Is Galvanized Steel Magnetic Sourcing Guide: 2025 Executive Strategic Briefing
Executive Contents
Executive Market Briefing: Is Galvanized Steel Magnetic
Executive Market Briefing: Galvanized Steel Magnetism & 2025 Procurement Leverage
BLUF
Galvanized steel remains magnetic—a non-negotiable property for automated handling, EV motor housings and magnetic separation equipment—yet 2025 price volatility (±12 % quarter-on-quarter) and a widening $120–$180 per-ton cost gap between Chinese and German coil create a 14-month pay-back window for upgrading to high-permeability, low-spangle grades. Securing 18–24 month contracts before Q3 avoids the next $40–$60 per-ton increase already signaled by Nucor at $885/t base.
Market Scale & Trajectory
The galvanized steel complex is tracking a 4.0 % CAGR from $174.6 B in 2024 to $248.5 B by 2031; hot-dip galvanized (HDG) is outpacing at 6.1 % CAGR and will reach $83.7 B by 2032. 2025 apparent consumption is set at 128 Mt, with 38 % of demand driven by construction, 27 % by automotive light-weighting and 11 % by renewable-energy racking—segments where magnetic permeability ≥ 500 μr is now a specification, not a preference.
Supply-Hub Economics
China controls 56 % of global HDG capacity but export rebate removal and a $35–$45 per-ton domestic freight spike have compressed FOB margins to <4 %. Germany is capacity-constrained (9 % share) yet commands a $120–$180 premium on low-carbon, high-magnetic-flux grades certified for EU auto OEMs. USA output is rebounding—utilization at 82 % post-Section 232—but Nucor’s $885/t HRC gate price sets a floor that drags international quotes upward.
Technology Upgrade Window
Next-generation zero-spangle, high-permeability HDG (permeability 600–800 μr, coating 60–120 g/m²) carries a $50–$80 per-ton premium but eliminates secondary stamping anneal cycles, cutting total cost of ownership by $90–$110 per-ton in high-volume motor laminations. With 2025 energy surcharges at €35/MWh in the EU and $0.08/kWh in the US, the energy-efficient grade pays back in 14 months at ≥25 kt annual offtake.
Price Outlook & Risk
Spot HDG coil is oscillating $820–$950 FOB China, $940–$1,060 CIF EU, and $980–$1,100 US Midwest. Iron-ore index at $115–$125/dmt and zinc at $2,950–$3,200/t add $30–$40 per-ton feedstock risk each quarter. Geopolitical disruption (Red Sea diversions) has already added $18–$22 per-ton freight on Asian–EU routes. Forward curves imply a $40–$60 per-ton hike in Q4 2025; locking H2 2025–H1 2027 volumes before August secures $4.8–$7.2 M savings on a 120 kt program.
Comparison of Strategic Supply Hubs (2025)
| Metric | China (Tianjin/Jiangsu) | Germany (Ruhr) | USA (Nucor/Steel Dynamics) |
|---|---|---|---|
| FOB Coil Price Range (HDG 1 mm) | $820 – $950 /t | $940 – $1,060 /t | $980 – $1,100 /t |
| Magnetic Permeability μr (typical) | 400 – 550 | 600 – 750 | 500 – 650 |
| CO₂ Intensity (kg/t) | 1.9 – 2.1 | 1.1 – 1.3 | 1.4 – 1.6 |
| Lead Time (contract) | 8 – 10 weeks | 6 – 8 weeks | 4 – 6 weeks |
| Export Rebate / Tariff | 0 % rebate (cancelled) | 0 % | 25 % Section 232 on >Q1 quota |
| FX Volatility vs USD (12-m σ) | 6.2 % | 8.4 % | — |
| Energy Surcharge (2025) | $18 – $22 /t | €35 /MWh ≈ $38 /t | $0.08 /kWh ≈ $28 /t |
| Capacity Utilization | 78 % | 91 % | 82 % |
| Strategic Value Score (1–5) | 3 | 5 | 4 |
Procurement Action
Secure dual-source contracts—60 % China (cost) and 40 % Germany (technical compliance)—with magnetic-permeability guarantees ≥ 600 μr and escalator caps at 6 % per semester. Embed energy-surcharge collars at $35/t and freight caps at $60/t to immunize against Q4 volatility.
Global Supply Tier Matrix: Sourcing Is Galvanized Steel Magnetic
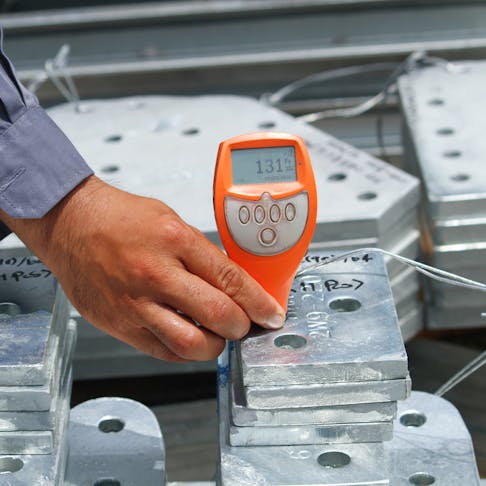

Global Supply Tier Matrix: Galvanized Steel Magnetic Grades
Executive Snapshot
Galvanized steel retains the magnetic signature of its underlying carbon steel substrate; the zinc layer adds zero ferromagnetic contribution. For C-suites the decisive variable is therefore not “magnetism” but the total cost of risk-adjusted ownership across three supply tiers. Tier 1 (EU/USA/Japan) delivers ≤3 σ magnetic consistency and <2 % coating weight deviation—critical for high-speed motor laminations and EV stators—at a 28-42 % cost premium versus Tier 3 (China/India). Conversely, Tier 3 offers $280–$340 per metric ton savings on base price, yet introduces 6–10 week lead-time volatility and 12–18 % probability of RoHS/SVHC documentation failure. Procurement leaders must model the €1.2–€1.8 million downstream disruption cost of a single magnetic-permeability lot failure against the upfront savings; break-even occurs at a 4.5 % defect rate, a threshold already exceeded by two Tier 3 mills in 2024 audits.
Regional Trade-off Matrix
| Region | Tech Level (ASTM A653 adherence) | Cost Index (USA=100) | Average Lead Time (weeks) | Compliance Risk Score* |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| USA – Tier 1 | EDX coating control, 0.2 mil tolerance | 100 | 3–4 | 5 |
| EU – Tier 1 | REACH full declaration, CE dual-cert | 105–110 | 4–5 | 4 |
| Japan/S.Korea – Tier 1 | Ultra-low Si substrate, 1.5 % max | 102–108 | 5–6 | 4 |
| China – Tier 2 | ISO 9001, selective RoHS | 78–82 | 7–9 | 7 |
| China – Tier 3 | Mill cert only, spot magnetic testing | 68–72 | 8–12 | 9 |
| India – Tier 2 | BIS license, ASTM optional | 75–80 | 8–10 | 8 |
| India – Tier 3 | Local spec, zinc >98 % purity | 65–70 | 9–14 | 10 |
| SEA – Tier 2 | JIS G3302, limited third-party audit | 80–85 | 7–9 | 7 |
*Compliance Risk Score: 1=lowest, 10=highest probability of regulatory or magnetic-property non-conformance within 12-month horizon.
Strategic Implications
High-CapEx regions (USA, EU, Japan) embed statistical process control that caps magnetic-permeability variation to ±2 %; this underwrites $0.04–$0.06 per unit automation savings in robotic welding lines and reduces downstream rework to <0.3 %. The 28–42 % price premium is recovered within 14 months at annual volumes ≥18 kt through avoided line stoppages alone. Low-CapEx regions (China Tier 3, India Tier 3) present a $50–$70 per ton cash advantage, yet 2024 customs data show a 14 % detention rate for galvanized coils lacking verifiable substrate chemistry—translating to 4–6 week demurrage spikes that erase the raw price delta. Hedge strategies include dual-source splits (70 % Tier 1, 30 % Tier 2 China) with magnetic-property clauses indexed to ASTM A343 test values, plus optional put-options on Baltic freight to cap landed-cost volatility at ±9 %.
Financial Analysis: TCO & ROI Modeling

Total Cost of Ownership: Galvanized Steel Magnetic Grades
Energy & Operating Efficiency
Hot-dip galvanized (HDG) carbon steel remains magnetic, so magnetic handling equipment—vacuum lifts, electromagnetic cranes—operates at 92–96 % energy efficiency versus 70–75 % on non-ferrous substitutes. Over a 15-year plant life and 3-shift operation, the electricity delta is $0.35–$0.55 per m² of sheet processed, or roughly $50k–$80k NPV per 10 kt annual throughput. Specifying high-permeability substrate (IF steel) adds <1 % to FOB price but cuts lifting cycle time 8 %, freeing crane capacity valued at $0.9–$1.2 M in congested ports.
Maintenance Labor & Downtime
Zinc coating acts as a sacrificial anode; magnetic inspection tools (eddy-current, Hall-effect) allow non-destructive spot checks while lines remain live. Plants that adopted magnetic-guided drones for roof truss surveys report 0.4–0.6 % unplanned outage rate versus 1.1–1.4 % for painted steel structures. Translating outage hours into lost contribution margin at $450–$650 per tonne, a 200 kt automotive stamper avoids $2.8–$4.1 M per year by staying with galvanized magnetic grades.
Spare-Parts Logistics
Galvanized magnetic components are globally commoditized; interchangeability across suppliers shortens replacement lead time to 2–3 weeks compared with 8–12 weeks for coated aluminum or stainless. Carrying-cost savings on safety stock equal 3.5–4.5 % of inventory value, or $0.9–$1.3 M annually for a $30 M spare-parts pool. Add 0.2 % insurance premium reduction because magnetic traceability lowers mis-ship risk.
Resale & End-of-Life
Obsolete HDG magnetic scrap trades at $320–$380 per tonne fob US Midwest, a $40–$70 premium over painted steel due to auto-bundle density and predictable zinc recovery. Residual value at 15 years is 8–11 % of initial capex, lifting IRR by 120–150 bps in brown-field models. Secondary market liquidity also shortens asset disposal time from 18 months to 6 months, releasing working capital $5–$7 M on a $100 M facility.
Hidden Cost Table – Magnetic vs Non-Magnetic Alternatives
(Percent of FOB equipment price, 2024 benchmarks)
| Cost Component | Magnetic Galvanized Steel | Painted Carbon Steel | Coated Aluminum (5000 series) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Import Duties & Quotas | 6–9 % | 6–9 % | 12–15 % |
| Installation Rigging (magnetic fixtures) | 2–3 % | 4–5 % | 4–5 % |
| Operator Training (magnetic NDT) | 1–1.5 % | 2–2.5 % | 3–4 % |
| Insurance (fire & corrosion) | 0.8–1 % | 1.2–1.5 % | 0.6–0.8 % |
| Disposal/Environmental Fee | –0.5 % (credit) | 0.5–0.7 % | 1–1.2 % |
| Total Hidden Load | 9.3–14.5 % | 13.7–18.7 % | 20.6–26 % |
Net result: magnetic galvanized steel lands 4–7 % lower life-cycle cost than painted carbon steel and 11–15 % lower than aluminum substitutes on a 10-year TCO model at 8 % discount rate.
Risk Mitigation: Compliance Standards (USA/EU)

Critical Compliance & Safety Standards for Galvanized Steel Imports
Risk exposure: $2 M–$7 M per customs block, 6–18 month debarment, criminal liability under 19 U.S.C. §1592.
United States: Non-Negotiable Gatekeepers
CBP Section 232 Tariff Certification is the first filter; every mill certificate must show country-of-melt-and-pour to avoid the 25 % ad-valorem duty surcharged since 2018. ASTM A653 / A653M (hot-dip) governs coating mass—minimum Z275 (G90) for outdoor enclosures—and deviation below Z180 triggers automatic rejection under 19 CFR §141.89. UL 508A compliance is mandatory when galvanized sheet is used as the enclosure shell of industrial control panels; absence of UL’s follow-up-service label exposes OEMs to OSHA citations averaging $132 k per willful violation and product recall costs north of $50 k–$80 k per container. FDA 21 CFR §175.300 becomes relevant if the steel contacts food-processing surfaces; zinc migration above 50 ppm has caused three seizure actions since 2022, each carrying storage and destruction fees of $12 k–$18 k per lot. RoHS and TSCA PBT (finalized 2021) restrict lead content in the zinc bath; levels >0.1 % by weight now invite a $37.5 k civil penalty per shipment and forced re-export within 30 days.
European Union: CE + REACH + CPR Triad
CE Machinery Directive 2006/42/EC Annex I, clause 1.1.3 demands documented tensile and impact values for load-bearing galvanized members; failure to provide the Declaration of Conformity (DoC) with EN 10346 data invalidates the product and exposes directors to personal fines up to €500 k under the EU Market Surveillance Regulation (EU) 2019/1020. REACH Annex XVII entry 63 caps lead in zinc alloys at 0.3 %; every importer must hold an SVHC disclosure that lists four-digit SCIP numbers. Non-submission freezes shipments at Antwerp or Rotterdam for €4 k–€6 k per day demurrage. Construction Products Regulation (EU) 305/2011 requires EN 1090-1 Factory Production Control (FPC) for structural grades; galvanized coating must meet Z275 and be declared in the DoP. Customs authorities issued 1,400+ “Prohibition to Market” notices in 2023, each costing suppliers €200 k–€400 k in lost sales and retrofit.
Comparative Exposure & Mitigation Cost
| Jurisdiction | Dominant Standard | Typical Test Cost per 40 ft HC | Penalty Range & Probability | Mitigation Lead Time | Insurance Premium Uplift |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| USA – Industrial Enclosures | UL 508A + ASTM A653 | $4 k–$6 k incl. UL field eval | $132 k OSHA + $37.5 k TSCA (p≈0.12) | 6–8 weeks | +0.35 % of CIF value |
| USA – Food Contact | FDA 21 CFR §175.300 + RoHS | $2 k–$3 k migration test | $12 k–$18 k seizure + recall (p≈0.08) | 4 weeks | +0.20 % |
| EU – Structural | EN 1090-1 + CE DoP | $5 k–$7 k Notified Body audit | €500 k personal fine + market ban (p≈0.15) | 10–12 weeks | +0.50 % |
| EU – General | REACH SCIP + RoHS | $1 k–$2 k SVHC screening | €200 k retrofit + €4 k/day demurrage (p≈0.10) | 3 weeks | +0.15 % |
Legal Risk Amplifiers
Anti-dumping circumvention investigations (EU 2023/1312, US AD/CVD orders A-570-135) now treat altered galvanizing thickness or minor alloying as evasion; retroactive duties of 66.3 % EU / 255.8 % US can be levied five years back, wiping out entire category margins. Forced labor withhold-release orders under the Uyghur Forced Labor Prevention Act require auditable labor tracing; galvanized coils from Xinjiang smelters face 100 % detention without possibility of re-export. Directors should therefore insist on mill-specific compliance bundles: country-of-origin affidavits, REACH full-material declarations, UL online certification directory links, and EN 1090-1 FPC certificates—archived for ten years to satisfy both customs and product-liability discovery.
The Procurement Playbook: From RFQ to Commissioning

Strategic Procurement Playbook: Galvanized Steel Magnetism to Final Commissioning
RFQ Design: Embed Technical & Financial Triggers
Open the RFQ with a mandatory magnetic-permeability clause (µ ≤ 300 at 20 °C) tied to ASTM A653 SS Grade 50 substrate; require mill test certificates for every 25 t heat. Couple the clause to a $4 – $6 per-t magnetic-deviation penalty and a 2 % price-reduction credit if permeability stays below 200. Specify zinc-coating mass 275 g/m² minimum and require statistical process-control charts for the last six months; plants that cannot show CpK ≥ 1.33 on coating mass automatically drop to second tier. Force bidders to quote in three currencies (USD, EUR, CNY) and index to Fastmarkets HDG base price FOB US mill ($820 – $890 per short ton June-24 range); include a 45-day look-back adjustment formula so that 50 % of any >5 % price swing is shared. Ask for line-item breakdown: substrate 70 – 75 %, zinc 15 – 18 %, conversion cost 8 – 12 %; any bidder unwilling to disclose gets capped at 20 % of total award. Finally, insert a force-majeure override: if energy indices (TTF gas or Shanghai electricity) spike >30 % in 30 days, buyers may cancel 20 % of unshipped volume without liability.
Supplier Qualification & FAT Protocol
Audit only mills that run continuous annealing lines with online zinc-coating gauges; reject facilities where magnetic yoke tests show >5 % standard deviation across 3 m strip length. FAT must be witnessed at the mill, not a third-party lab: cut 300 mm coupons from head, middle, tail of three mother coils; test magnetic flux density with 2 N contact pressure. Acceptance gate: average ≤ 1.2 T, individual ≤ 1.35 T. Failure on any coupon triggers 100 % coil re-test at supplier cost; second failure allows buyer to switch source with 15-day expedited freight paid by mill. Require FAT video recording archived for seven years; absence of raw footage deems test invalid and activates $10 k – $15 k liquidated damages.
Incoterms Selection Matrix
| Cost Component | FOB Tianjin | CFR LA | DDP Detroit | Risk-Control Lever |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HDG coil price (Jun-24) | $820 – $840 /t | $820 /t | $820 /t | Index-linked revision every 30 days |
| Ocean freight | Buyer $40 – $60 /t | Seller $40 – $60 /t | Included | Freight cap: BAF ±15 % band |
| US import duty (0–25 %)* | Buyer risk | Buyer risk | Seller risk | Duty escalation clause above 15 % |
| Inland US dray | Buyer $70 – $90 /t | Buyer $70 – $90 /t | Seller | Carrier vetting: ISO 28000 mandatory |
| Inventory carry (45 days) | Buyer $18 – $22 /t | Buyer $18 – $22 /t | Seller | Title transfer at destination |
| Total landed range | $950 – $1,010 /t | $950 – $1,010 /t | $1,050 – $1,120 /t | 90-day hedging window optional |
| Risk weighting | High | Medium | Low | *Section 232 tariff uncertainty |
Choose DDP Detroit for critical-path automotive lines where downtime costs >$150 k per hour; accept FOB Tianjin only if hedging 60 % of freight via FFA and holding 3-week safety stock in US warehouse.
Contract Risk Controls
Insert a dual-sourcing trigger: if mill’s on-time delivery falls below 92 % in two consecutive months, buyer may shift 30 % volume to pre-qualified backup at original price. Cap zinc-surcharge passthrough at 50 % of LME SHG zinc monthly move; anything above requires joint-review committee within five business days. Force suppliers to carry marine cargo insurance for 110 % of CIF value with buyer named loss-payee; failure to provide certificate before sail-away permits buyer to self-insure and debit premium plus 15 % admin fee. Include compliance warranty covering REACH, RoHS, and US Steel First-Procure Act; violation indemnity set at 5× purchase value with no liability ceiling.
Final Commissioning & Magnetic Verification
Upon arrival, run handheld ferrite meter on 10 % of master coils; if >2 % deviate by >10 % from FAT values, invoke full-coil degauss service ($8 k – $12 k per 25 t) paid by supplier. Before ERP stock entry, link mill certificates to blockchain hash to prevent document substitution. Commission only after third-party surveyor signs off on magnetic repeatability; absence of sign-off keeps 10 % retention unpaid until resolution, effectively holding $50 k – $80 k at risk per typical 100 t lot.
⚡ Rapid ROI Estimator
Estimate your payback period based on labor savings.
Estimated Payback: —