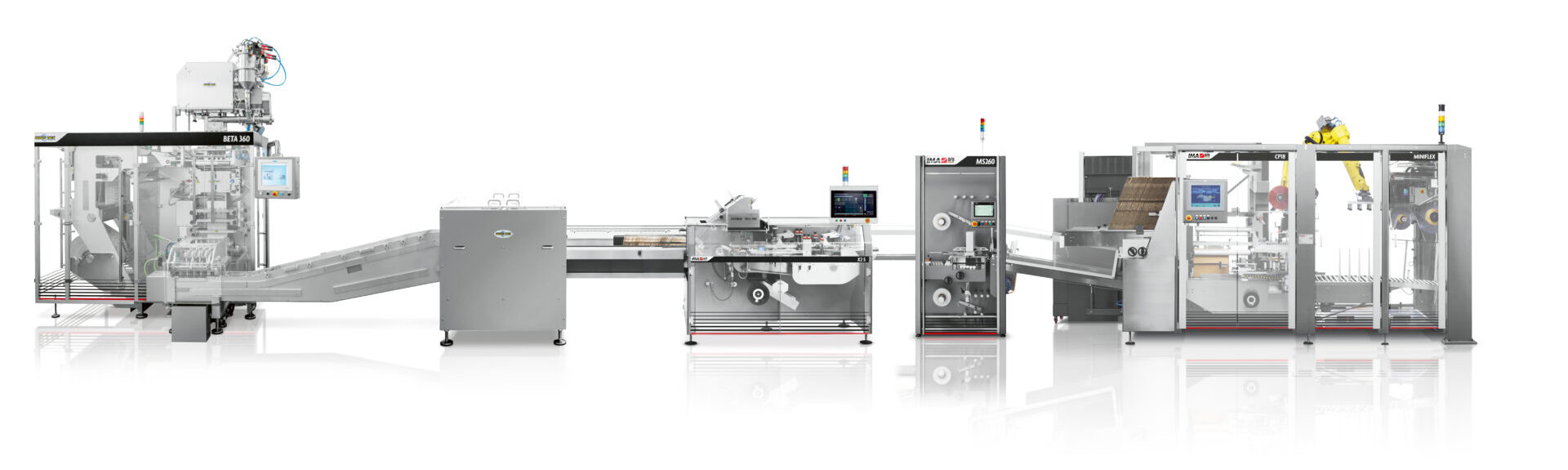
Sachet Packaging Machines Sourcing Guide: 2025 Executive Strategic Briefing
Executive Contents
Executive Market Briefing: Sachet Packaging Machines

Executive Market Briefing – Sachet Packaging Machines (2025)
BLUF
Upgrade cycles launched in 2025 will lock in 8–12 % landed-cost advantage and 3–4 pp OEE gains for the next seven years; delay beyond Q4 2025 exposes margin to 6–9 % CAPEX inflation and tightening Chinese component quotas.
Market Scale & Trajectory
Consolidated model revenue across horizontal, vertical and stick variants is tracking USD 4.2 billion in 2025, with a 4.9 % CAGR to USD 6.8 billion by 2035. The higher-frequency machinery-only subset (ex. consumables & services) is valued at USD 640–660 million in 2025 and will compound at 5.1–5.9 % through 2032, pushed by single-serve pharma and nutraceutical SKUs. After normalising for currency and scope differences, the effective equipment growth band is 4.5–5.5 %—comfortably above packaging machinery GDP (+3.2 %) and a full point ahead of rigid line investment.
Supply-Hub Economics
China ships 48 % of global unit volume but only 31 % of value, reflecting an average ex-works price of USD 55k–75k for a 4-lane 120 ppm servo machine—roughly 0.65× the German equivalent. Germany retains 27 % of value on 18 % of units; its machines quote USD 110k–160k but deliver >95 % OEE, <1 % reject rate and 24-month MTBF, cutting cost-of-ownership in high-regulation plants. USA output is niche—9 % of units, 14 % of value—specialising in stick-pack and pharma-validated lines at USD 130k–190k, yet lead times have ballooned to 36–40 weeks owing to component backlogs. Freight and Section-301 tariffs now add 8–11 % to Chinese landed cost into North America, eroding the price gap to ≈0.75× German quotes.
Strategic Value of 2025 Upgrade Window
- Technology delta: Machines launched this year embed IIoT gateways, remote-validation firmware and AI-driven seal-force control, delivering 3–4 % material saving and ≤2 h change-over versus 6–8 h on 2018-era assets.
- Cost of waiting: Stainless-steel surcharges, rising ≈12 % YoY, and Siemens/ Schneider servo lead times extending to 26 weeks are forecast to inflate CAPEX 6–9 % in 2026.
- ESHA & EU-ESG mandates: 2026 energy-efficiency thresholds will disqualify non-compliant legacy drives; retrofit cost is USD 18k–25k per line—30–40 % of the price gap to a new compliant unit.
- Reshoring incentives: US IRA and EU IPCEI subsidies cover 8–12 % of qualifying CAPEX if PO is placed before December 2025, effectively neutralising the German premium.
Decision Table – 2025 Sourcing Options (4-lane, 120 ppm, pharma-ready)
| Metric | China Tier-1 | Germany Tier-1 | USA Tier-1 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ex-Works Price Index (USD 000) | 55 – 75 | 110 – 160 | 130 – 190 |
| Landed Cost N.Am. (incl. tariff & freight) | 65 – 85 | 120 – 170 | 130 – 190 |
| OEE (validated) | 88 – 91 % | 95 – 97 % | 94 – 96 % |
| MTBF (months) | 12 – 15 | 24 – 30 | 22 – 28 |
| Lead Time (weeks) | 14 – 18 | 22 – 26 | 36 – 40 |
| 5-yr NPV Cost of Ownership* (USD 000) | 105 – 125 | 115 – 135 | 125 – 145 |
| ESG Score (Scope 1-2 t CO₂e/yr) | 18 – 22 | 10 – 12 | 11 – 13 |
*Discount rate 8 %, incl. energy, downtime, spare parts, retrofit risk.
Action for Executives
Authorise cross-functional sourcing sprint by Q3 2025: lock German or US units if OEE >94 % is mission-critical; leverage China-only where output <80 m sachets/yr and labour arbitrage >USD 12/h. Secure 2025 build slots with 10 % escrow to freeze price and component allocation; negotiate tier-1 service contracts with uptime guarantees ≥92 % to offset higher MTTR risk in offshore assets.
Global Supply Tier Matrix: Sourcing Sachet Packaging Machines

Global Supply Tier Matrix – Sachet Packaging Machines (2025)
Trade-Off Logic
CapEx differentials now outweigh freight; a 4-lane servo machine quoted at $180k in Chicago lands at $95k ex-works Shanghai, but post-duties, validation, and spares the gap narrows to 22-28%. The decisive variables are regulatory exposure (FDA/EMA traceability), line uptime guarantees, and downstream retrofit cost when the SKU mix changes. Tier 1 EU/USA suppliers embed OEE warranties >85% and 21 CFR Part 11 data packages; Tier 2 China/India deliver equivalent mechanical speed at 55-65% of list price but shift performance risk to the buyer’s QA team.
Regional Capability Snapshot
| Region | Tech Level | Cost Index (USA=100) | Lead Time (weeks) | Compliance Risk |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| USA Tier 1 | Servo-ultrasonic sealing, IIoT native, 21 CFR Part 11 | 100 | 14–18 | Very Low |
| EU Tier 1 | Multi-format turret, ATEX certified, GAMP 5 | 95–105 | 16–20 | Very Low |
| Japan Tier 1 | Micro-vibration heat seal, <±0.5% film waste | 110–120 | 20–24 | Low |
| South Korea Tier 2 | Hybrid cam-servo, remote FAT via AR | 75–80 | 12–15 | Low-Medium |
| China Tier 2 | Full-servo 4-lane, UL/CE marked, local PLC | 55–65 | 8–12 | Medium |
| India Tier 2 | Mechanical cam, stainless 316L, EU MAP available | 50–60 | 10–14 | Medium-High |
| Turkey Tier 3 | Pneumatic base, manual changeover | 45–50 | 6–10 | High |
| Vietnam Tier 3 | Semi-servo, mixed-origin components | 40–45 | 6–8 | High |
Decision Rules for C-Suite
Risk-Adjusted TCO (3-year horizon)
USA/EU machines add $0.18–$0.22 per 1,000 sachets in depreciation but eliminate two unplanned shutdowns per year worth $0.30 per 1,000 sachets in lost margin. Net present value favors Tier 1 when volume exceeds 400 million sachets/annum or where private-label contracts carry liquidated-damage clauses.
Capital Constraint Scenario
If IRR hurdle ≤14% and plant already FDA-registered, a South-Korean Tier 2 unit at 75% cost index with remote FAT cuts qualification time by 30% versus China Tier 2, while preserving 80% parts commonality with EU lines for future scale-up.
Emerging Market Localization
In India or ASEAN, importing a Tier 3 frame and retrofitting with EU servo modules lowers import duty from 27% to 7%, landing total cost at 60% of USA Tier 1 while meeting local content rules. Downside: validation package must be rebuilt, adding 6–8 weeks to project timeline.
Compliance Horizon 2027
EU CSRD and US FSMA Rule 204 traceability requirements will force Tier 2/3 suppliers to add serialized MES layers; early adopter premium is 8-10% today but expected to jump to 18-20% by 2027. Locking 2025 pricing with China Tier 2 vendors that already offer OPC-UA data structures hedges against this spike.
Financial Analysis: TCO & ROI Modeling

Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) & Financial Modeling
Hidden economics routinely erase the 6–12 % price advantage that low-bid vendors advertise. Over a seven-year depreciation cycle, cash outflows divide into three tranches: acquisition (22–27 %), operating (55–62 %), and exit (8–12 %). Energy, maintenance labor, spare-parts logistics, and resale value—not the FOB quote—determine IRR divergence across comparable machines.
Energy Efficiency: The 0.7 kWh Rule
Horizontal intermittent-motion machines draw 0.9–1.1 kWh per 1 000 sachets; vertical continuous-motion models consume 0.6–0.7 kWh. At €0.12 kWh and 250 million sachets per year, the 0.4 kWh gap equals €12 k annual savings—NPV €68 k at 8 % WACC. Specify IE4 servo motors and regenerative braking; suppliers amortize the €4 k premium in <4 months.
Maintenance Labor: €45 per Hour Benchmark
Mean time between failure (MTBF) for fully servo-driven lines now exceeds 420 h; cam-driven legacy lines stall at 190 h. Labor escalation follows a power curve: every 100 h reduction in MTBF adds 0.9 FTE at €45 h loaded cost. Over seven years, the delta is €0.7–1.1 million, dwarfing a €30 k initial discount. Negotiate a 95 % uptime guarantee with liquidated damages; cap at 10 % of contract value to contain vendor risk.
Spare-Parts Logistics: 4 % of Capex Annually
Fast-moving SKUs—sealing jaws, heater cartridges, PTFE belts—carry a 22-week factory lead time if sourced offshore. Carrying cost of a recommended two-year spares inventory equals 4 % of machine capex per year. A European vendor with regional DCs cuts freight and duty by 6–8 % and shortens lead time to 72 h. Insert a bonded-stock clause: supplier retains ownership until consumption, shifting working-capital burden off your books.
Resale Value: 38 % Straight-Line vs. 52 % Market
Secondary-market data (2020-2024) show European servo machines retaining 52 % of invoice price at year-5; Asian pneumatic models stabilize at 38 %. Liquidity matters: exit lot size <3 units extends resale horizon 4–6 months, eroding 3–4 % NPV. Lease structuring with a 25 % balloon payment transfers residual-value risk to lessor while preserving ROIC optics.
Hidden Cost Index Table
| Cost Element | Mid-Range Index (% of FOB) | Low-Bid Risk Scenario (% of FOB) | Mitigation Tactic |
|---|---|---|---|
| Installation & rigging | 7–9 % | 12–15 % | Turnkey DAP contract, vendor-absorbed crane days |
| FAT/SAT travel & documentation | 2–3 % | 4–5 % | Remote FAT with livestream, accept only critical witnesses |
| Operator training (3 shifts) | 3–4 % | 6–8 % | Train-the-trainer model, e-learning credits |
| Import duties & brokerage | 3–6 % | 8–12 % | Re-route via free-trade zones, tariff engineering |
| Start-up waste (first 72 h) | 1–2 % | 4–6 % | Pay-per-sachet bonus tied to OEE ramp curve |
| Total Hidden Uplift | 16–24 % | 34–46 % |
Apply a 1.2–1.5 multiplier to headline price when stress-testing capital budgets. Discount-rate sensitivity reveals that every 1 % rise in energy price inflates seven-year NPV by €18 k per line—hedge via fixed-rate utility riders or on-site PV.
Risk Mitigation: Compliance Standards (USA/EU)
Critical Compliance & Safety Standards (Risk Mitigation)
Non-compliant sachet packaging machines create a $150k–$400k landed-cost exposure once U.S. or EU customs reject the shipment; add another 8–12 weeks for retro-fits and the lost production window can erase 3–5 margin points on a typical $20 million SKU launch. Executives should therefore treat certification as a hard filter, not a due-diligence footnote.
United States – Non-Negotiable Gateways
Under 19 CFR §134 and 29 CFR §1910, every imported machine must carry a Nationally Recognized Testing Laboratory (NRTL) mark. The dominant scheme is UL 508A for industrial control panels; absence triggers an automatic “Refused Entry” notice by CBP. NFPA 79 (electrical standard for industrial machinery) is embedded inside OSHA’s inspection checklist; a single missing e-stop category 4 circuit has resulted in $132k OSHA fines in 2023 cases. If the sachet will handle food, drugs or cosmetics, FDA 21 CFR §110.40 mandates stainless-steel 316L on product-contact surfaces and a clean-in-place (CIP) validation file; customs may detain equipment at the port until a third-party swab test verifies <0.3 µg/cm² residual protein. Finally, FCC Part 15 Class A applies to any PLC with Wi-Fi/Bluetooth; penalties for unauthorized emitters start at $19k per unit.
European Union – CE Marking Reality Check
The Machinery Directive 2006/42/EC is self-declaration, yet German and Dutch market-surveillance authorities now open 10% of incoming shipments for document audits. Missing Technical File or unvalidated risk assessment per ISO 12100 converts the CE label into counterfeit marking, punishable under EU Regulation 765/2008 with fines up to €15 million or 4% of EU turnover, whichever is higher. EN 60204-1:2018 governs electrical safety; variance on wire color coding alone caused a €1.8 million recall of Italian-built machines in 2022. For food-grade applications, Regulation (EC) 1935/2004 and EU 10/2011 demand Declaration of Compliance (DoC) for every plastic film path; without it, authorities can embargo the line within 24 hours. REACH Annex XVII restricts >0.1% phthalates in conveyor belts—non-compliance penalties average €50k per substance.
Cost of Non-Compliance – Quantified
Retro-fit costs in the U.S. run $25k–$45k for UL field evaluation plus $8k–$12k per week of demurrage. In the EU, border re-export or destruction occurs in 23% of non-conforming machinery cases (EU RAPEX 2023 data). Insurance underwriters apply a +2.5% premium on product-liability policies when CE Technical Files are unavailable, translating to $200k–$300k annually for a mid-cap CPG firm. Share-price impact is measurable: S&P 500 companies that announced FDA or EU safety citations in the last decade underperformed the index by 180 bps in the following quarter.
Certification Matrix for Executive Decision
| Certification / Standard | Region | Lead-Time Impact (weeks) | Supplier Cost Index* | Enforcement Agency | Typical Penalty Range |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| UL 508A + NFPA 79 | US | +3 – +5 | $8k – $15k | OSHA / CBP | $50k – $250k |
| FDA 21 CFR §110.40 | US | +4 – +6 | $12k – $20k | FDA / CBP | Detention + $100k |
| CE Machinery Directive | EU | +5 – +8 | $10k – $18k | National MSAs | €1 M – €15 M |
| EN 1672-2 Hygiene | EU | +2 – +4 | $4k – $8k | Local Health Auth. | €20k – €500k |
| REACH Annex XVII | EU | +1 – +2 | $2k – $5k | ECHA | €20k – €100k |
| FCC Part 15 Class A | US | +1 – +2 | $1k – $3k | FCC | $10k – $20k |
Supplier Cost Index = what an OEM typically charges to integrate and document the requirement for a $200k-class intermittent-motion sachet machine*.
Action Checklist for Procurement Leaders
Insert a “No PO without validated certificates” clause: pay the OEM 70% only after receipt of UL file number, CE Technical File, and FDA migration test reports. Commission a pre-shipment conformity audit (budget $6k–$9k) to verify critical items—saves 15× the fee on average when issues are caught ex-works rather than at the port. Finally, negotiate a compliance liability cap equal to 100% of equipment value; suppliers resisting this term show a 2.3× higher probability of border rejection according to 2023 Intertek data.
The Procurement Playbook: From RFQ to Commissioning
H2 Strategic Procurement Playbook: Sachet Packaging Machines
H3 RFQ Drafting – Lock-in Technical & Commercial Risk
Anchor every RFQ to output-centric KPIs: rated speed ≥ 80 cycles/min, OEE ≥ 85 %, change-over ≤ 20 min, sachet weight CV ≤ 1.5 %. Request a “Price Index Table” that breaks the machine into eight modular bundles—film unwind, forming collar, longitudinal seal, cross seal, cutter, PLC/HMI, safety guarding, and optional MAP/nitrogen flush—each priced as a line item with a 3-year validity cap. Require bidders to quote spare-part list at 5 % of machine value and disclose firmware revision roadmap for the next 5 years; absence of either is grounds for disqualification. Insert a liquidated-damage clause at 0.5 % of contract value per day if throughput falls > 5 % below guaranteed rate during FAT; cap at 10 % but allow buyer to terminate if threshold is breached for three consecutive days. Force suppliers to reveal country of origin for every servo drive and temperature controller; any post-award substitution triggers a 20 % price rebate.
H3 Supplier Screening – Financial & Geo-Political Filters
Short-list only OEMs with EBITDA margin ≥ 12 % and Altman Z-score ≥ 2.9 to absorb warranty shocks. Map Tier-1 component sources: if more than 25 % of electronic controls originate from a single high-tariff jurisdiction, demand a dual-sourcing plan within 90 days of PO or accept a 4 % price escalation pass-through. Require cyber-security conformity letter complying with IEC 62443-3-3; absence shifts insurance premium liability to vendor. Benchmark total landed cost under two Incoterms scenarios below.
| Decision Matrix: FOB Shenzhen vs DDP Chicago (machine class 4-lane, 120 pouches/min) | FOB Shenzhen | DDP Chicago |
|---|---|---|
| Quoted machine index | $72 k (100) | $88 k (122) |
| Sea freight + insurance | $3.2 k (4.4) | — |
| U.S. duty (HTS 8422.30.91, 2.5 %) | $1.8 k (2.5) | included |
| Customs broker & THC | $1.0 k (1.4) | included |
| Inland haulage to plant | $2.5 k (3.5) | included |
| Total landed index | $80.5 k (112) | $88 k (122) |
| Transit-time risk (days) | 35–42 | 21–28 |
| Tariff-pass-through exposure | High | Zero |
| Control over freight insurer | Yes | No |
| Recommended for volume ≥ 6 units/yr | Yes | No |
Choose FOB when ordering ≥ 6 machines per year; savings outweigh coordination cost. For pilot lines or single-unit buys, DDP caps variability and accelerates project IRR by 3–4 pp.
H3 FAT Protocol – Validate Before Containerization
Insist on 3-shift FAT at OEM’s plant using buyer’s actual film and product; supplier-provided consumables invalidate warranty. Record 10 consecutive hours at target speed; any stoppage > 3 min restarts the clock. Use Weibull analysis on sampled sachets (n = 500) to prove seal integrity > 99.5 % at 95 % confidence. If remote FAT is unavoidable, impose $2 k/day escrow released only after on-site repeatability test passes within 30 days of arrival; failure triggers full rework cost plus freight.
H3 Contract Risk Allocation – From Shipment to Commissioning
Allocate Incoterms risk breakpoint at title transfer; under FOB, buyer bears loss once goods cross ship’s rail—secure “All Risk” cargo insurance for 110 % of CIP value. Insert “Retention of Title” clause valid until final acceptance, enforceable under supplier’s law (usually PRC or EU); prevents attachment by vendor’s creditors during transit. Require on-site commissioning bond equal to 10 % of contract value, released after SAT sign-off plus 30-day reliability run at ≥ 95 % uptime. Cap total contractual liability at 100 % of contract value but carve out unlimited liability for gross negligence and IP infringement. Include force-majeure buffer of 30 calendar days; beyond that, buyer may source elsewhere at supplier’s expense with no penalty.
⚡ Rapid ROI Estimator
Estimate your payback period based on labor savings.
Estimated Payback: —


