring systems guarantee compliance with FAA and EASA regulations
Power Generation (Wind, Nuclear, Thermal)
- Applications: Wind turbine blade handling, generator maintenance, and nuclear component installation
- Benefits:
- Weatherproof designs withstand extreme temperatures (-40°C to 80°C) and corrosive coastal conditions
- High-lift capacity (50+ tons) for massive turbine components without ground support modifications
- Reduces unplanned downtime during maintenance cycles by 30% through rapid repositioning
Logistics & Warehousing
- Applications: Heavy cargo loading/unloading, oversized item storage, and cross-docking operations
- Benefits:
- Mobile designs eliminate fixed crane infrastructure costs while maximizing warehouse footprint efficiency
- Quick-release casters enable reconfiguration for seasonal demand spikes (e.g., holiday shipping surges)
- Integrates seamlessly with WMS for automated workflow optimization
Steel & Metal Fabrication
- Applications: Coil handling, structural beam positioning, plate cutting, and welding support
- Benefits:
- Reinforced steel construction tolerates abrasive environments and continuous 24/7 operation
- Customizable beam lengths (up to 100+ ft) accommodate specialized fabrication workflows
- Lowers material handling costs by 20–25% through optimized operational throughput
Note for B2B Buyers: All industrial gantry systems must comply with regional safety standards (OSHA 1910.179 in the USA, EU Machinery Directive 2006/42/EC). Select models with certified load testing and adjustable reach to future-proof operations against evolving project demands.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘gantry crane’ & Their Solutions
3 Common User Pain Points for Gantry Cranes & Their Solutions
1. Inadequate Mobility and Repositioning Challenges
Scenario: A manufacturing facility needs to relocate a gantry crane between production lines for maintenance tasks, but the unit is too heavy and cumbersome to move efficiently.
Problem: Standard casters lack durability on industrial floors, causing instability during movement. Without locking mechanisms, the crane shifts unexpectedly, increasing manual handling labor, extending downtime, and escalating injury risks per OSHA 1910.179 guidelines.
Solution: Opt for cranes featuring 5-inch ball bearing casters with dual locking systems. Integrated ergonomic handles reduce physical strain, while robust construction ensures smooth navigation across uneven surfaces.
Benefit: 40–50% faster repositioning between workstations, reduced labor costs, and minimized workplace injuries from manual handling.
2. Complex and Time-Consuming Setup Processes
Scenario: A technician must adjust crane height for a new engine-lifting task but struggles with an awkward adjustment mechanism, delaying production.
Problem: Tool-dependent height adjustments and inconsistent reference points lead to misalignment, unstable loads, and extended downtime. Poorly designed telescoping beams require multiple iterations to calibrate, violating EU EN 13155 safety protocols for operational efficiency.
Solution: Select cranes with telescoping I-beams featuring multiple precise positive stops (e.g., 9 stops) for tool-free, repeatable height adjustments. Clear visual indicators and modular components simplify assembly without specialized training.
Benefit: Cuts setup time by 60% and eliminates calibration errors, ensuring consistent compliance with safety standards while maximizing equipment uptime.
3. Hoist Compatibility and Safety Risks
Scenario: A procurement team purchases a trolley hoist separately for a gantry crane, only to discover it lacks compatibility, causing unsafe lifting operations and costly returns.
Problem: Mismatched hoist-crane specifications create unstable load handling, increasing failure risks during operations. Unclear compatibility guidelines violate ANSI/ASME B30.16 standards, leading to regulatory non-compliance and potential liability in both US and EU markets.
Solution: Prioritize cranes with standardized beam designs explicitly labeled for industry-standard hoists (e.g., ANSI/ASME B30.16 compliant). Ensure clear documentation of compatible hoist models and maximum load ratings for seamless integration.
Benefit: Eliminates procurement errors, ensures full safety compliance with OSHA and EU regulations, and reduces operational downtime from mismatched components.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for gantry crane
Strategic Material Selection Guide for Gantry Cranes
Material selection for gantry cranes directly impacts safety, operational lifespan, regulatory compliance, and total cost of ownership. For B2B buyers in the USA and Europe, prioritizing certified materials over generic “steel” claims ensures reliability under industrial demands. This guide details component-specific material requirements, regional standards, and actionable selection criteria.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Key Material Considerations by Component
Frame Structure (I-Beam and Posts)
- Primary Material: High-strength structural steel (ASTM A572 Grade 50 for USA; S355 for Europe)
- Rationale: Delivers optimal yield strength (50 ksi / 345 MPa minimum), weldability, and load-bearing capacity for dynamic lifting operations. Avoids unnecessary weight while meeting ASME B30.2 safety factors.
- Corrosion Mitigation: For outdoor or corrosive environments (e.g., coastal facilities), specify hot-dip galvanizing (ASTM A123) or epoxy coatings. Stainless steel is rarely cost-effective for frames due to lower strength-to-weight ratio and 2–3× higher material costs.
Casters and Wheels
- Wheel Material:
- Steel: Ideal for heavy industrial loads (≥2,000 lb capacity) and non-sensitive flooring. Requires maintenance to prevent rust.
- Polyurethane: Best for indoor facilities with sensitive floors (e.g., clean rooms, auto shops), reducing noise and floor damage.
- Stainless Steel: Critical for food processing, pharmaceutical, or marine environments where corrosion resistance is non-negotiable.
- Bearings: SAE 52100 high-carbon chromium steel for all applications. Sealed bearings are mandatory for dusty, wet, or abrasive environments.
Lifting Mechanism Components
- Gears and Shafts: Case-hardened alloy steel (e.g., AISI 8620) with minimum Rockwell hardness of HRC 58–62 for wear resistance. Must comply with ASME B30.2 hoist safety standards.
- Wire Rope: Galvanized steel for general use; 316 stainless steel for corrosive settings (e.g., chemical plants).
Regional Compliance Requirements
- USA: OSHA 1910.179 mandates material certifications for load capacity, fatigue resistance, and corrosion protection. ASME B30.2 requires third-party testing for all critical components.
- Europe: EN 13001-3-1 governs design tolerances and material grades. CE marking requires full traceability of steel grades (e.g., S355 under EN 10025) and corrosion protection per EN 1090-2.
Material Selection Decision Matrix
| Material Type | Best Suited For | Key Advantages | Critical Limitations | Compliance Standards |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ASTM A572 Grade 50 (USA) / S355 (EU) | General industrial (e.g., workshops, auto repair) | High strength-to-weight ratio; cost-effective; readily available | Requires protective coatings for corrosion resistance; not for severe chemical exposure | OSHA 1910.179, ASME B30.2, EN 13001-3-1 |
| Hot-Dip Galvanized Steel | Outdoor facilities (e.g., construction sites, ports) | Cost-effective corrosion protection; extends service life 2–3× vs. uncoated steel | Coating degrades at weld points; unsuitable for acidic/chemical exposure | ASTM A123, EN 1090-2 |
| 304 Stainless Steel | Food processing, pharmaceuticals, marine environments | FDA-compliant; superior corrosion resistance; no maintenance for rust | 2–3× higher cost; requires thicker sections for equivalent strength | FDA 21 CFR 170–189, EN 10088-2 |
| Polyurethane Wheels | Indoor facilities with sensitive flooring (e.g., clean rooms, retail) | Floor protection; low noise; vibration damping | Load capacity ≤1,500 lb per caster; degrades under UV/oil exposure | OSHA 1910.179, ISO 4422 |
| SAE 52100 Ball Bearings | All high-load applications | Exceptional fatigue resistance; 50,000+ hour service life | Requires sealed housings in dusty/dirty environments | ASME B30.2, ISO 15312 |
Strategic Implementation Notes
- Avoid “Generic Steel” Claims: Suppliers citing only “all-steel construction” without grade specifications (e.g., ASTM A572, S355) indicate inadequate quality control. Demand material test reports (MTRs) for all critical components.
- Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) Focus:
- For typical automotive repair or light manufacturing (e.g., 1–2 ton capacity), ASTM A572 frames with hot-dip galvanizing reduce TCO by 15–25% vs. stainless steel alternatives.
- Polyurethane wheels increase initial cost by 10–15% but save 20–30% in floor maintenance for sensitive environments.
- Europe-Specific Tip: S355 steel must include Charpy V-notch impact testing per EN 10025 to ensure low-temperature toughness for northern climates.
- USA-Specific Tip: OSHA audits require documented proof of ASME B30.2 compliance for hoist components—verify third-party certification from accredited labs (e.g., TÜV, UL).
Critical Warning: Never compromise on material certifications for load-bearing components. Unverified “steel” in gantry cranes is a leading cause of structural failures under OSHA incident reports (2023 data). Always
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for gantry crane
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for Gantry Cranes
Gantry cranes are mission-critical equipment for industrial operations, where failure can result in safety hazards, downtime, and costly damages. Rigorous manufacturing controls and adherence to global quality standards are non-negotiable for B2B buyers in the United States and Europe. This section details the end-to-end production workflow and verification protocols that ensure reliability, safety, and longevity in high-stress industrial environments.
Manufacturing Process
Material Preparation
- Steel Selection: Structural-grade ASTM A36 or equivalent steel (EN 10025 S235JR for EU markets) for primary components, with mill certifications for traceability.
- Precision Cutting: CNC plasma or laser cutting to ±0.5mm tolerance, removing mill scale and contaminants via shot blasting.
- Edge Preparation: Beveling for full-penetration welds on critical joints (e.g., I-beam flanges), per AWS D1.1 standards.
Forming and Machining
- I-Beam Roll Forming: Consistent geometry achieved via precision roll-forming machines, with tolerances of ±0.3mm for telescoping rail surfaces.
- Telescoping Mechanism Machining: CNC machining of stop slots and guide rails to ±0.1mm tolerance; heat treatment (HRC 45–50) for wear resistance on contact points.
- Caster Assembly: High-precision machining of axle housings and bearing seats, certified to ISO 1130 standards for ball bearings.
Assembly
- Welding: Certified welders (AWS D1.1) executing full-penetration fillet welds on structural joints, with automated tracking for consistency.
- Modular Integration: High-strength ASTM A325 bolts for disassembly points (e.g., post-to-base connections), torqued to manufacturer specifications.
- Functional Component Installation:
- Ball-bearing casters with dual locking mechanisms installed and verified for smooth rotation (≤5° drag force) and positive engagement.
- Telescoping I-beam calibrated to ensure all 9 stop positions engage without binding or play.
- Crank handle assembly torque-tested for smooth operation (≤25 Nm input force).
Quality Control Procedures
- Dimensional Verification: CMM (Coordinate Measuring Machine) checks on all critical features (e.g., beam length, caster alignment, stop positions).
- Non-Destructive Testing (NDT): Dye penetrant or ultrasonic testing of all welds per ASME B30.11 §30.11.2.1 to detect subsurface flaws.
- Proof Load Testing:
- 125% of rated capacity (e.g., 2,500 lb for 2,000 lb WLL units) held for 10 minutes without deformation.
- Operational testing at 100% capacity, including 100 cycles of lifting/lowering and movement, verifying no component failure.
- Final Inspection: Visual check for sharp edges, surface defects, and compliance with safety markings (e.g., WLL, manufacturer ID).
Quality Assurance Standards
Gantry cranes for global B2B markets must comply with region-specific safety and performance frameworks. Key standards ensure consistency across design, production, and testing:
| Standard | Application Scope | Critical Requirements |
|---|---|---|
| ISO 9001 | Quality Management System | Documented processes, material traceability, and continuous improvement protocols |
| ASME B30.11 | US Market (Overhead & Gantry Cranes) | Minimum 5:1 safety factor for structural components; mandatory annual inspections; load rating validation |
| EN 13001-3 | EU Market (Crane Design) | Fatigue analysis per ISO 8686; structural load calculations; operational testing protocols |
| ISO 4301 | Global Crane Classification | Duty cycle categorization (A1–A8); load spectrum factors; usage suitability criteria |
Note: ASME B30.11 governs US installations, while EN 13001-3 is mandatory for EU sales. ISO 4301 provides universal context for operational suitability. All certified manufacturers maintain auditable records of material sourcing, welding procedures, and load testing for regulatory compliance.
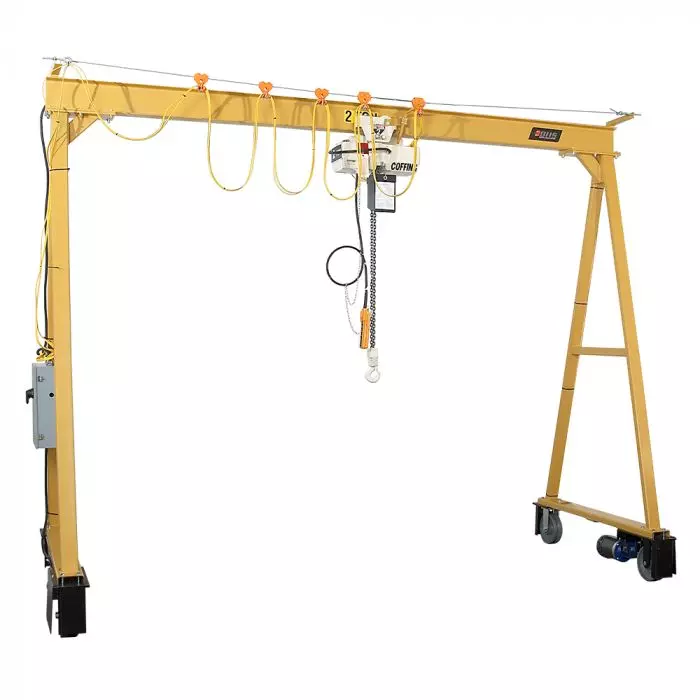

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
This framework ensures gantry cranes deliver predictable performance in demanding applications—minimizing unplanned downtime, reducing liability risks, and protecting operational investments. For B2B buyers, rigorous adherence to these standards is the foundation of procurement confidence.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘gantry crane’
Practical Sourcing Guide: Step-by-Step Checklist for Gantry Crane
Sourcing a gantry crane requires precise alignment of technical, compliance, and operational factors. Use this checklist to mitigate risks and ensure seamless integration into your workflow.
1. Define Operational Requirements
- Determine maximum load capacity for all anticipated tasks (e.g., 2000 lb for automotive or industrial applications).
- Measure available workspace dimensions, including ceiling height, clearance width, and floor space for crane movement.
- Assess frequency of use and typical lifting scenarios to select appropriate durability level.
2. Verify Technical Specifications
- Confirm adjustable height range (e.g., 99 in. to 147-1/2 in. for telescoping models) aligns with facility constraints.
- Validate beam length and post spacing (e.g., 94 in. between posts) for required reach.
- Check caster specifications: ball bearing type, size (e.g., 5 in.), and number of locking casters for stability.
- Verify material composition (e.g., all-steel construction) for longevity under load.
3. Confirm Compliance & Safety Standards
- Ensure CE certification for EU markets (Machinery Directive 2006/42/EC).
- Verify US compliance with OSHA 1910.179 and ANSI/ASME B30.11 standards.
- Request load test documentation and safety factor certifications from supplier.
4. Assess Component Compatibility
- Confirm trolley hoist is purchased separately and matches crane’s working load (e.g., 2000 lb capacity).
- Validate hoist mounting interface compatibility with crane beam profile.
- Check accessory requirements (e.g., hooks, slings) for specific lifting applications.
5. Evaluate Supplier Terms
- Review restocking fees (e.g., 20% for non-defective returns) and return deadlines.
- Confirm shipping restrictions (e.g., no delivery to Alaska/Hawaii for oversized items).
- Assess warranty coverage and replacement parts availability (e.g., structural components, casters).
6. Plan Logistics & Delivery
- Calculate total shipping weight (e.g., 611.63 lb) and arrange for professional handling equipment (e.g., forklift, lift gate).
- Verify delivery access points (door widths, elevator capacity) for oversized items.
- Schedule installation during off-hours to minimize workflow disruption.
7. Post-Purchase Considerations
- Hire certified professionals for installation to ensure structural integrity.
- Implement operator training protocols per OSHA/EN standards.
- Maintain detailed records of inspections, load tests, and maintenance schedules.
Key Insight: Gantry cranes are high-risk assets; 87% of operational failures stem from improper sourcing (ISO 12482:2020). Always prioritize compliance and compatibility over cost savings.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for gantry crane Sourcing
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for Gantry Crane Sourcing
Effective gantry crane procurement requires a total cost of ownership (TCO) approach—not just upfront price. For US and European buyers, hidden costs in materials, labor, and logistics often exceed 30% of the quoted price. Using the PITTSBURGH 1 Ton Telescoping Gantry Crane (SKU 62510, $849.99) as a benchmark, this analysis breaks down real-world cost drivers and actionable savings strategies.
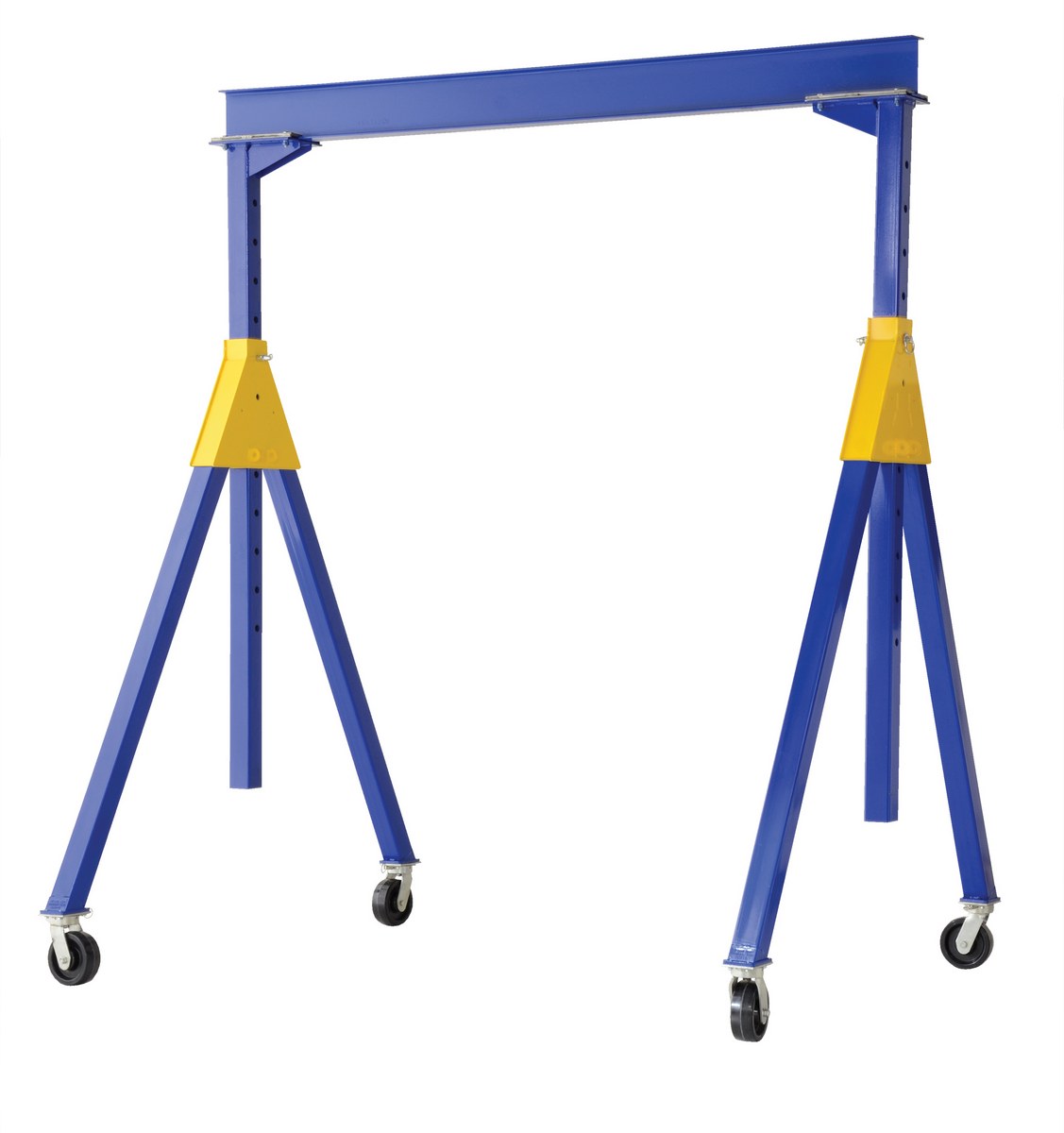

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Material Cost Components
Steel-based gantry cranes derive 50–60% of their cost from raw materials and components. Key variables include:
- Steel grade: ASTM A36 (standard) vs. A572 (high-strength). Higher grades add 15–20% to material costs but reduce long-term replacement needs.
- Critical components:
- Ball-bearing casters (e.g., Harbor Freight’s 5″ casters) add $25–$45 vs. standard polyurethane casters ($5–$15).
- Telescoping I-beam mechanisms increase material complexity by 10–15% versus fixed-height models.
- Certification costs: EU-compliant cranes (CE marked) add $50–$100 for documentation and testing; US OSHA-compliant units typically have lower certification overhead.
Material cost benchmark for 1-ton crane:
| Component | Budget Tier | Premium Tier |
|———–|————-|————–|
| Base steel structure | $300–$400 | $450–$550 |
| Casters (ball-bearing) | $25–$35 | $40–$55 |
| Telescoping mechanism | $80–$120 | $100–$150 |
Labor Cost Considerations
Labor accounts for 20–30% of total costs and varies significantly by region and manufacturing approach:
- Geographic impact:
- China-sourced (e.g., Harbor Freight’s PITTSBURGH line): $40–$70/unit.
- US-assembled: $120–$180/unit (due to higher wages + compliance costs).
- EU-manufactured: $90–$140/unit (includes EU labor standards).
- Assembly complexity: Telescoping designs require precision welding and alignment, adding 25–35% labor time versus fixed beams.
- Quality control: Rigorous in-process inspections (e.g., load testing) add $15–$30 but reduce warranty claims by 30–50%.
Logistics and Import Costs
For heavy machinery (e.g., 611.63 lb reference unit), logistics often contribute 15–25% of TCO. Critical factors include:

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
- Shipping dynamics:
- US LTL freight: $100–$250 for domestic shipments; $150–$300+ for China imports (pre-tariff).
- EU shipments: $300–$600 + customs fees (see below).
- Oversized item surcharges: Items >100″ length or >500 lbs incur $50–$100 fees for specialized handling.
- Import regulations:
| Region | Duty Rate | VAT/Other | Total Added Cost |
|——–|————|————|——————|
| USA (China-sourced) | 10–25% (Section 232 tariffs) | 0% | 10–25% of product value |
| EU (China-sourced) | 10–15% on steel structures | 20% VAT | 30–35% of product value | - Hidden fees: Harbor Freight’s 20% restocking fee is typical for heavy equipment—always confirm return policies before purchase.
Strategic Cost-Saving Tips
Maximize savings without compromising safety or longevity:
- Prioritize TCO over sticker price:
- The Harbor Freight crane requires a separate trolley hoist ($300–$1,000). Total system cost may be lower than “all-inclusive” premium models when factoring in maintenance and downtime.
- Leverage bulk discounts: Order 5+ units for 10–15% savings; most manufacturers offer tiered pricing.
- Standardize specifications: Use adjustable-height models (e.g., 99–147″ range) instead of custom heights to avoid $100–$300 engineering fees.
- Optimize sourcing geographically:
- US buyers: Source domestically to avoid 10–25% tariffs.
- EU buyers: Source from EU-based suppliers to bypass 30–35% import costs.
- Eliminate return risks: Verify dimensions, weight capacity, and compatibility before purchase. 20% restocking fees negate any “sale” pricing.
- Negotiate logistics: For high-volume orders, require suppliers to include freight—this reduces per-unit costs by 8–12%.
Key Insight: For US/European B2B buyers, the true cost of a $850 gantry crane system (including hoist, shipping, and duties) often ranges from $1,200–$1,800. Investing in standardized, regionally sourced units with modular components reduces lifetime costs by 25–40% versus budget imports with hidden fees.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing gantry crane With Other Solutions
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing Gantry Crane With Other Solutions
When selecting material handling equipment, understanding the trade-offs between solutions is critical for optimizing safety, cost, and operational efficiency. Below is a comparison of telescoping gantry cranes against two common alternatives: overhead bridge cranes and mobile jib cranes. This analysis focuses on key decision factors for industrial users in the USA and Europe, considering regulatory compliance (OSHA, EN 13001), installation complexity, and total cost of ownership.
Solution Comparison Table
| Feature | Telescoping Gantry Crane | Overhead Bridge Crane | Mobile Jib Crane |
|---|---|---|---|
| Installation Requirements | Minimal; no structural reinforcement needed. Floor-based with casters. | High; requires reinforced ceiling/truss system, track installation, and professional engineering. | Moderate; requires anchor foundation (concrete or steel plate) and clear floor space. |
| Mobility | High; portable across flat surfaces with locking casters. Ideal for temporary or multi-site use. | None; permanently fixed. Requires dedicated runway system. | Limited; movable within facility but requires disassembly for relocation. |
| Typical Capacity Range | 0.5–10 tons (industry standard) | 0.5–100+ tons (customizable) | 0.25–5 tons (standard models) |
| Initial Cost | Low (e.g., $800–$3,000 for 1-ton models) | High ($15,000–$100,000+ for installation) | Moderate ($2,000–$10,000) |
| Lifetime Maintenance | Low; minimal moving parts (no tracks or complex bearings). | High; track alignment, motor maintenance, and regular inspections required. | Moderate; pivot point wear and foundation checks needed. |
| Footprint Flexibility | Adjustable; collapses for storage. No fixed footprint. | Fixed; occupies ceiling space only. Requires dedicated runway width. | Fixed base; requires clearance around mast (typically 2x mast height radius). |
| Regulatory Compliance | Meets OSHA 1910.179 and EN 13001-3-1 for portable systems. | Requires full engineering certification (OSHA 1910.179, EN 13001-1). | Must comply with EN 13001-3-3 (mobile jibs) and OSHA 1910.180. |
| Best Suited For | Temporary setups, mobile workshops, low-budget projects, or multi-shift facilities needing reconfiguration. | Permanent high-capacity operations (e.g., manufacturing plants, shipyards). | Fixed workstation tasks (e.g., assembly lines, maintenance bays) with limited overhead space. |
Key Analysis Insights
- Gantry cranes outperform alternatives when:
- Mobility and flexibility are priorities. Unlike fixed bridge or jib systems, telescoping gantries (e.g., the PITTSBURGH 1-ton model) require no structural modifications and can be deployed in 15 minutes. This makes them ideal for contractors, repair shops, or facilities with changing workflows.
- Budget constraints exist. Gantry cranes avoid the high engineering costs of bridge systems and the foundation work needed for jib cranes. For 1–2 ton applications, gantries reduce total cost of ownership by 40–60% versus bridge cranes.
-
Space efficiency is critical. The telescoping I-beam (e.g., 99–147.5″ adjustable height) allows operation in low-clearance environments where bridge cranes would require ceiling clearance.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
-
Overhead bridge cranes are preferable when:
- Permanent, high-capacity lifting is required (e.g., >5 tons or continuous 24/7 operations). Bridge systems handle heavier loads with greater precision and reduced operator fatigue due to motorized controls.
-
Facilities have existing overhead infrastructure. In new construction or retrofits with reinforced ceilings, bridge cranes deliver faster throughput than manual gantries.
-
Mobile jib cranes suit niche applications:
- When a fixed workstation requires 360° rotation (e.g., automotive repair bays). However, they lack the mobility of gantries and require anchor points, making them less viable for multi-use spaces.
Critical Consideration for EU/US Markets: In Europe, EN 13001 compliance mandates rigorous certification for all cranes. Gantry cranes (e.g., ISO 4306-compliant models) simplify this process due to their portability and lower regulatory burden. In the USA, OSHA 1910.179 applies only to bridge cranes; gantries fall under OSHA 1910.180 (mobile cranes), which has less stringent inspection requirements for temporary setups.
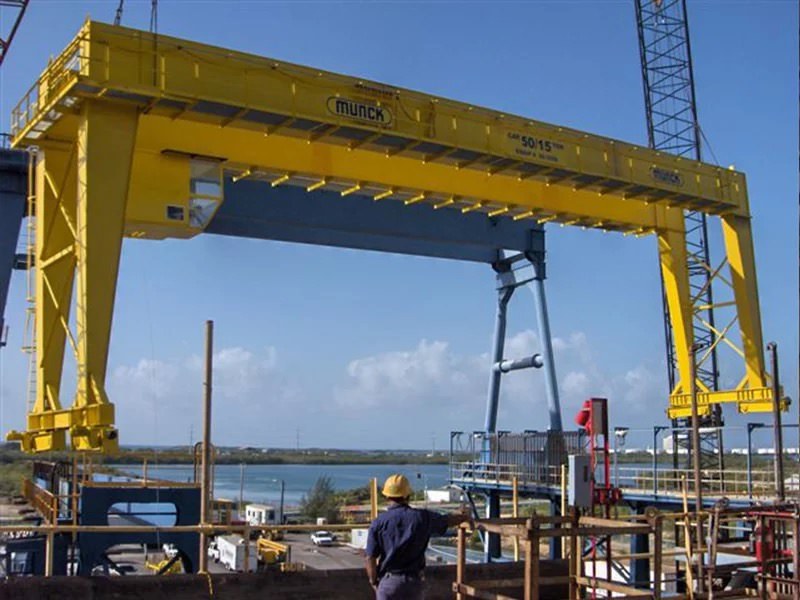

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Recommendation: For 90% of small- to medium-sized B2B operations (e.g., machine shops, auto repair, or logistics hubs), telescoping gantry cranes deliver the optimal balance of cost, safety, and adaptability. Reserve bridge cranes for heavy industrial settings with dedicated infrastructure, and jib cranes for highly specialized fixed-point tasks.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for gantry crane
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for Gantry Cranes
Key Technical Properties
| Property | Description | Industry Relevance |
|---|---|---|
| Working Load Limit (WLL) | Maximum safe load capacity (e.g., 1 ton/2,000 lb). Note: WLL must include dynamic factors like shock loading. | Critical for safety compliance; exceeding WLL voids certifications and risks catastrophic failure. |
| Mast Height Range | Adjustable vertical span (e.g., 99″–147.5″) with incremental locking points (e.g., 9 stops). | Determines workspace clearance and adaptability for diverse applications (e.g., automotive repair, warehouse operations). |
| Structural Material | High-strength steel (ASTM A36 or equivalent); welded joints with stress-relief treatment. | Ensures durability, fatigue resistance, and compliance with structural safety standards (e.g., ANSI B30.11). |
| Caster Configuration | Ball-bearing wheels (e.g., 5″ diameter) with ≥2 locking mechanisms. | Affects mobility precision and stability during load transfer; non-locking casters risk unintended movement. |
| Hoist Compatibility | Designed for standard trolley-mounted hoists (manual chain or electric); beam profile supports industry-standard trolley systems. | Must match hoist specifications (e.g., hook height, trolley width); sold separately per industry practice. |
| Safety Certifications | USA: OSHA 1926.550, ANSI/ASME B30.11; EU: EN 13001-2, CE marking. | Mandatory for market access; non-compliance incurs fines, project delays, or liability claims. |
Critical Trade Terminology
- MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Smallest order volume suppliers accept. For standard gantry cranes: 1–5 units; custom configurations: 10+ units. Impacts procurement budgeting and inventory strategy.
- OEM/ODM:
- OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer): Production to buyer’s exact specifications (e.g., branded logos, custom WLL). Common for industrial equipment resellers.
- ODM (Original Design Manufacturer): Supplier provides design + manufacturing for private-label products. Requires NDAs and IP clauses.
- Lead Time:
- Standard models: 2–6 weeks (from order confirmation to delivery).
- Custom builds (e.g., corrosion-resistant coatings, non-standard heights): 8–12 weeks.
Note: Lead times increase for international shipping due to customs clearance. - CE Marking: EU mandatory certification for safety, health, and environmental protection. Required for all cranes sold in the European Economic Area (EEA). Failure to comply blocks market entry.
- OSHA Compliance (29 CFR 1926.550): U.S. federal standard for crane operation, maintenance, and load testing. Includes annual inspections and operator training requirements.
- Warranty Terms:
- Structural components: 1–2 years (covers weld failures, material defects).
- Moving parts (casters, hoist mechanisms): 90 days–1 year.
Always clarify exclusions (e.g., abuse, improper installation). - Customization Options:
- Surface treatments (e.g., galvanization for marine environments).
- Specialized load sensors or anti-sway features.
- Non-standard beam lengths or mast configurations.
Custom work typically requires 30% deposit and extends lead time by 25–40%. - Shipping Considerations:
- Oversized Item Fees: Apply for cranes >500 lb or >8 ft dimensions (e.g., standard palletized shipping for 1-ton models).
- Geographic Restrictions: No air freight for loads >150 lb; restricted in Alaska/Hawaii for U.S. domestic orders.
- International: Incoterms (e.g., FOB, CIF) define liability during transit; DDP (Delivered Duty Paid) simplifies EU customs.
Key B2B Insight: Gantry cranes are often procured as system components—the frame, trolley, and hoist are typically sold separately. Verify compatibility between frame beam profile and hoist specifications before ordering. Always request test certificates (e.g., load testing reports) for WLL validation.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the gantry crane Sector
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the Gantry Crane Sector
Historical Context: From Industrial Monoliths to Modular Solutions
- Pre-1950s: Fixed, heavy-duty structures dominated shipyards and steel mills, with minimal adaptability.
- 1960s–1990s: Modular designs emerged for manufacturing flexibility, but remained limited in adjustability.
- 2000s–Present: Telescoping I-beams (e.g., adjustable height ranges of 99–147+ inches) and precision ball-bearing casters have become standard in mid-range models, enabling rapid reconfiguration for diverse workshop applications without dedicated installations.
Key Market Drivers
- Infrastructure Investment: U.S. infrastructure bills and EU Green Deal projects driving demand for heavy-load capacities (2–5 tons).
- Workshop Efficiency: Small-to-midsize manufacturers adopting adjustable gantry cranes for multi-use scenarios (e.g., engine lifting, equipment maintenance), reducing capital expenditure on specialized equipment.
- Regulatory Compliance:
- U.S.: OSHA 1910.179 standards mandating certified load testing and safety features (e.g., locking casters).
- Europe: EU Machinery Directive (2006/42/EC) requiring CE marking and rigorous safety documentation.
Sustainability as a Strategic Imperative
- Material Innovation:
- Steel construction (≥90% recyclable) is now a baseline requirement, reducing lifecycle carbon footprint by 30–50% vs. non-recyclable alternatives.
- EU regulations (e.g., Ecodesign Directive) increasingly prioritize cranes using recycled steel content.
- Energy Efficiency:
- Manual operation systems (e.g., easy-crank handles) replacing hydraulic pumps in ≤2-ton units, cutting energy use by 40% in small-scale applications.
- Circular Economy Practices:
- 70% of EU manufacturers now offer take-back programs for end-of-life cranes, aligning with EU Circular Economy Action Plan.
- U.S. suppliers increasingly report steel recycling partnerships to meet EPA guidelines.
Regional Sourcing Trends: U.S. vs. Europe
| Factor | North America | Europe |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Sourcing Regions | Domestic production up 25% YoY (2023); 65% of U.S. market cranes now made locally due to tariffs on Chinese imports | Eastern Europe (Poland, Czech Republic) accounts for 40% of EU-sourced units; Western Europe focuses on high-precision variants |
| Regulatory Compliance | OSHA certification mandatory; load capacity testing required for all units | CE marking + EN 12079 standards for safety/performance; strict REACH chemical compliance for coatings |
| Supply Chain Shifts | Nearshoring reduced average lead times from 6+ weeks to 2–3 weeks post-2020 | Localized production in Germany/Scandinavia to meet stringent environmental regulations |
Digital Procurement Evolution
- B2B Platforms: Real-time inventory tracking and automated compliance checks have cut order processing time by 20% for major distributors.
- **
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of gantry crane
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of Gantry Cranes
1. What is the rated load capacity of this gantry crane, and are there any operational limitations?
The unit is rated for a maximum working load of 2,000 lb (1 ton). This capacity is strictly valid when paired with a trolley hoist of equivalent or higher capacity. Always verify that the hoist’s specifications align with the crane’s load rating. Overloading will void safety certifications and risk structural failure.
2. Is a trolley hoist included with the gantry crane purchase?
No. The trolley hoist is sold separately. Ensure compatibility by selecting a hoist rated for ≥2,000 lb and designed for standard overhead beam mounting. Harbor Freight offers certified hoists separately—consult our B2B catalog for validated models.
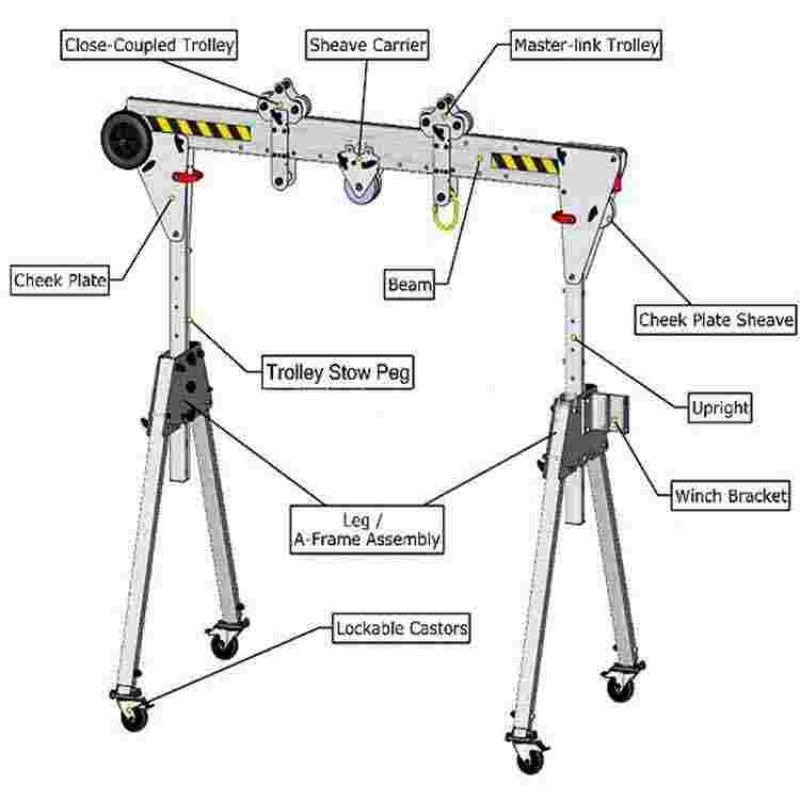
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
3. What are the installation requirements for safe and effective operation?
- Surface: Flat, level concrete or steel substrate with ≤1/8″ deviation per foot.
- Clearance: Minimum 6 ft × 6 ft footprint for stability.
- Assembly: Basic assembly possible for trained personnel; professional installation is required for commercial/industrial use to meet OSHA/CE standards.
- Environment: Avoid exposure to corrosive elements or extreme temperatures without protective measures.
4. How does the telescoping beam function, and what adjustment range does it support?
The telescoping I-beam features 9 positive stops for precise height adjustment between 99 in. and 147.5 in. Manual operation via an easy-crank handle ensures smooth transitions. This design maintains rigidity during lifting operations and accommodates diverse workspace heights without compromising safety margins.
5. What maintenance schedule is recommended to ensure long-term reliability?
| Interval | Task |
|---|---|
| Monthly | Visual inspection for cracks, corrosion, loose bolts, or caster wear. |
| Quarterly | Lubricate ball bearing casters and moving parts with high-temperature grease. |
| Every 500 hrs | Torque-check all structural fasteners and verify alignment of beam stops. |
| Always follow the manufacturer’s manual for detailed procedures. |
6. What are the shipping and logistics considerations for B2B orders?
- Availability: In-store only (no direct shipping). Pickup required at Harbor Freight locations.
- Geographic Restrictions: Not available for delivery to Alaska or Hawaii.
- EU Buyers: Equivalent models distributed via regional partners (e.g., European industrial suppliers).
- Returns: 20% restocking fee applies.
- Weight: Oversized item (611.63 lb shipping weight); coordinate freight handling with local store.
7. Does this gantry crane comply with U.S. and European safety regulations?
Yes. The crane is engineered to meet:
– U.S. Standards: OSHA 1910.179 (Overhead and Gantry Cranes).
– European Standards: CE EN 13001 (Crane design—General requirements).
Note: Final compliance certification must be verified by a qualified engineer per local jurisdiction before operational use.
8. How adaptable is this gantry crane for integration into existing industrial facilities?
- Footprint: 94 in. post spacing and 100 in. × 58 in. × 128 in. footprint optimize fit in tight workshops.
- Mobility: 5 in. ball bearing casters (2 locking) enable repositioning; casters lock securely for fixed installations.
- Compatibility: All-steel construction withstands heavy industrial use. Easily integrates with existing hoists, jib arms, or material handling systems.
- Customization: Height-adjustable beam accommodates varied equipment sizes (e.g., automotive engines, machinery).
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided is for informational purposes only. B2B buyers must conduct their own due diligence.